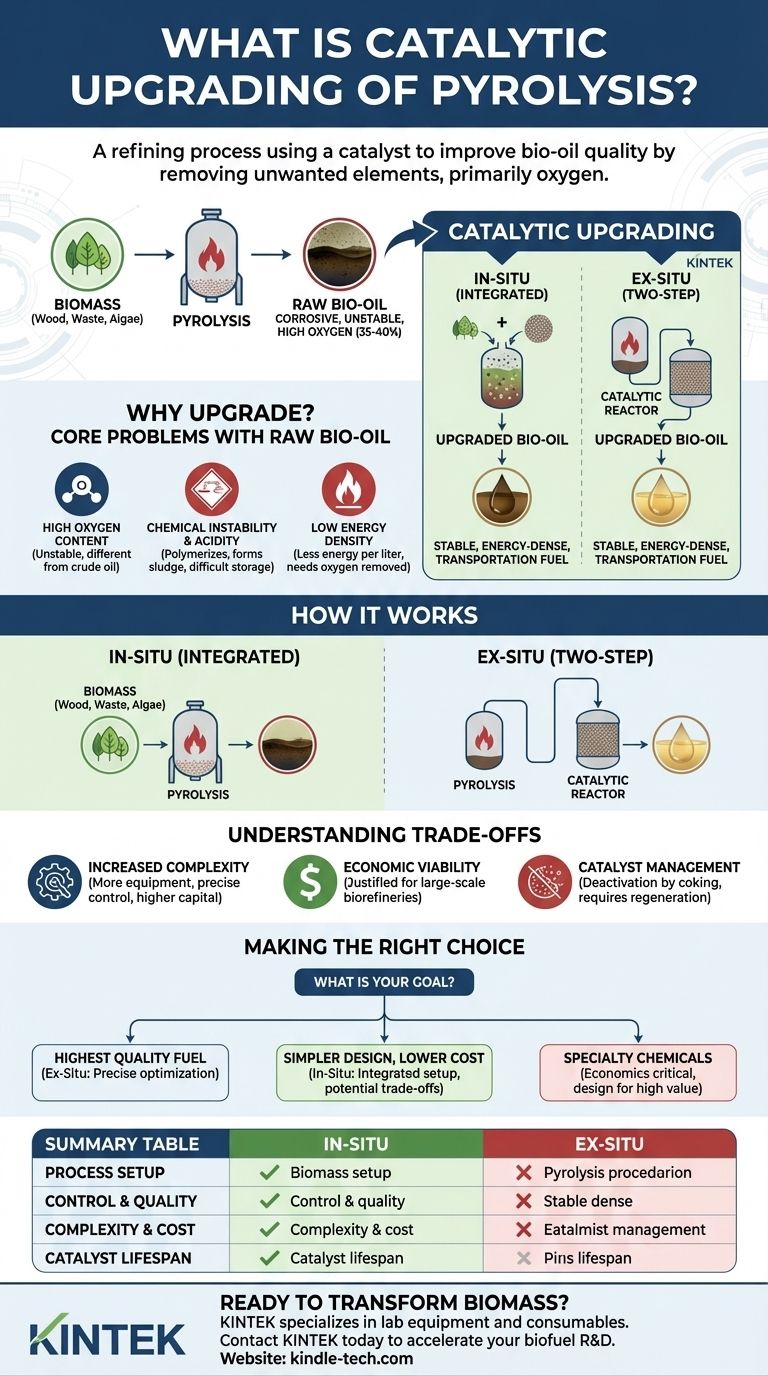
In short, catalytic upgrading of pyrolysis is a refining process that uses a catalyst to chemically improve the quality of the bio-oil produced from biomass. Its primary goal is to remove unwanted elements, mainly oxygen, to make the bio-oil more stable, energy-dense, and suitable for use as a transportation fuel or chemical feedstock.
The central challenge with standard pyrolysis is that the resulting bio-oil is corrosive and unstable due to high oxygen content. Catalytic upgrading is the critical step that transforms this crude, low-grade liquid into a valuable, higher-grade product resembling conventional fuel.
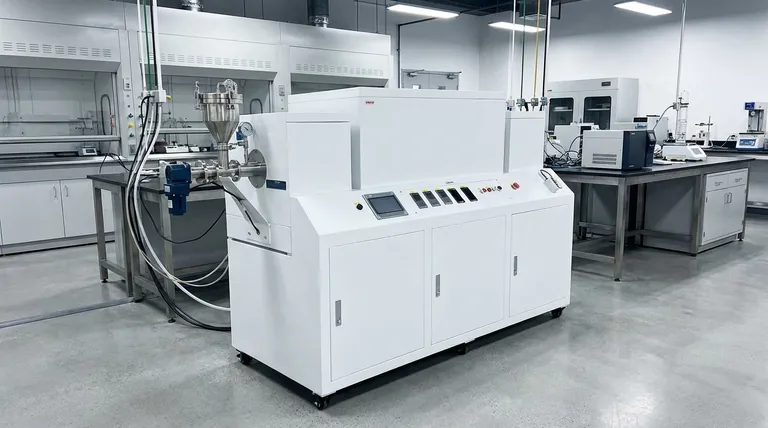

The Core Problem: Why Raw Bio-Oil Needs Upgrading
Raw liquid (bio-oil) produced from the initial pyrolysis of materials like wood, agricultural waste, or algae is not ready for direct use in engines or refineries. It possesses several fundamental chemical challenges that upgrading is designed to solve.
High Oxygen Content
The most significant issue is the high concentration of oxygen in the bio-oil, often making up 35-40% of its weight. This oxygen is bound in various chemical compounds that make the oil unstable and fundamentally different from petroleum crude oil.
Chemical Instability and Acidity
The oxygen-containing compounds make the bio-oil acidic and reactive. Over time, it can polymerize, increasing its viscosity and forming sludge, which makes storage and transport difficult.
Low Energy Density
The presence of so much oxygen means the bio-oil contains less energy per liter compared to conventional fossil fuels. To be a viable fuel alternative, its energy density must be increased, which is achieved by removing the oxygen.
How Catalytic Upgrading Works
Catalytic upgrading introduces a catalyst into the pyrolysis process to selectively target and promote the chemical reactions that remove oxygen. This is typically done in one of two primary configurations.
In-Situ Upgrading: The Integrated Approach
In this method, the catalyst is mixed directly with the biomass feedstock inside the main pyrolysis reactor. As the biomass breaks down, the resulting vapors immediately interact with the catalyst.
This approach is simpler in terms of equipment design but offers less control over the reaction conditions and can lead to faster deactivation of the catalyst.
Ex-Situ Upgrading: The Two-Step Approach
This method separates the process into two distinct stages. First, the biomass is heated in a pyrolysis reactor to produce vapors. These vapors are then passed over a separate, dedicated reactor bed containing the catalyst.
Ex-situ upgrading provides much greater control over the process, allowing operators to optimize temperatures and pressures for both pyrolysis and upgrading independently. This often results in a higher quality final product.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While catalytic upgrading is essential for producing high-quality biofuels, it introduces layers of complexity and cost that must be carefully evaluated.
Increased Operational Complexity
Adding a catalytic stage, especially an ex-situ reactor, requires more sophisticated equipment and precise process control. This increases both the initial capital investment and the day-to-day operational challenges.
Economic Viability at Scale
The additional costs associated with the catalyst and the upgrading reactor can be difficult to justify for smaller-scale plants. The economic benefits are often only realized in larger, more integrated biorefinery operations.
Catalyst Management
Catalysts do not last forever. They can become deactivated by carbon deposits (coking) or contaminants in the feedstock, requiring periodic regeneration or replacement, which adds another layer of operational cost and complexity.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use catalytic upgrading and the choice between in-situ and ex-situ methods depends entirely on your end-product goals and operational constraints.
- If your primary focus is producing the highest quality drop-in fuel: Ex-situ upgrading is the superior method because it allows for precise optimization of the deoxygenation reactions.
- If your primary focus is a simpler design with lower initial capital cost: In-situ upgrading offers a more integrated and straightforward equipment setup, though potentially at the cost of fuel quality and catalyst lifespan.
- If your primary focus is producing specialty chemicals instead of fuel: The economics become even more critical, as the process must be carefully designed to justify the higher complexity and operational costs.
Ultimately, catalytic upgrading is the key enabling technology that bridges the gap between raw biomass and a finished, high-value liquid fuel.
Summary Table:
| Feature | In-Situ Upgrading | Ex-Situ Upgrading |
|---|---|---|
| Process Setup | Catalyst mixed with biomass in reactor | Separate reactor for vapors after pyrolysis |
| Control & Quality | Lower control, potentially lower product quality | Higher control, superior product quality |
| Complexity & Cost | Simpler equipment, lower initial cost | More complex, higher capital investment |
| Catalyst Lifespan | Faster deactivation possible | Longer lifespan with optimized conditions |
Ready to transform your biomass into high-value fuel?
Choosing the right pyrolysis and catalytic upgrading strategy is critical for your project's success and economic viability. KINTEK specializes in providing robust lab equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research and process development.
Our experts can help you select the right setup—whether for initial testing or scaling up—ensuring you achieve the desired bio-oil quality efficiently.
Contact KINTEL today to discuss your laboratory needs and how our solutions can accelerate your biofuel research and development.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the range of pyrolysis? Master Temperature Control for Optimal Bio-Product Yields
- What are the factors affecting the yield of bio-oil from the pyrolysis of coconut shell? Control 4 Key Parameters
- How is a high-temperature calcination furnace utilized in BZY20 Sol-gel? Achieve Pure Cubic Perovskite Phases
- What are the equipment requirements for loading platinum (Pt) onto composite supports? Precise Stirring for High Dispersion
- What are the process advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for WS2 powder? Achieve Superior Material Crystallinity



















