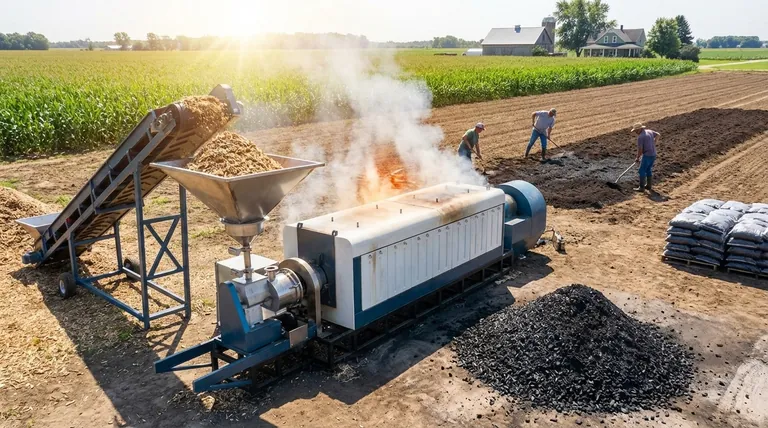
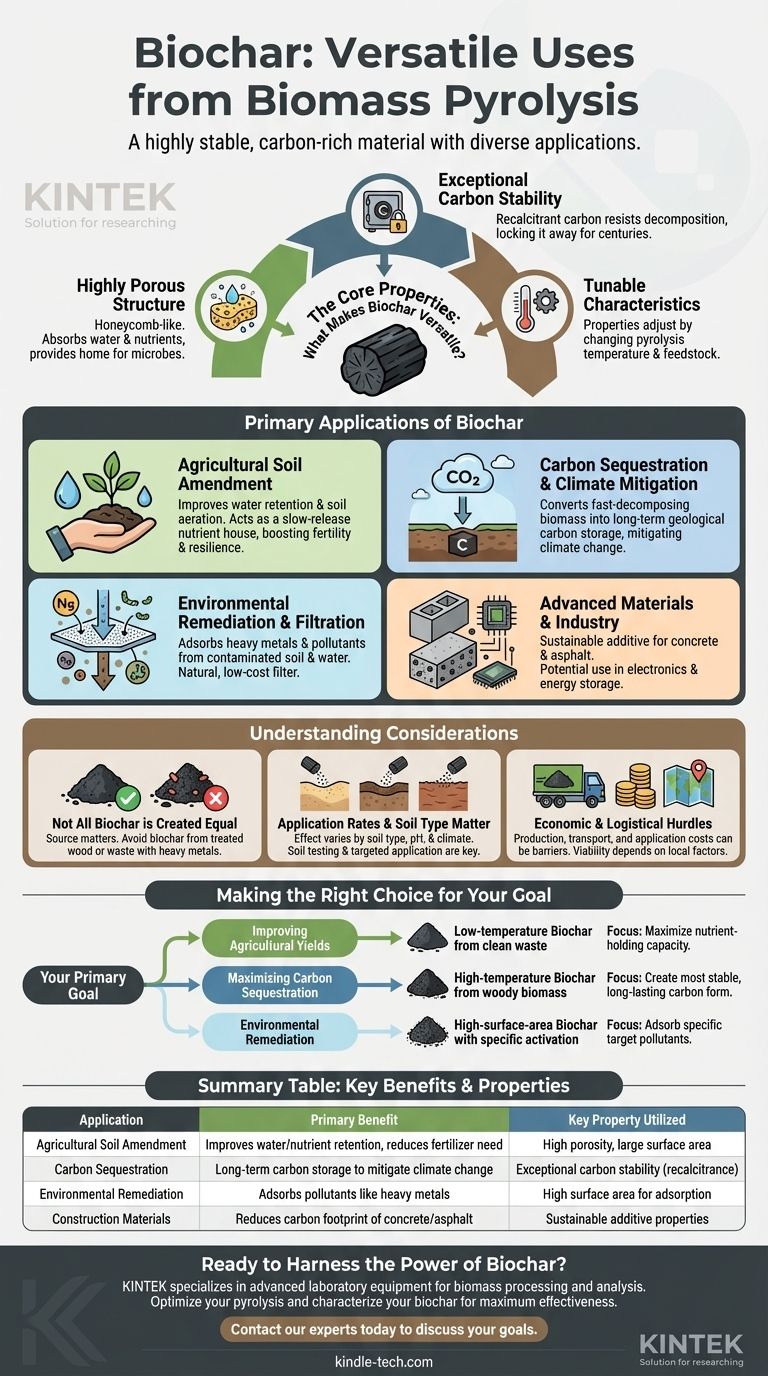
In short, biochar is a highly stable, carbon-rich material with a vast range of applications. Produced through the high-temperature, low-oxygen process of pyrolysis, biochar is most commonly used as a potent agricultural soil amendment. However, its unique properties also make it valuable for carbon sequestration, environmental remediation, and as an additive in construction materials.
The true value of biochar lies not in a single application, but in its fundamental properties: a highly porous, sponge-like structure and an exceptionally stable carbon form. Understanding these two characteristics is the key to unlocking its potential across industries.

What Makes Biochar So Versatile? The Core Properties
The effectiveness of biochar stems directly from its physical and chemical nature, which is determined by the feedstock used and the specific conditions of the pyrolysis process.
A Highly Porous Structure
Pyrolysis creates a microscopic, honeycomb-like structure within the char. This results in an incredibly high surface area relative to its volume.
This structure acts like a sponge, allowing biochar to absorb and retain water, nutrients, and beneficial microorganisms when added to soil.
Exceptional Carbon Stability
The carbon in biochar is highly recalcitrant, meaning it resists decomposition. Unlike raw biomass that decays and releases its carbon back into the atmosphere as CO2, biochar locks that carbon away in a solid, stable form for centuries, if not millennia.
This stability is the foundation of its role in carbon sequestration.
Tunable Characteristics
Not all biochar is the same. By adjusting the pyrolysis temperature and the biomass feedstock (e.g., wood chips, agricultural waste, manure), producers can create biochars with different properties.
For example, higher temperatures generally create biochar with a higher surface area, ideal for filtration, while lower temperatures may produce biochar better suited for holding nutrients in soil.
Primary Applications of Biochar in Detail
Biochar's core properties translate into several powerful, real-world applications that address critical agricultural and environmental challenges.
Agricultural Soil Amendment
This is the most well-known use of biochar. When mixed into soil, its porous structure improves both water retention and aeration, making crops more resilient to drought and reducing the need for irrigation.
It also acts as a slow-release housing for nutrients from fertilizer, preventing them from washing away and reducing overall fertilizer demand. This enhances soil fertility and reduces chemical runoff into waterways.
Carbon Sequestration and Climate Mitigation
By converting carbon from fast-decomposing biomass into highly stable biochar, the pyrolysis process creates a powerful tool for carbon removal.
When this biochar is incorporated into the soil, it effectively transfers carbon from the active atmospheric cycle into a long-term geological storage sink, directly mitigating climate change.
Environmental Remediation and Filtration
Biochar’s high surface area makes it an excellent adsorbent. It can bind to heavy metals, pesticides, and other organic pollutants in contaminated soil or water.
This property is being leveraged in water filtration systems and for cleaning up industrial sites, where biochar acts as a natural, low-cost filter to trap harmful substances.
Advanced Materials and Industry
Emerging applications are exploring biochar's use as a sustainable additive. It can be incorporated into concrete and asphalt to reduce the carbon footprint of construction materials and, in some cases, improve their physical properties.
Its conductive nature also opens possibilities for its use in electronics and energy storage devices.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
While biochar has immense potential, its effective use requires a clear understanding of its limitations and the factors that govern its performance.
Not All Biochar is Created Equal
The source of the biomass is critical. Biochar made from wood treated with chemicals or from waste containing heavy metals is unsuitable for agriculture as it could introduce toxins into the soil.
Always ensure the biochar is certified or tested for its intended application to avoid unintended negative consequences.
Application Rates and Soil Type Matter
Biochar is not a universal solution that can be applied indiscriminately. Its effect varies significantly depending on the existing soil type, pH, and climate.
Applying too much or the wrong kind of biochar can have neutral or even detrimental effects. Soil testing and targeted application are essential for achieving positive results.
Economic and Logistical Hurdles
The cost of producing, transporting, and applying biochar can be a significant barrier to widespread adoption.
The economic viability often depends on local factors, such as the availability of cheap biomass, the market price for agricultural products, and the potential for revenue from carbon credits.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal biochar and application strategy depend entirely on your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is improving agricultural yields: Use biochar produced at lower temperatures from clean agricultural or forestry waste to maximize its nutrient-holding capacity.
- If your primary focus is maximizing carbon sequestration: Opt for biochar made from dense, woody biomass at higher pyrolysis temperatures to create the most stable and long-lasting form of carbon.
- If your primary focus is environmental remediation: Select a high-surface-area biochar specifically engineered to adsorb the target pollutants you need to remove from soil or water.
Ultimately, viewing biochar as a versatile and tunable material, rather than a single product, is the key to applying it effectively to solve complex challenges.
Summary Table:
| Application | Primary Benefit | Key Property Utilized |
|---|---|---|
| Agricultural Soil Amendment | Improves water/nutrient retention, reduces fertilizer need | High porosity, large surface area |
| Carbon Sequestration | Long-term carbon storage to mitigate climate change | Exceptional carbon stability (recalcitrance) |
| Environmental Remediation | Adsorbs pollutants like heavy metals from soil/water | High surface area for adsorption |
| Construction Materials | Reduces carbon footprint of concrete/asphalt | Sustainable additive properties |
Ready to harness the power of biochar for your specific application?
Whether your goal is to enhance soil fertility, achieve carbon removal targets, or develop effective remediation solutions, the right pyrolysis equipment is critical for producing high-quality, tailored biochar.
KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory equipment and consumables for biomass processing and analysis. Our expertise can help you select the right tools to optimize your pyrolysis process and characterize your biochar for maximum effectiveness.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your biochar research and application goals!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
People Also Ask
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds



















