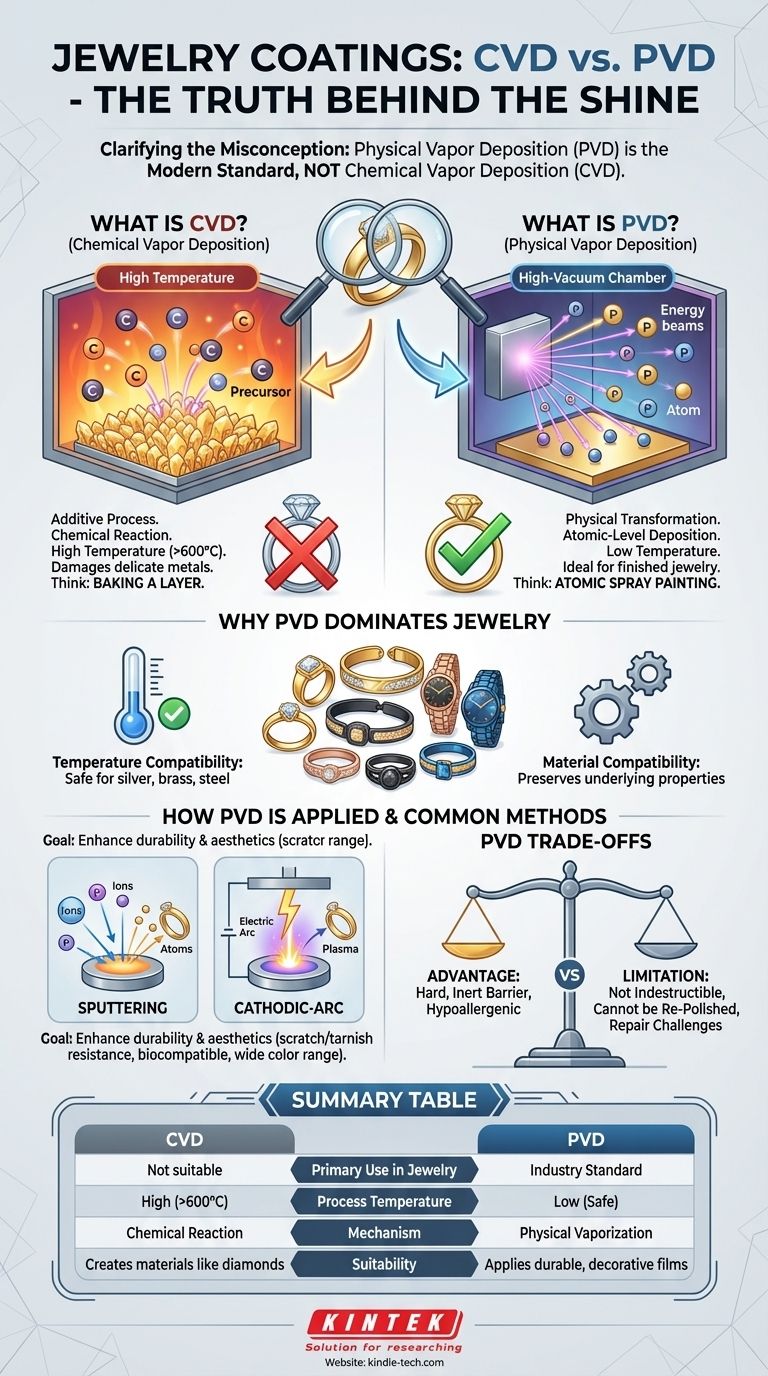
While the term is sometimes used incorrectly, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is not the primary process used for modern jewelry coatings. The technology you are likely seeking is Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), a process that applies a thin, durable, and decorative metallic film to a piece of jewelry in a vacuum environment. This distinction is critical because PVD is far better suited to the temperature sensitivities and material requirements of the jewelry industry.
The core principle to understand is this: while your question is about CVD, the technology that actually produces the durable, colorful coatings on modern jewelry is Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD). The difference is that PVD uses physical methods to vaporize a coating material, whereas CVD uses chemical reactions—a process generally less suitable for finished jewelry.

The Fundamental Distinction: CVD vs. PVD
To understand why the industry relies on PVD, we must first clarify the difference between these two powerful coating technologies. They achieve a similar outcome—a thin film—but through entirely different mechanisms.
What is Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)?
CVD is an additive process where a substrate (the object to be coated) is exposed to one or more volatile chemical precursors. In a high-temperature reaction chamber, these gases react or decompose on the substrate's surface to produce the desired solid coating.
Think of it as baking a layer onto a surface. The heat and chemical interaction are what create the new, solid film. This process is exceptional for creating ultra-pure, high-performance materials like synthetic diamonds or semiconductor films.
What is Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)?
PVD, in contrast, involves physically transforming a solid coating material into a vapor, which then condenses onto the substrate. This happens inside a high-vacuum chamber, ensuring the vapor travels in a straight line to the target object.
Imagine this as an atomic-level spray painting process. A solid block of the coating material is bombarded with energy, blasting off individual atoms or molecules that then deposit as a thin, uniform layer onto the jewelry.
Why PVD Dominates in Jewelry
The jewelry industry almost exclusively uses PVD for two key reasons: temperature and material compatibility.
CVD processes often require very high temperatures (often >600°C) to initiate the necessary chemical reactions. These temperatures would damage or destroy most metals used in jewelry, such as sterling silver, brass, or even stainless steel.
PVD, on the other hand, can be performed at much lower temperatures. This makes it ideal for coating finished, often delicate, pieces of jewelry without altering the properties of the underlying metal.
How PVD Is Applied in the Jewelry Industry
The goal of using PVD on jewelry is to enhance both its durability and its aesthetic possibilities, far beyond what traditional metals can offer.
The Goal: Durability and Aesthetics
A PVD coating, though only a few microns thick, creates an extremely hard and inert surface barrier. This layer dramatically increases resistance to scratches, abrasion, and tarnishing.
Furthermore, PVD allows manufacturers to apply a wide array of colors. By using materials like titanium nitride or zirconium nitride, they can create finishes that perfectly mimic yellow gold, rose gold, or produce modern colors like black, chocolate, or blue on a durable and inexpensive base like stainless steel.
Common PVD Methods
As the references note, two primary PVD methods are used for decorative coatings:
- Sputtering: In this process, the solid coating material (the "target") is bombarded with high-energy ions, which physically knock atoms off its surface. These "sputtered" atoms then travel through the vacuum and deposit onto the jewelry.
- Cathodic-Arc: This method uses a high-current electric arc to strike the target material, creating a tiny, intensely hot spot. This vaporizes the material into a highly ionized plasma, which is then steered toward the jewelry to form an exceptionally dense and well-adhered coating.
Understanding the Trade-offs of PVD Coatings
While PVD is a superior technology for this application, it's essential to approach it with a clear understanding of its strengths and limitations.
The Advantage: A Hard, Inert Barrier
The primary benefit is durability. A PVD coating is significantly harder than traditional electroplating. It is also biocompatible and hypoallergenic, as it seals the base metal (which might contain nickel) from contacting the skin.
The Limitation: It's Still a Coating
PVD is incredibly tough, but it is not indestructible. A deep gouge or scratch from a sharp, hard object can penetrate the coating and expose the base metal underneath.
Unlike solid gold jewelry, a PVD-coated piece cannot be re-polished to remove scratches, as doing so would remove the colored coating itself.
The Challenge: Repair and Resizing
Similarly, standard jewelry repair work like soldering to resize a ring is generally not possible on a PVD-coated item. The heat from a jeweler's torch would destroy the coating, and it cannot be easily reapplied outside of a specialized industrial facility.
How to Evaluate Coated Jewelry
Understanding the technology behind the finish allows you to make an informed choice based on your specific needs.
- If your primary focus is durability for daily wear: Look for jewelry that explicitly states it uses a PVD coating, especially on a strong base metal like stainless steel or titanium.
- If your primary focus is achieving a specific modern color: PVD is the superior technology for achieving rich, lasting colors like black, blue, or a consistent rose gold tone that won't tarnish.
- If your primary focus is long-term value and repairability: Choose solid precious metals like gold or platinum, as they can be polished, repaired, and resized throughout their lifetime.
By knowing the difference between the process and the promise, you can select jewelry that truly aligns with your expectations for both beauty and performance.
Summary Table:
| Feature | CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) | PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Use in Jewelry | Not suitable for finished jewelry | Industry standard for coatings |
| Process Temperature | High (>600°C) | Low (jewelry-safe) |
| Mechanism | Chemical reaction & decomposition | Physical vaporization & deposition |
| Suitability | Creates materials (e.g., diamonds) | Applies durable, decorative films |
Upgrade your jewelry production with professional PVD solutions from KINTEK!
Are you looking to enhance the durability, color variety, and aesthetic appeal of your jewelry pieces? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables, including state-of-the-art PVD systems tailored for the jewelry industry. Our technology ensures a hard, scratch-resistant, and tarnish-proof coating that elevates your product quality and customer satisfaction.
Let us help you achieve consistent, vibrant finishes on metals like stainless steel, titanium, and more—all while maintaining the integrity of your delicate jewelry items.
Contact us today to explore how our PVD solutions can transform your jewelry line!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- VHP Sterilization Equipment Hydrogen Peroxide H2O2 Space Sterilizer
- Molybdenum Tungsten Tantalum Special Shape Evaporation Boat
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of plasma enhanced CVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What is the principle of plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? Achieve Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the drawbacks of PECVD? Understanding the Trade-offs of Low-Temperature Deposition
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















