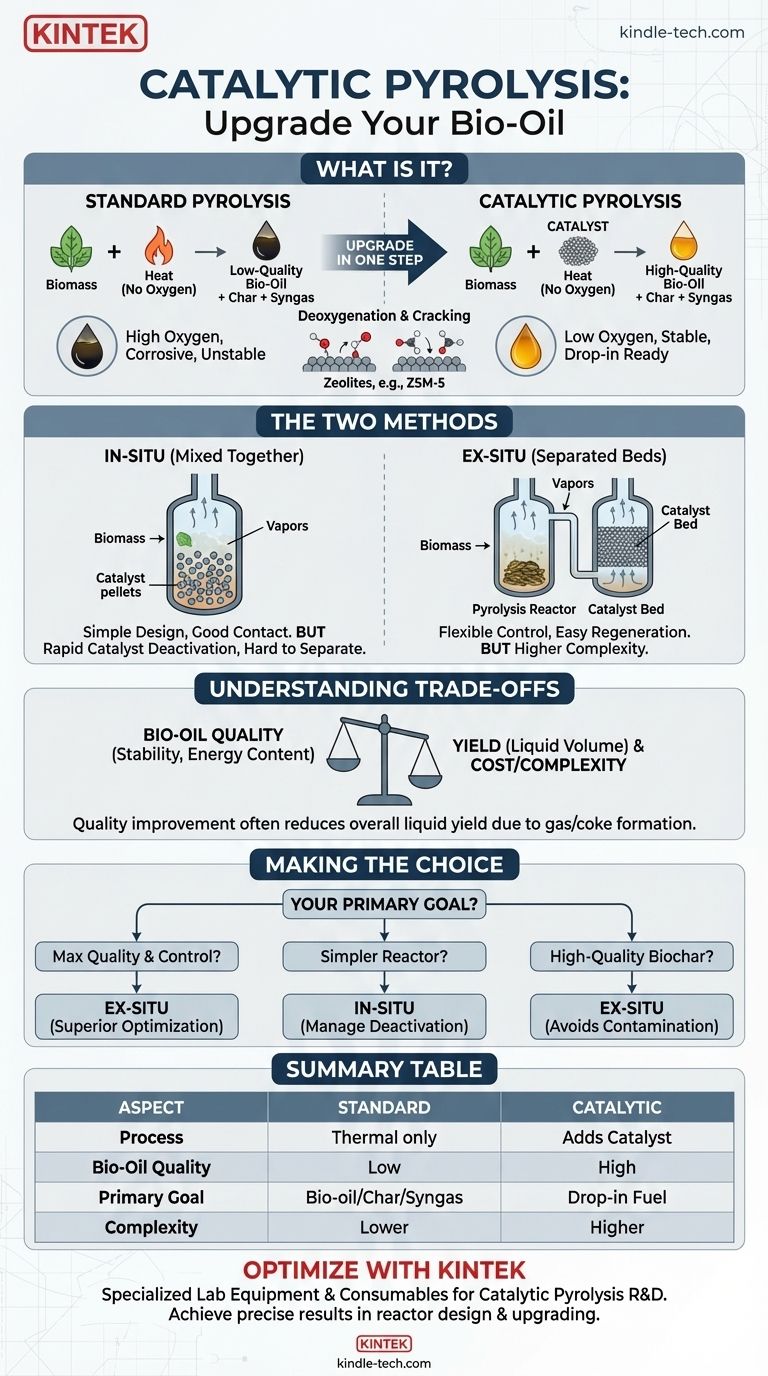
In short, catalytic pyrolysis is an advanced thermochemical process that uses a catalyst to break down materials like biomass or plastics in the absence of oxygen. Unlike standard pyrolysis, the catalyst actively steers the chemical reactions to produce a higher-quality, more stable, and more valuable liquid fuel, often called bio-oil.
The core purpose of catalytic pyrolysis is not just to break down materials, but to upgrade the resulting vapors in a single, integrated step. It addresses the fundamental quality issues—high oxygen content, instability, and corrosiveness—that plague the oil produced by conventional pyrolysis.

First, Understanding Standard Pyrolysis
The Basic Process
Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of organic material at elevated temperatures in an oxygen-free environment. If oxygen were present, the material would simply burn (combust).
Instead, the lack of oxygen forces long-chain molecules within the feedstock (like wood, agricultural waste, or plastic) to break apart into smaller, different molecules.
The Three Products
This process typically yields three distinct products:
- Bio-oil (or Pyrolysis Oil): A dark, viscous liquid that is energy-dense but also acidic, unstable, and high in oxygen.
- Biochar: A solid, carbon-rich material similar to charcoal.
- Syngas: A mixture of non-condensable gases like carbon monoxide, hydrogen, and methane.
The Role of the Catalyst: Upgrading in a Single Step
Why a Catalyst is Necessary
The raw bio-oil from standard pyrolysis is difficult to use directly as a fuel. It has a high oxygen content (35-40%), which makes it corrosive, thermally unstable, and immiscible with conventional hydrocarbon fuels.
To make it a viable "drop-in" fuel, this oil requires significant and costly secondary upgrading. The catalyst is introduced to perform this upgrading during the pyrolysis process itself.
How Catalysts Improve Bio-Oil Quality
Catalysts provide a surface that promotes specific chemical reactions which would otherwise not occur or would happen too slowly.
Their primary function is deoxygenation—removing oxygen atoms from the vapor molecules. This is achieved through reactions like decarboxylation and decarbonylation, which improve the final oil's stability and heating value. Catalysts also facilitate cracking, breaking down large, heavy molecules into smaller, more desirable hydrocarbon compounds.
Common Catalysts Used
The most common catalysts are zeolites, particularly ZSM-5, which are highly effective at deoxygenating pyrolysis vapors and converting them into aromatic hydrocarbons similar to those found in gasoline.
The Two Primary Methods: In-Situ vs. Ex-Situ
The critical distinction in catalytic pyrolysis lies in where the catalyst is placed relative to the initial breakdown of the biomass. This is the difference between the in-situ and ex-situ methods.
In-Situ Catalytic Pyrolysis (Mixed Together)
In this configuration, the catalyst and the biomass feedstock are mixed together directly within the pyrolysis reactor.
The primary advantage is the excellent contact between the fresh pyrolysis vapors and the catalyst, which can enhance reaction efficiency. The reactor design can also be simpler and potentially less expensive.
However, the in-situ method suffers from rapid catalyst deactivation. The catalyst becomes quickly coated in char and heavy carbon deposits (coke), losing its effectiveness. Separating the spent catalyst from the biochar for regeneration is also very difficult.
Ex-Situ Catalytic Pyrolysis (Separated Beds)
In the ex-situ approach, pyrolysis and catalysis occur in two separate stages. First, the biomass is broken down in a standard pyrolysis reactor. Then, the resulting hot vapors are immediately passed into a second, separate reactor containing the catalyst bed.
This separation provides tremendous process flexibility. The temperatures for pyrolysis and catalysis can be optimized independently. Most importantly, it makes catalyst regeneration far simpler, as the catalyst bed can be isolated and subjected to a regeneration cycle without disrupting the entire system.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Catalyst Deactivation and Cost
Catalysts are not a one-time-use ingredient; they are a continuous operational factor. They are expensive and inevitably deactivate over time due to coke formation and poisoning from contaminants in the feedstock. The energy and complexity required for regeneration are significant operational costs.
Yield vs. Quality
There is an unavoidable trade-off. While catalytic pyrolysis dramatically improves the quality of the bio-oil, it often reduces the overall yield of the liquid product. This is because the desired reactions (like deoxygenation) often convert some of the vapor into additional gas and coke, which deposits on the catalyst.
Process Complexity
Introducing a catalyst adds a significant layer of complexity to the design, operation, and control of a pyrolysis system compared to a non-catalytic process. This increases both capital and operational expenditures.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision between standard, in-situ, and ex-situ catalytic pyrolysis depends entirely on the desired end-product and operational constraints.
- If your primary focus is maximizing bio-oil quality and process control: Ex-situ is the superior choice, offering independent optimization and far easier catalyst management.
- If your primary focus is a simpler reactor design with potentially lower initial capital cost: In-situ may be considered, but you must be prepared to manage the challenge of rapid catalyst deactivation.
- If your primary focus is producing high-quality biochar: Ex-situ is the only viable catalytic option, as the in-situ process contaminates the char with catalyst, diminishing its value.
Ultimately, catalytic pyrolysis represents a crucial technological step in transforming low-value biomass and waste into high-value fuels and chemicals.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Standard Pyrolysis | Catalytic Pyrolysis |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Thermal decomposition without oxygen | Adds a catalyst to upgrade vapors during pyrolysis |
| Bio-Oil Quality | High oxygen content, unstable, corrosive | Lower oxygen, stable, higher heating value |
| Primary Goal | Produce bio-oil, biochar, and syngas | Produce high-quality, drop-in ready fuel |
| Complexity | Lower complexity and cost | Higher complexity due to catalyst management |
| Key Advantage | Simpler operation | Superior fuel quality and chemical production |
Ready to optimize your pyrolysis process? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for catalytic pyrolysis research and development. Whether you're exploring catalyst performance, reactor design, or bio-oil upgrading, our solutions help you achieve precise, reliable results. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's unique needs in biomass conversion and sustainable fuel production.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
- High Pressure Laboratory Autoclave Reactor for Hydrothermal Synthesis
- Mini SS High Pressure Autoclave Reactor for Laboratory Use
- Stainless High Pressure Autoclave Reactor Laboratory Pressure Reactor
People Also Ask
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas



















