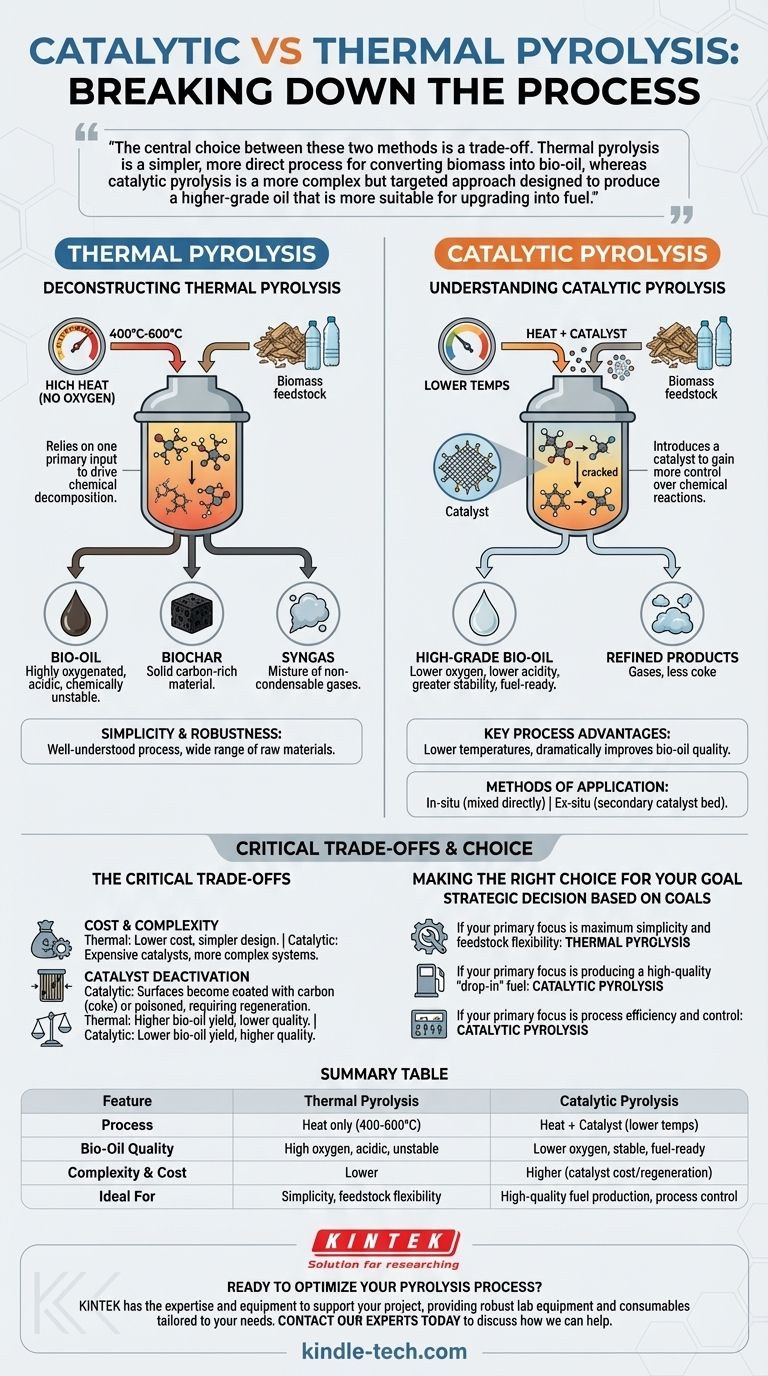
At its core, the difference is simple: Thermal pyrolysis uses only high heat to break down materials in the absence of oxygen, while catalytic pyrolysis uses both heat and a catalyst. The addition of a catalyst fundamentally changes the process, allowing for lower temperatures and creating a higher-quality, more refined final product.
The central choice between these two methods is a trade-off. Thermal pyrolysis is a simpler, more direct process for converting biomass into bio-oil, whereas catalytic pyrolysis is a more complex but targeted approach designed to produce a higher-grade oil that is more suitable for upgrading into fuel.
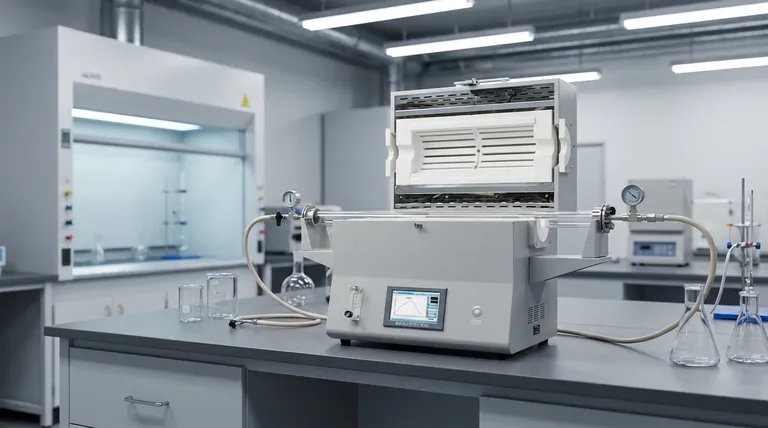

Deconstructing Thermal Pyrolysis
Thermal pyrolysis is the foundational process, relying on one primary input to drive the chemical decomposition of organic material.
The Role of High Heat
This method subjects feedstock, like biomass or plastic, to high temperatures, typically ranging from 400°C to 600°C. This is done within a reactor that has no oxygen to prevent combustion.
The intense heat is sufficient to break the complex chemical bonds within the material.
The Resulting Products
Thermal pyrolysis produces three main outputs: bio-oil (a liquid), biochar (a solid carbon-rich material), and syngas (a mixture of non-condensable gases).
The bio-oil produced is often highly oxygenated, acidic, and chemically unstable, making it difficult to use as a direct fuel without significant further processing.
Simplicity and Robustness
The primary advantage of thermal pyrolysis is its relative simplicity. The process is well-understood and can be applied to a very wide range of raw materials without requiring precise chemical compatibility.
Understanding Catalytic Pyrolysis
Catalytic pyrolysis introduces a new element—a catalyst—to gain more control over the chemical reactions and steer them toward a more desirable outcome.
The Catalyst's Function
A catalyst is a substance that accelerates chemical reactions without being consumed. In pyrolysis, its job is to more effectively "crack" the large organic molecules released during initial heating.
This selective cracking results in smaller, more stable molecules, fundamentally altering the composition of the final bio-oil.
Key Process Advantages
The use of a catalyst provides two major benefits. First, it often allows the process to run at lower temperatures, which can reduce energy consumption.
Second, and more importantly, it dramatically improves the quality of the bio-oil. The oil has lower oxygen content, lower acidity, and greater stability, making it more akin to conventional crude oil and easier to upgrade into transportation fuels.
Methods of Application
Catalysts can be introduced in two primary ways. In-situ catalytic pyrolysis involves mixing the catalyst directly with the feedstock before or during heating.
Ex-situ catalytic pyrolysis keeps them separate. The initial thermal pyrolysis occurs, and then the resulting vapors are passed over a secondary, dedicated catalyst bed for upgrading.
The Critical Trade-offs
While catalytic pyrolysis offers a higher-quality product, this advantage comes with significant operational and economic considerations.
Cost and Complexity
Catalysts, especially those containing precious metals or specifically engineered zeolites, can be expensive. This adds a significant cost to the overall process that thermal pyrolysis avoids.
The system's design, whether in-situ or ex-situ, is also inherently more complex than a simple thermal reactor.
Catalyst Deactivation
Catalysts do not last forever. Over time, their surfaces can become coated with carbon deposits (coke) or poisoned by contaminants in the feedstock.
This deactivation requires a regeneration step (e.g., burning off the coke) or eventual replacement of the catalyst, adding another layer of operational complexity and cost.
Product Yield vs. Quality
There is often an inverse relationship between bio-oil quality and quantity. While catalytic pyrolysis improves oil quality, it often increases the production of gases and coke.
This means the total yield of liquid bio-oil can be lower compared to thermal pyrolysis, a critical factor for economic viability.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal method depends entirely on the intended use of the final products and the economic constraints of the project.
- If your primary focus is maximum simplicity and feedstock flexibility: Thermal pyrolysis is the more direct and robust method for converting raw materials into a basic bio-oil, biochar, and syngas.
- If your primary focus is producing a high-quality "drop-in" fuel: Catalytic pyrolysis is essential for creating a more stable, deoxygenated oil that requires less intensive downstream upgrading.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency and control: Catalytic pyrolysis allows for lower operating temperatures and provides a greater degree of control over the chemical composition of your end products.
Ultimately, choosing between them is a strategic decision balancing upfront simplicity against the value of a more refined output.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Thermal Pyrolysis | Catalytic Pyrolysis |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Heat only (400-600°C) | Heat + Catalyst (lower temps) |
| Bio-Oil Quality | High oxygen, acidic, unstable | Lower oxygen, stable, fuel-ready |
| Complexity & Cost | Lower | Higher (catalyst cost/regeneration) |
| Ideal For | Simplicity, feedstock flexibility | High-quality fuel production, process control |
Ready to Optimize Your Pyrolysis Process?
Whether your goal is simple biomass conversion with thermal pyrolysis or producing high-grade, fuel-ready bio-oil with catalytic pyrolysis, KINTEK has the expertise and equipment to support your project. We specialize in providing robust lab equipment and consumables tailored to your specific research and production needs.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can help you achieve superior results and efficiency in your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What precautions should be taken when using a tube furnace? Ensure Safe, Effective High-Temperature Processing
- What is a tubular furnace used for? Precision Heating for Material Synthesis & Analysis
- How does a quartz tube vacuum furnace contribute to the crystallization process of Ag-doped Li-argyrodite electrolytes?
- What is the role of a quartz tube in the preparation of Mo2Ga2C powder precursors? Essential Synthesis Benefits
- How does a high-temperature tube furnace facilitate the phase transformation of alumina products? Master Thermal Control



















