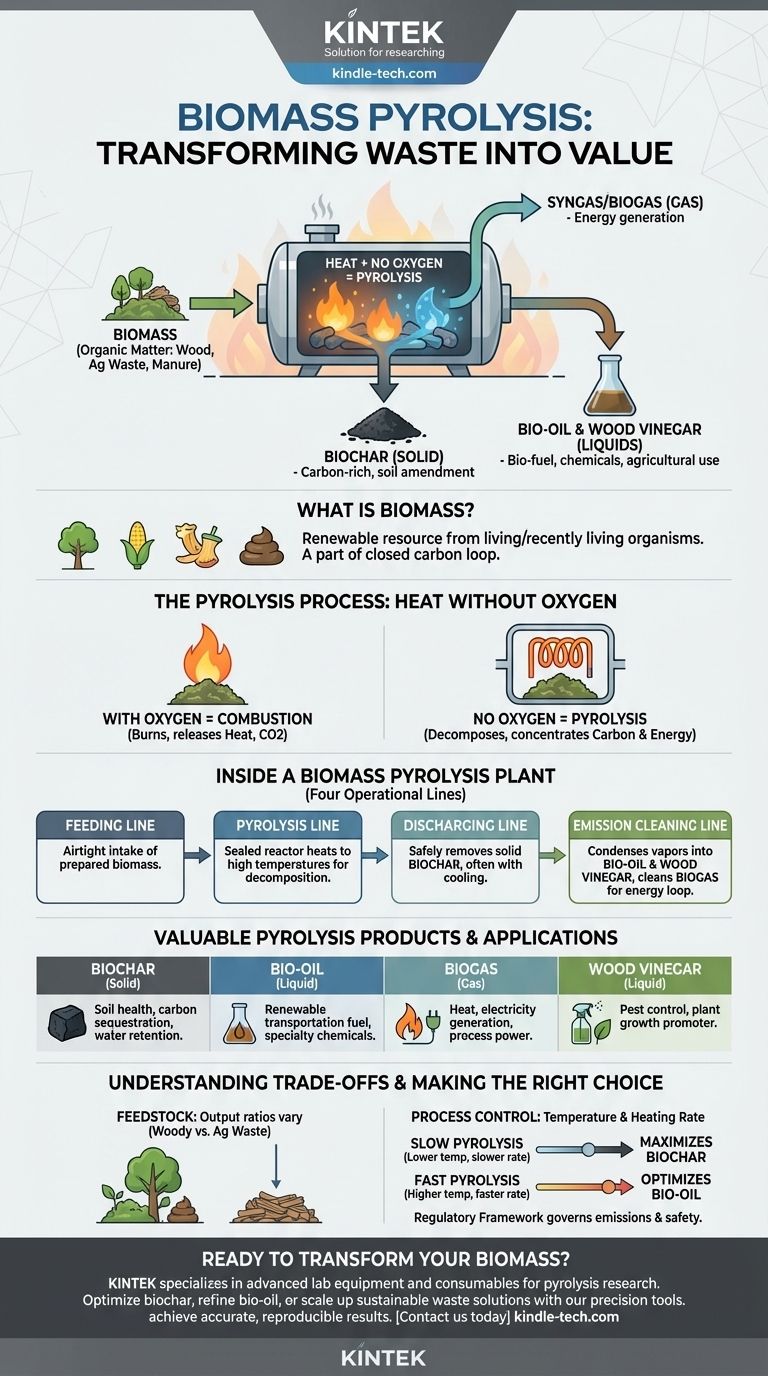
Biomass pyrolysis is a thermochemical process that converts organic matter into more valuable products by heating it in an oxygen-free environment. Unlike burning, which is combustion, pyrolysis causes the material to decompose, breaking it down into a carbon-rich solid (biochar), a liquid (bio-oil), and a combustible gas (syngas). Biomass itself is simply any material derived from living or recently living organisms, such as wood, agricultural waste, or manure.
At its core, biomass pyrolysis is not about destruction but transformation. It is a controlled method for deconstructing raw organic matter to capture and concentrate its stored carbon and energy into more stable and useful forms.

What Constitutes Biomass?
Biomass is a broad term for a vast renewable resource. Understanding its nature is key to understanding its potential.
The Foundation of Organic Matter
Biomass includes any material from plants or animals. This can range from dedicated energy crops to agricultural and forestry residues, food waste, and even sewage sludge.
A Renewable Carbon Source
Because plants absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere as they grow, using biomass for energy can be part of a closed carbon loop. It provides a way to tap into a renewable source of carbon and energy, unlike finite fossil fuels.
Deconstructing the Pyrolysis Process
Pyrolysis is a precise and controlled reaction. The absence of a key element—oxygen—is what defines the entire process and its outcomes.
The Critical Role of Heat Without Oxygen
When you heat biomass in the presence of oxygen, it burns (combusts), releasing its energy as heat and light while converting carbon into CO2.
By removing oxygen, pyrolysis prevents combustion. Instead, the high heat breaks the complex chemical bonds within the biomass, causing it to decompose into simpler, more stable components.
The Goal: Concentrating Carbon and Energy
The fundamental goal is to drive off the water and volatile organic compounds from the raw biomass. This process preserves the carbon in a more concentrated, energy-dense form, significantly increasing its value and utility.
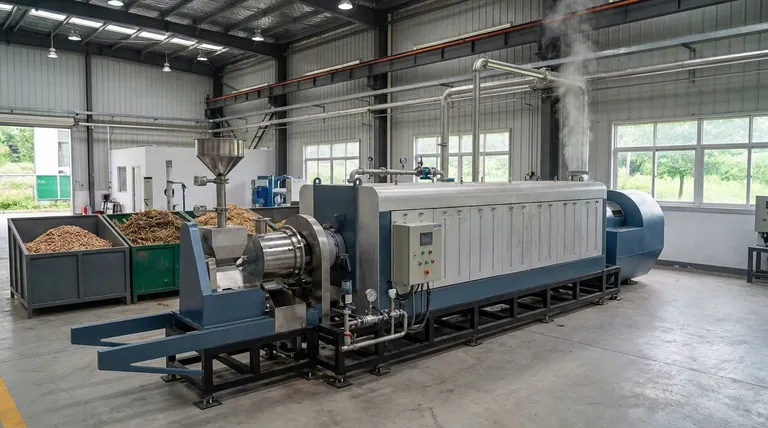
Inside a Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
A modern pyrolysis plant is a highly engineered system designed to manage the process efficiently and safely. It is typically organized into four distinct operational lines.
The Feeding Line
This is the initial stage where raw biomass is prepared and loaded into the system. The material must be fed into the reactor while maintaining an airtight, oxygen-free seal.
The Biomass Pyrolysis Line
This is the heart of the plant, containing the sealed reactor. Here, the biomass is heated to high temperatures, triggering the decomposition that separates it into solid, liquid, and gas phases.
The Discharging Line
Once the reaction is complete, the solid product, biochar (or biomass charcoal), must be removed. This is often done using a water-cooling discharger to safely handle the hot material and prevent it from combusting upon contact with air.
The Emission Cleaning Line
The gases and vapors produced during pyrolysis are processed here. Vapors are cooled and condensed into liquids like bio-oil (tar) and wood vinegar. The remaining non-condensable biogas is cleaned and can be used to heat the reactor itself, creating a self-sustaining energy loop.
The Valuable Products of Pyrolysis
The output of a pyrolysis plant is not a single product but a slate of valuable materials, each with distinct applications.
Biochar (The Solid)
This stable, carbon-rich material is similar to charcoal. It is an excellent soil amendment, improving water retention and fertility, and serves as a powerful method for long-term carbon sequestration.
Bio-oil & Wood Vinegar (The Liquids)
After condensing the hot vapors, a dark, viscous liquid known as bio-oil is collected. It is an energy-dense liquid that can be refined into transportation fuels or used to produce specialty chemicals. Wood vinegar is a valuable co-product used in agriculture.
Biogas (The Gas)
The non-condensable gases produced are rich in hydrogen, methane, and carbon monoxide. This biogas is a fuel that can be burned to generate heat or electricity, often used to power the pyrolysis plant itself.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, pyrolysis is not a one-size-fits-all solution. The outcomes are highly dependent on specific process parameters and goals.
Feedstock Determines Output
The type of biomass used significantly impacts the final product yields. Woody biomass will produce different ratios of char, oil, and gas compared to agricultural waste or manure.
Process Control is Everything
The two most critical variables are temperature and heating rate. Lower temperatures and slower heating rates (slow pyrolysis) tend to maximize the yield of biochar. Conversely, very high temperatures and rapid heating (fast pyrolysis) are optimized to produce the highest possible yield of bio-oil.
The Regulatory Framework
Operating a pyrolysis facility involves navigating policies designed to promote renewable energy while ensuring environmental safety. These regulations govern emissions, product standards, and handling procedures, adding a layer of complexity to any project.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The "best" approach to pyrolysis depends entirely on your desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is soil improvement and carbon sequestration: You should prioritize a slow pyrolysis process to maximize the production of high-quality biochar.
- If your primary focus is producing renewable liquid fuels: You should implement a fast pyrolysis system designed to optimize the yield and quality of bio-oil.
- If your primary focus is sustainable waste management: Pyrolysis offers a robust method for converting diverse organic waste streams into valuable, stable, and easily transportable products.
Ultimately, biomass pyrolysis is a key technology for converting low-value organic materials into high-value resources for a more circular economy.
Summary Table:
| Pyrolysis Product | Description | Key Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Biochar (Solid) | Carbon-rich, stable charcoal | Soil amendment, carbon sequestration, filtration |
| Bio-oil (Liquid) | Energy-dense liquid from condensed vapors | Renewable fuel, chemical production |
| Biogas (Gas) | Combustible gas (H2, CH4, CO) | Heat/electricity generation, process energy |
| Wood Vinegar (Liquid) | Agricultural co-product | Pest control, plant growth promoter |
Ready to transform your biomass into high-value products?
KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research and development. Whether you're optimizing biochar for soil health, refining bio-oil for energy, or scaling up a sustainable waste management solution, our precision tools help you achieve accurate, reproducible results.
Contact us today to explore how our solutions can enhance your biomass pyrolysis projects and drive your sustainable innovation forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs















