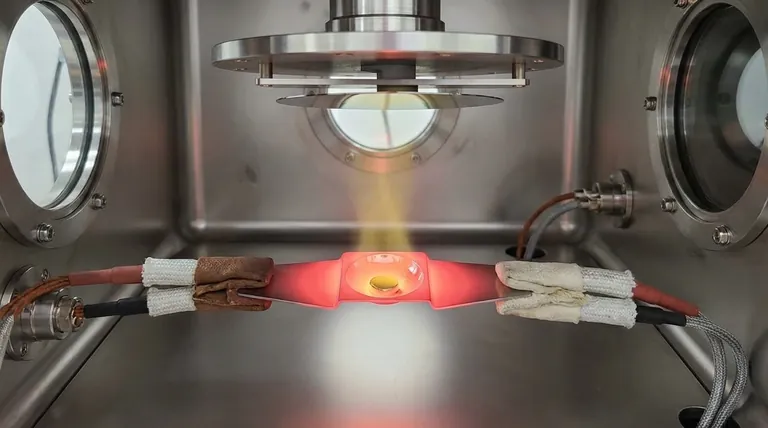
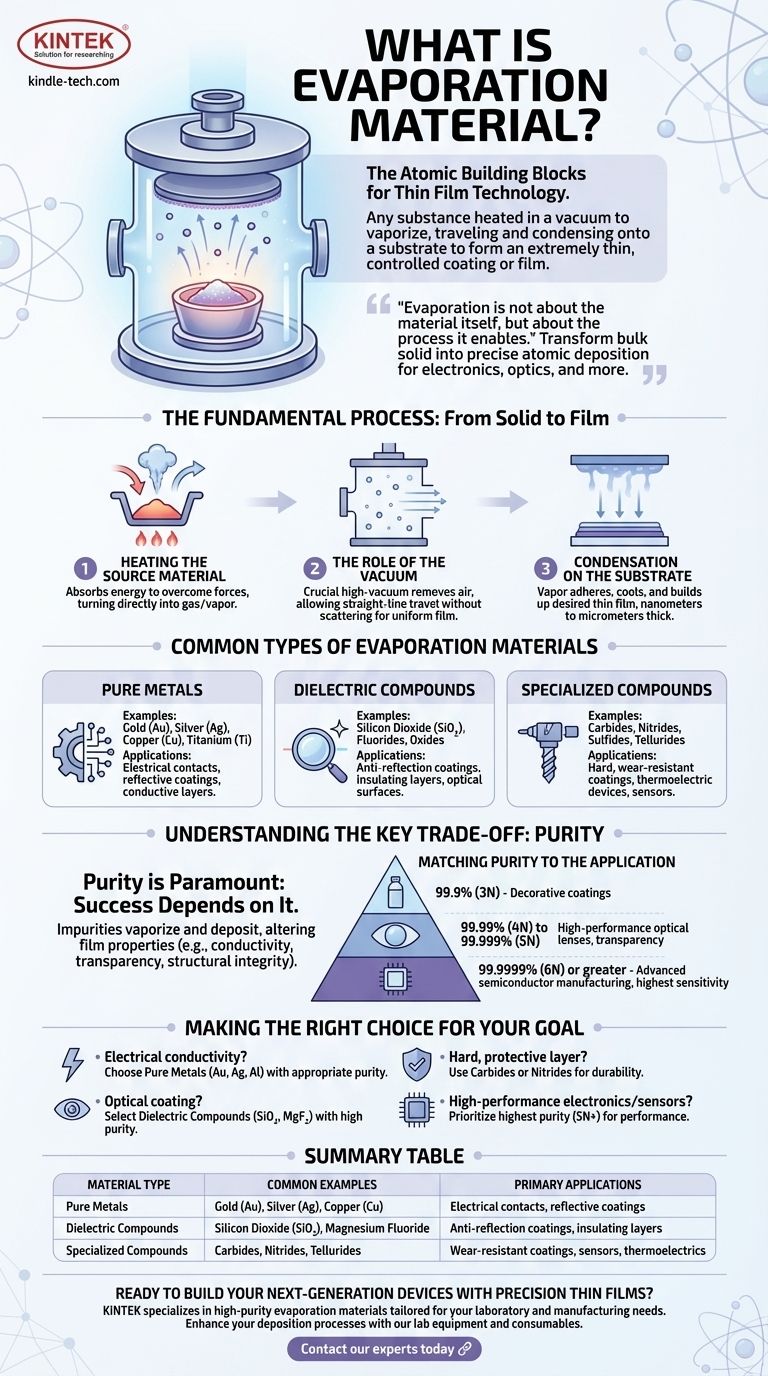
In essence, an evaporation material is any substance—from pure metals to complex compounds—that is heated in a vacuum until it vaporizes. This vapor then travels and condenses onto a target surface, known as a substrate, to form an extremely thin and highly controlled coating or film.
Evaporation is not about the material itself, but about the process it enables. The goal is to transform a bulk solid material into a vapor that can be precisely deposited, atom by atom, to build functional thin films for applications ranging from electronics to optics.

The Fundamental Process: From Solid to Film
The creation of a thin film via evaporation is a multi-step physical process that relies on a highly controlled environment. Each stage is critical to the quality of the final coating.
Heating the Source Material
The process begins by heating the evaporation material inside a vacuum chamber. As the material absorbs energy, its atoms or molecules gain enough momentum to overcome the forces holding them in a solid or liquid state, transitioning directly into a gas or vapor.
The Role of the Vacuum
This vaporization occurs within a high-vacuum environment. The vacuum is crucial because it removes air and other particles, ensuring the vaporized material can travel in a straight line from the source to the substrate without collisions, which would otherwise scatter the atoms and prevent a uniform film.
Condensation on the Substrate
When the vapor stream reaches the cooler substrate surface, it rapidly cools, condenses, and adheres. This process builds up the desired thin film, often just a few nanometers to micrometers thick, layer by layer.
Common Types of Evaporation Materials
The specific material chosen is dictated entirely by the desired properties of the final film. Materials are often categorized by their electrical, optical, or mechanical characteristics.
Pure Metals
Metals are among the most common evaporation materials. They are used when electrical conductivity or reflectivity is required.
- Examples: Gold (Au), Silver (Ag), Copper (Cu), and Titanium (Ti).
- Applications: Electrical contacts in microchips, reflective coatings for mirrors, and conductive layers in displays.
Dielectric Compounds
These materials are electrical insulators and are often transparent at certain wavelengths, making them ideal for optical applications.
- Examples: Silicon Dioxide (SiO2), Fluorides (e.g., Magnesium Fluoride), and various Oxides.
- Applications: Anti-reflection coatings on lenses, insulating layers in capacitors, and protective optical surfaces.
Specialized Compounds
A vast range of other compounds are used for more specific and demanding applications.
- Examples: Carbides, Nitrides, Sulfides, and Tellurides.
- Applications: Hard, wear-resistant coatings for tools (Carbides, Nitrides) or components in thermoelectric devices and sensors (Tellurides, Sulfides).
Understanding the Key Trade-off: Purity
For evaporation materials, purity is not a minor detail—it is often the most critical factor determining the success of the final product.
Why Purity Is Paramount
Any impurity present in the source material will also be vaporized and deposited into the final thin film. These unwanted atoms can drastically alter the film's intended properties, such as degrading its electrical conductivity, reducing its optical transparency, or compromising its structural integrity.
Matching Purity to the Application
The required purity level, which can range from 99.9% to an exceptional 99.99999%, depends entirely on the application's sensitivity.
- A simple decorative coating on a consumer product may only require 99.9% (3N) purity.
- A high-performance optical lens might demand 99.99% (4N) to 99.999% (5N) purity to ensure transparency.
- Advanced semiconductor manufacturing requires the highest purities, often 99.9999% (6N) or greater, as even a few stray atoms can ruin a microchip.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct evaporation material and purity level is a foundational decision in thin-film deposition. Your choice should be guided by the primary function of the coating you intend to create.
- If your primary focus is electrical conductivity or contacts: Choose a pure metal like gold, silver, or aluminum with a purity level appropriate for the device's sensitivity.
- If your primary focus is an optical coating (e.g., anti-reflection): Select a dielectric compound like Silicon Dioxide or Magnesium Fluoride, ensuring high purity for maximum transparency.
- If your primary focus is a hard, protective layer: Use a carbide or nitride material known for its durability and wear resistance.
- If your primary focus is high-performance electronics or sensors: Prioritize the highest possible material purity (5N or greater) above all other factors, as performance is directly tied to a lack of contamination.
Ultimately, these materials are the atomic-level building blocks that enable much of our modern technology.
Summary Table:
| Material Type | Common Examples | Primary Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Pure Metals | Gold (Au), Silver (Ag), Copper (Cu) | Electrical contacts, reflective coatings |
| Dielectric Compounds | Silicon Dioxide (SiO₂), Magnesium Fluoride | Anti-reflection coatings, insulating layers |
| Specialized Compounds | Carbides, Nitrides, Tellurides | Wear-resistant coatings, sensors, thermoelectrics |
Ready to build your next-generation devices with precision thin films? KINTEK specializes in providing high-purity evaporation materials—from pure metals to complex compounds—tailored for your specific laboratory and manufacturing needs. Whether you're developing advanced semiconductors, optical coatings, or durable protective layers, our materials ensure the performance and reliability your applications demand. Contact our experts today to discuss your project requirements and discover how KINTEK's lab equipment and consumables can enhance your deposition processes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Vacuum Cold Trap Direct Cold Trap Chiller
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- What is thermal effect via evaporation? A Simple Guide to Thin-Film Deposition
- What is the vacuum level of a thermal evaporator? Achieve Purity with High Vacuum (10⁻⁵ to 10⁻⁷ Torr)
- What is the thermal evaporation technique? A Guide to Thin-Film Deposition for Your Lab
- How is deposition time calculated? Mastering the Clock for Strategic Legal Advantage
- What are the uses of evaporation in industry? From Food Concentration to High-Tech Thin Films



















