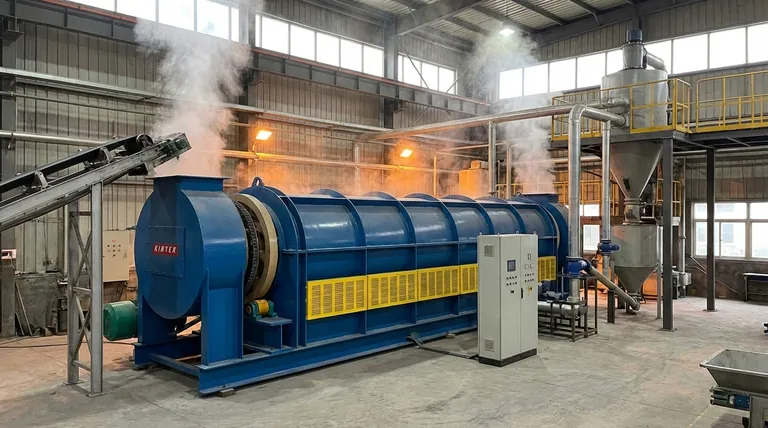
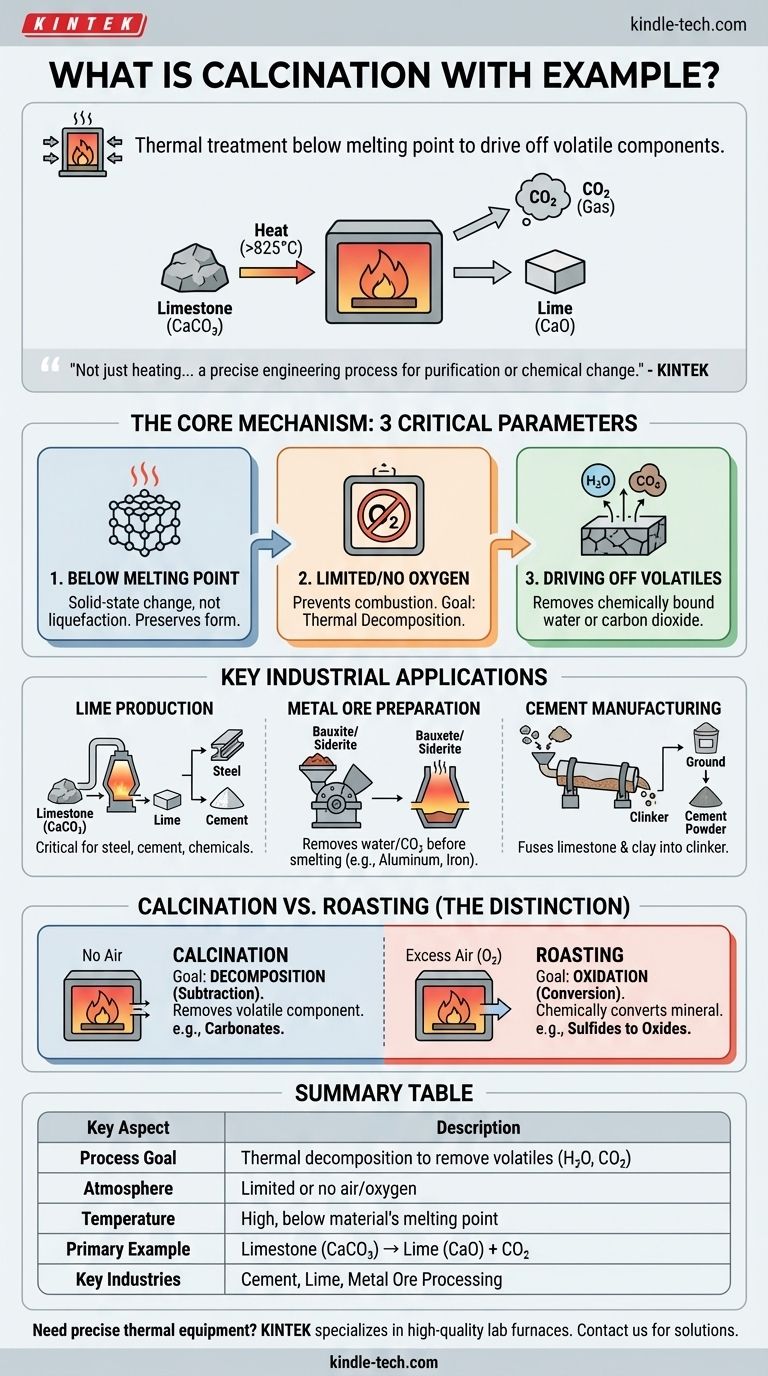
At its core, calcination is a thermal treatment process where a solid material is heated to a high temperature, below its melting point, in the absence or a limited supply of air. This controlled heating is not meant to melt the substance but to cause thermal decomposition, driving off volatile components. The most common example is heating limestone (calcium carbonate) to produce lime (calcium oxide) and release carbon dioxide gas.
Calcination is not simply about heating something up. It is a precise engineering process designed to purify a material or change its chemical composition by using heat to break bonds and drive off specific volatile substances like water or carbon dioxide.

The Core Mechanism: What Happens During Calcination?
Calcination is defined by three critical parameters: temperature, atmosphere, and the resulting chemical change. Understanding each is key to grasping the process.
Heating Below the Melting Point
The temperature is raised high enough to break chemical bonds but is intentionally kept below the material's melting point. The goal is to induce a change within the solid-state, not to liquefy it.
This preserves the material's solid form while altering its chemical makeup, often making it more porous or reactive for subsequent steps.
Limited or No Oxygen
The process occurs in an environment with very little or no oxygen. This is a crucial distinction from other heat treatment processes.
The lack of oxygen prevents combustion or oxidation. The objective is thermal decomposition (breaking down with heat), not a reaction with the surrounding air.
Driving Off Volatile Substances
The primary purpose of calcination is to remove a volatile fraction from the solid. This typically involves driving off chemically bound water (hydrates) or carbon dioxide (from carbonates).
For example, when limestone (CaCO₃) is calcined, the heat breaks it down into solid lime (CaO) and carbon dioxide gas (CO₂), which escapes.
Key Industrial Applications
Calcination is a foundational process in several major industries, used to prepare materials for further processing or to create a finished product.
Producing Lime from Limestone
This is the quintessential example. Limestone is heated to over 825°C (1517°F), causing the reaction: CaCO₃(s) → CaO(s) + CO₂(g).
The resulting product, lime (CaO), is a critical component in the manufacturing of steel, cement, and numerous chemical processes.
Preparing Metal Ores
In metallurgy, calcination is a common preparatory step before smelting. It removes water from hydrated ores like bauxite (aluminum ore) or siderite (iron ore).
It also removes carbon dioxide from carbonate ores like smithsonite (ZnCO₃) or calamine (a mix of zinc ores), making the subsequent metal extraction more efficient.
Manufacturing Cement
The production of Portland cement involves heating a mixture of limestone and clay in a kiln to about 1450°C (2640°F).
This calcination process drives off CO₂ and chemically fuses the materials into a new substance called "clinker." The clinker is then ground into the fine powder we know as cement.
Understanding the Key Distinction: Calcination vs. Roasting
Many people confuse calcination with roasting, another high-temperature process used in metallurgy. The difference lies in the atmospheric conditions and the intended chemical reaction.
The Goal of Calcination: Decomposition
As established, calcination uses heat in the absence of air to break down a compound. It is a process of subtraction, where a volatile component is removed from the ore.
The Goal of Roasting: Oxidation
Roasting, by contrast, is performed in an excess of air. Its purpose is to chemically convert a mineral into a new state through oxidation. A common use is converting sulfide ores into more easily processed oxides (e.g., 2ZnS + 3O₂ → 2ZnO + 2SO₂).
Making the Right Choice for Your Analysis
To correctly identify the process you are observing, focus on the inputs and the intended output.
- If the primary goal is to remove water or CO₂ from a carbonate or hydrate: You are observing calcination, which uses heat to thermally decompose a compound.
- If the primary goal is to react a sulfide ore with oxygen to form an oxide: You are observing roasting, which leverages both heat and excess air to trigger oxidation.
- If the primary goal is to produce cement clinker or industrial lime: You are observing one of the most widespread and critical applications of calcination.
Understanding this fundamental difference between thermal decomposition (calcination) and oxidation (roasting) is the key to mastering these core industrial processes.
Summary Table:
| Key Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Process Goal | Thermal decomposition to remove volatile substances (e.g., H₂O, CO₂) |
| Atmosphere | Limited or no air/oxygen |
| Temperature | High, but below the material's melting point |
| Primary Example | Limestone (CaCO₃) → Lime (CaO) + Carbon Dioxide (CO₂) |
| Key Industries | Cement production, lime manufacturing, metal ore processing |
| Contrasting Process | Roasting (uses excess air for oxidation) |
Need precise thermal processing equipment for your lab or production line?
Calcination is a critical step in many industrial and research applications, requiring reliable and accurate heating equipment. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab furnaces and thermal processing solutions designed for processes like calcination, roasting, and more.
Our equipment offers the precise temperature control and atmospheric conditions necessary to achieve consistent, high-purity results, whether you are processing minerals, synthesizing materials, or developing new products.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss how our specialized thermal equipment can enhance the efficiency and accuracy of your material processing workflows.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of reactors in plastic pyrolysis? Choose the Right System for Your Waste
- What are the types of pyrolysis reactors used in industry? Choose the Right Technology for Your Product
- What are the products of pyrolysis of wood? A Guide to Biochar, Bio-oil, and Syngas Yields
- What are the zones in rotary kiln in cement production? Master the Core Process for High-Quality Clinker
- What is the principle of rotary kiln? Mastering Continuous Thermal Processing



















