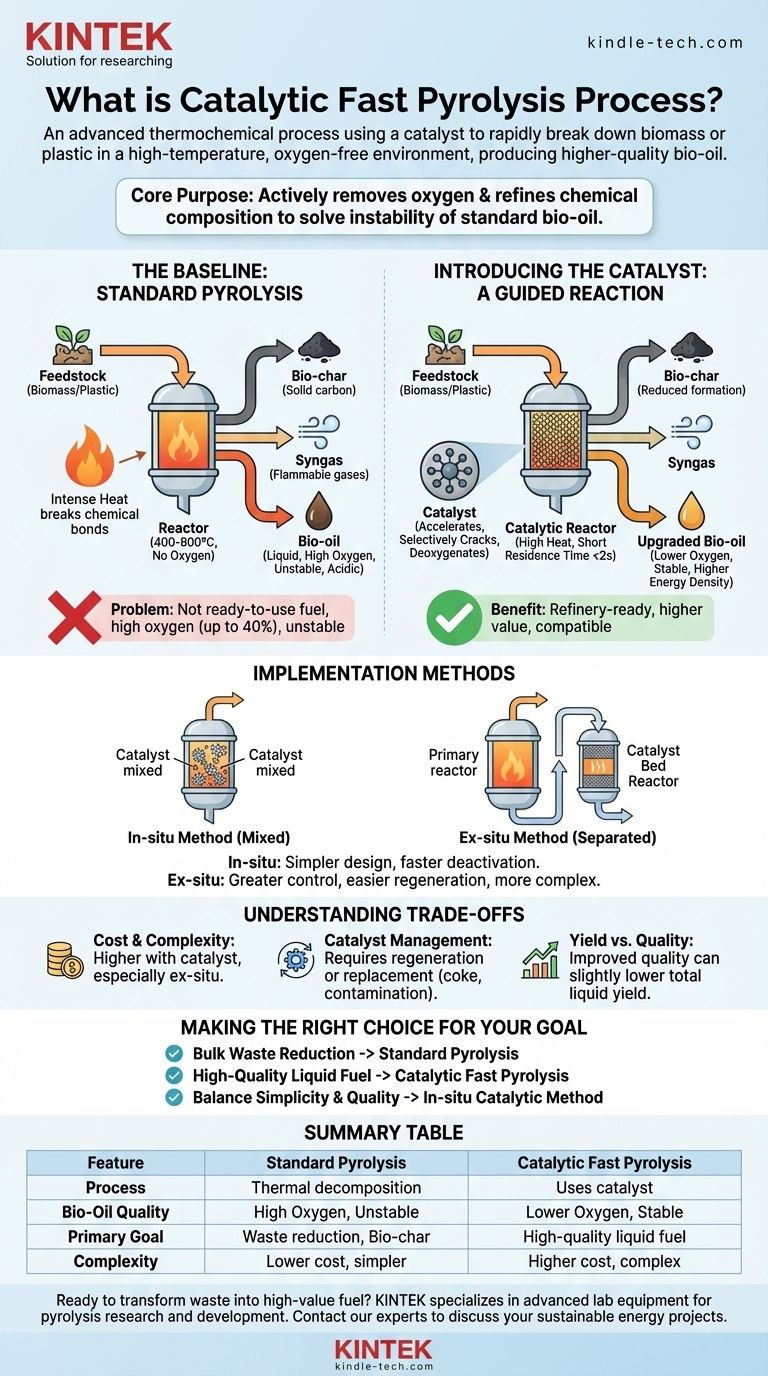
Catalytic fast pyrolysis is an advanced thermochemical process that uses a catalyst to rapidly break down materials like biomass or plastic in a high-temperature, oxygen-free environment. Unlike standard pyrolysis, the catalyst actively guides the chemical reactions to upgrade the resulting vapors, producing a higher-quality, more stable liquid fuel known as bio-oil.
The core purpose of adding a catalyst to the fast pyrolysis process is to solve the fundamental problem of standard bio-oil: its high oxygen content and instability. The catalyst actively removes oxygen and refines the chemical composition of the oil as it forms, making it more valuable and easier to use.

The Baseline: Understanding Standard Pyrolysis
The Core Process
Pyrolysis is a method of thermal decomposition. Feedstock, such as wood chips or plastic waste, is heated to high temperatures (typically 400-900°C) inside a reactor where there is no oxygen.
Without oxygen, the material doesn't combust. Instead, the intense heat breaks the complex chemical bonds, deconstructing the material into simpler components.
The Standard Outputs
This process yields three primary products:
- Bio-char: A solid, carbon-rich material similar to charcoal, often used for soil amendment.
- Syngas: A mixture of flammable gases that can be used to generate heat for the process itself.
- Bio-oil: A liquid created by condensing the pyrolysis vapors.
The Problem with Standard Bio-Oil
The bio-oil produced from standard pyrolysis is not a ready-to-use fuel. It is a complex emulsion containing a wide variety of oxygenated organic compounds, polymers, and a significant amount of water.
This high oxygen content (up to 40% by weight) makes the oil acidic, unstable, and gives it a lower energy value compared to conventional fossil fuels, posing significant challenges for storage and upgrading.
Introducing the Catalyst: A Guided Reaction
The Role of the Catalyst
A catalyst is a substance that accelerates a chemical reaction without being consumed by it. In catalytic pyrolysis, its job is to promote specific reactions that are essential for improving the bio-oil.
The catalyst selectively cracks large, oxygenated molecules and facilitates deoxygenation reactions, effectively refining the vapors before they are condensed into liquid.
How "Fast" Pyrolysis Maximizes Oil Production
The "fast" in fast pyrolysis refers to the extremely high heating rates and very short residence time of the vapors in the reactor (often less than two seconds). This technique is specifically designed to minimize the formation of char and gas, thereby maximizing the yield of the liquid bio-oil.
Key Benefits of the Catalytic Approach
The primary advantage is a significantly upgraded bio-oil. The resulting liquid has a lower oxygen content, reduced acidity, and a higher concentration of valuable aromatic compounds. This makes the oil more stable, energy-dense, and more compatible with existing refinery infrastructure for further processing.
Implementation: In-situ vs. Ex-situ Methods
The In-situ Method
In an in-situ (or "in-place") configuration, the catalyst is mixed directly with the feedstock material inside the main pyrolysis reactor.
This approach is simpler in terms of equipment design. However, it can lead to faster catalyst deactivation from direct contact with char and makes catalyst recovery more difficult.
The Ex-situ Method
In an ex-situ (or "out-of-place") setup, the pyrolysis process and the catalytic upgrading are separated. The feedstock is heated in a primary reactor, and the resulting hot vapors are then passed through a second, separate reactor containing the catalyst bed.
This dual-bed design offers greater control over the process and makes it easier to regenerate or replace the catalyst. However, it requires a more complex and potentially more expensive plant design.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Cost and Complexity
Introducing a catalytic stage, especially an ex-situ reactor, adds significant mechanical complexity and cost to a pyrolysis plant compared to a standard, non-catalytic unit.
Catalyst Management
Catalysts degrade over time due to coke formation and contamination. They require periodic regeneration (burning off the carbon build-up) or complete replacement, which adds an operational cost and layer of complexity to the process.
Yield vs. Quality
Often, the catalytic cracking process that improves oil quality can also produce more non-condensable gases. This can sometimes result in a slightly lower total liquid yield, presenting a classic trade-off between the quantity and the quality of the final product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use catalytic pyrolysis depends entirely on the desired end-product.
- If your primary focus is bulk waste reduction to produce bio-char: Standard, non-catalytic pyrolysis is the most direct and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is producing a higher-quality, refinery-ready liquid fuel: Catalytic fast pyrolysis is the necessary and superior technology.
- If your primary focus is balancing process simplicity with some oil quality improvement: The in-situ catalytic method offers a viable compromise.
Ultimately, catalytic fast pyrolysis represents a critical technological step toward converting low-value biomass and waste into a more viable and sustainable liquid fuel source.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Standard Pyrolysis | Catalytic Fast Pyrolysis |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Thermal decomposition without catalyst | Uses a catalyst to guide chemical reactions |
| Bio-Oil Quality | High oxygen content, acidic, unstable | Lower oxygen, stable, higher energy density |
| Primary Goal | Bulk waste reduction, bio-char production | High-quality, refinery-ready liquid fuel |
| Complexity | Lower cost and simpler design | Higher cost, more complex (especially ex-situ) |
Ready to transform your biomass or plastic waste into high-value fuel? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment for pyrolysis research and development. Our solutions help you optimize catalytic processes, analyze bio-oil quality, and scale your technology from lab to pilot plant. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your sustainable energy projects with precision equipment and consumables tailored for laboratory innovation.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
People Also Ask
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- What is the process of biomass fast pyrolysis? Turn Biomass into Bio-Oil in Seconds
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success



















