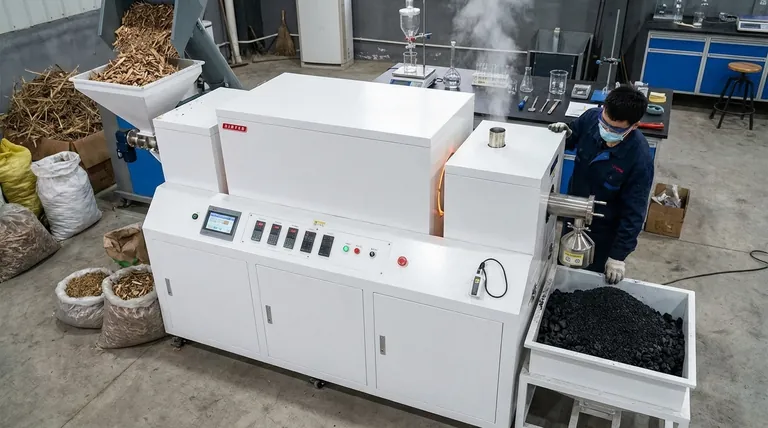
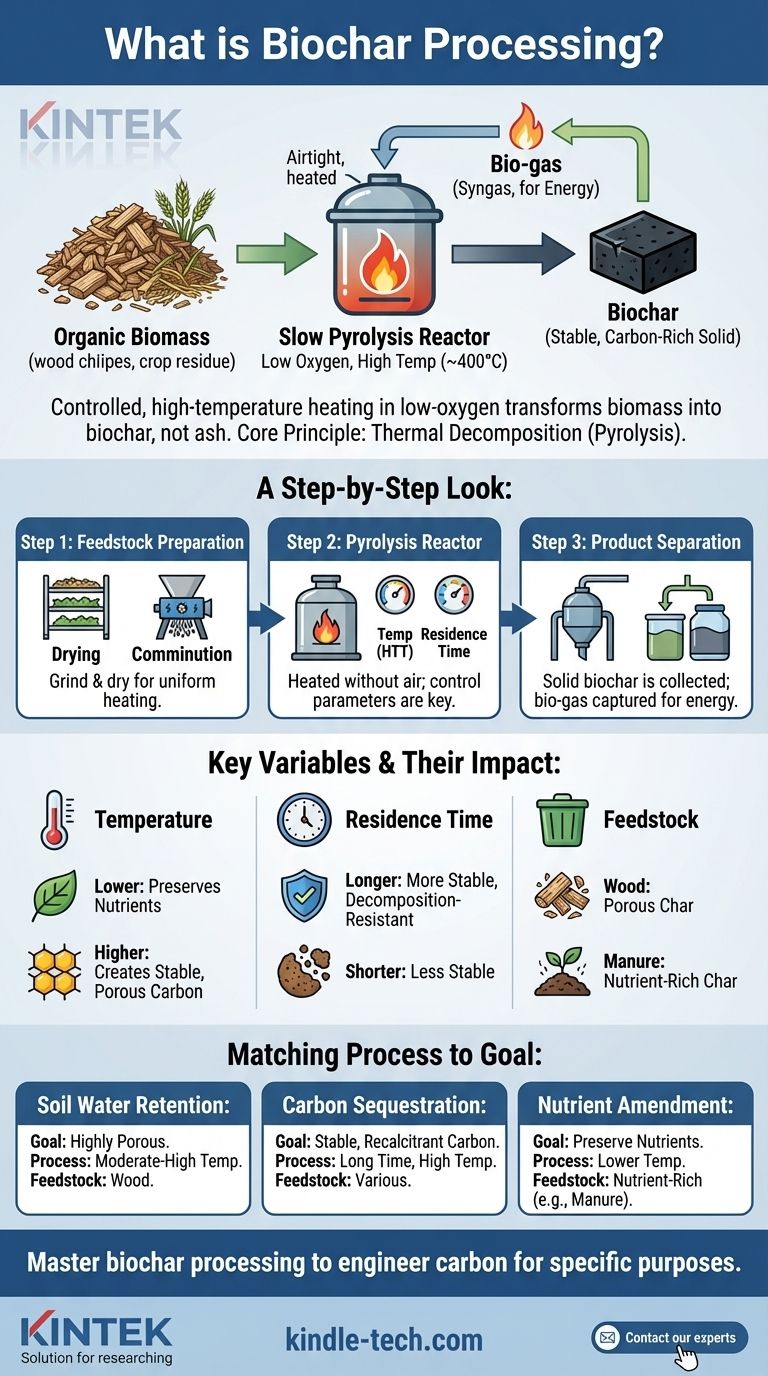
In essence, biochar processing is the controlled, high-temperature heating of organic material (biomass) in a low-oxygen environment. This process, known as slow pyrolysis, transforms materials like wood, crop residue, or manure into a stable, carbon-rich solid called biochar, rather than allowing them to burn into ash.
The core principle of biochar processing is not simply to burn biomass, but to thermally decompose it. By carefully controlling temperature, heating time, and the type of biomass used, producers can engineer biochar with specific properties for goals ranging from soil improvement to carbon sequestration.

The Core Principle: Slow Pyrolysis
Slow pyrolysis is the foundational technique for producing high-quality biochar. It differs significantly from simple burning or other thermal processes.
What is Pyrolysis?
Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of materials at elevated temperatures in an inert atmosphere. It involves a change in chemical composition and is irreversible.
Think of it as "pressure cooking" organic matter instead of burning it. Without oxygen, the material breaks down into a solid carbon structure (biochar) and volatile gases (bio-gas), rather than combusting into ash and smoke.
Why Slow Pyrolysis is Key
The "slow" in slow pyrolysis is deliberate. The process uses relatively lower temperatures (around 400°C) and longer heating periods, often lasting several hours.
This combination maximizes the yield of the solid char, which typically makes up 25-35% of the final product mass. Faster forms of pyrolysis at higher temperatures are optimized to produce bio-oil, not biochar.
A Step-by-Step Look at Biochar Processing
The production of biochar is a multi-stage process where each step influences the quality of the final product.
Step 1: Feedstock Preparation
Before heating, the raw biomass must be prepared. This usually involves two key actions: drying and comminution (grinding or shredding).
Drying the material is critical for an efficient process, while grinding it into smaller, uniform pieces ensures it heats evenly within the reactor.
Step 2: The Pyrolysis Reactor
The prepared biomass is fed into an airtight vessel. It is heated in the absence of air to the target temperature.
The two most critical parameters to control here are the Highest Treatment Temperature (HTT) and the residence time (how long the material is held at that temperature).
Step 3: Product Separation
As the biomass decomposes, it separates into solid and gaseous components. The solid that remains is the biochar.
The gases, known as bio-gas or syngas, are captured. This bio-gas can often be repurposed to provide the energy needed to fuel the pyrolysis process itself, creating a more sustainable system.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Key Variables and Their Impact
The specific properties of biochar are not accidental; they are a direct result of the processing conditions. Understanding these variables is crucial to producing biochar for a specific application.
The Role of Temperature
Temperature is arguably the single most important variable. Lower temperatures tend to produce a char with more nutrients preserved from the original biomass.
Higher temperatures create a more stable, highly porous carbon structure with greater surface area, which is ideal for long-term carbon sequestration and water retention.
The Impact of Residence Time
A longer residence time ensures a more complete and stable carbonization of the biomass. This results in a final product that is highly resistant to decomposition in the soil.
Shorter residence times may leave more volatile compounds in the char, making it less stable over the long term.
The Feedstock Factor
The choice of starting material has a profound effect on the final product. The "feedstock" can be anything from wood chips and straw to manure and food waste.
A wood-based feedstock will produce a different biochar than a manure-based one. The latter will naturally result in a product with a higher concentration of nutrients like phosphorus and potassium. This inherent variability is a key challenge and opportunity in the field.
Matching the Process to the Goal
To apply this effectively, you must align the processing parameters with your intended outcome.
- If your primary focus is soil water retention: Prioritize a process using moderate to high temperatures to create a highly porous biochar with maximum surface area.
- If your primary focus is long-term carbon sequestration: Use a slow process with a long residence time and higher temperatures to create the most stable, recalcitrant form of carbon.
- If your primary focus is nutrient amendment: Use a nutrient-rich feedstock (like manure) and lower pyrolysis temperatures to preserve the inherent nutrients in the final biochar.
Ultimately, mastering biochar processing is about deliberately controlling these variables to engineer a carbon product for a specific purpose.
Summary Table:
| Variable | Impact on Biochar | Ideal for Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | Lower temps preserve nutrients; higher temps create stable, porous carbon. | Soil amendment: Lower temps. Carbon sequestration: Higher temps. |
| Residence Time | Longer times create a more stable, decomposition-resistant char. | Long-term carbon storage: Longer residence time. |
| Feedstock | Wood creates porous char; manure creates nutrient-rich char. | Water retention: Wood. Nutrient amendment: Manure. |
Ready to engineer the perfect biochar for your specific application?
The right lab equipment is critical for precise control over pyrolysis temperature, residence time, and feedstock preparation. KINTEK specializes in the laboratory reactors, furnaces, and consumables needed for reliable biochar research and quality control.
Let us help you optimize your process for superior results in soil health or carbon sequestration. Contact our experts today to discuss your project needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the main types of biomass conversion processes? Unlock the Best Pathway for Your Energy Needs
- Why are high temperatures required when sintering stainless steels? Unlock Pure, High-Density Results
- What temperature is needed for pyrolysis waste? A Guide to Optimizing Your Waste-to-Value Process
- What are the characteristics of the slipping, slumping, and rolling modes of bed motion? Optimize Your Rotary Process
- How do high-temperature reaction furnaces control in-situ MMCs? Master Material Precision and Structural Integrity



















