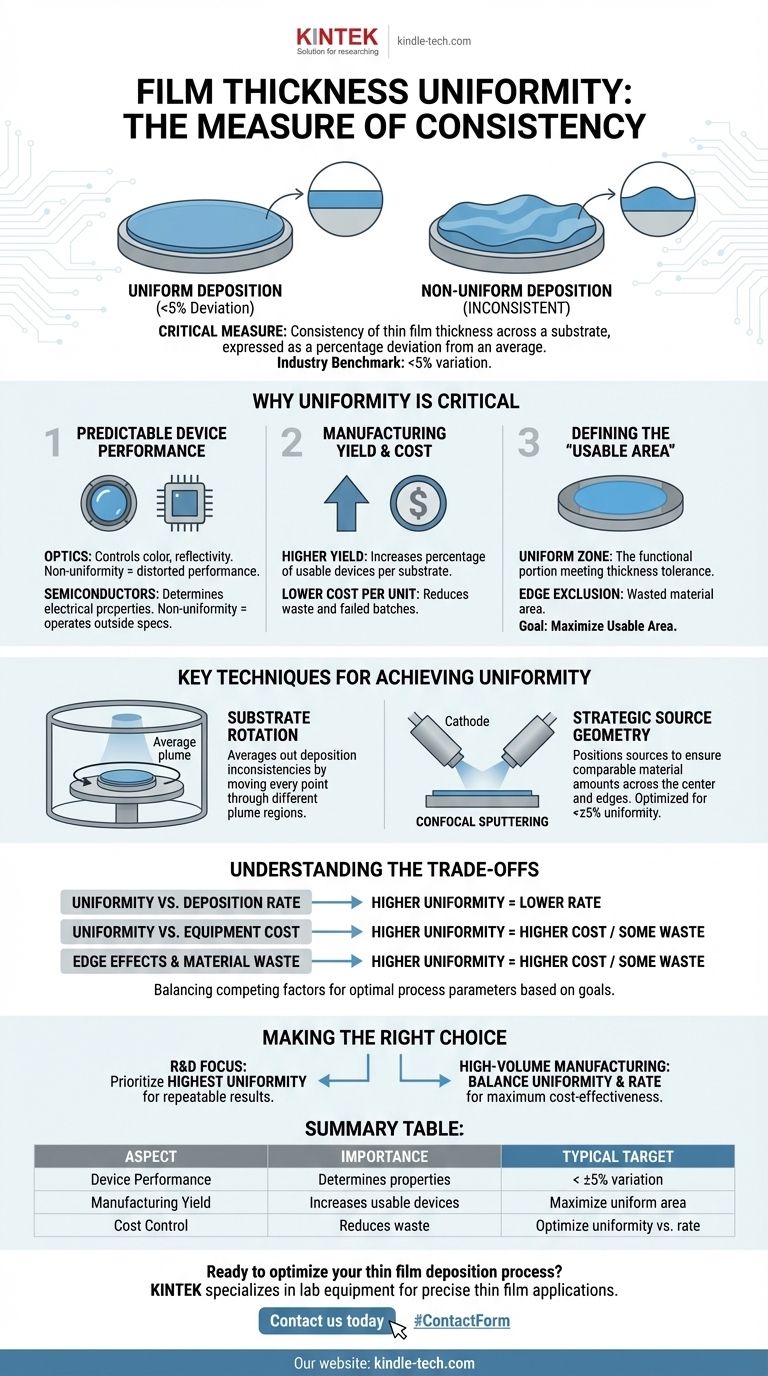
At its core, film thickness uniformity is a critical measure of how consistent the thickness of a deposited thin film is across the surface of a substrate. This consistency is not absolute; it is typically expressed as a percentage deviation from an average thickness. For example, a common industry benchmark for a "uniform area" is one where the film's thickness varies by less than 5% from the average value across that specific zone.
Film thickness uniformity is not merely a geometric property; it is a direct predictor of a device's functional performance and manufacturing yield. The goal is to control the deposition process so that every critical area of a substrate receives a nearly identical amount of material, ensuring predictable and reliable outcomes.

Why Uniformity is a Critical Metric
Achieving a specific thickness is only half the battle. Ensuring that thickness is consistent across the entire functional area of a substrate is what determines success or failure in many applications.
Predictable Device Performance
Slight variations in thickness can cause significant changes in a material's physical properties.
In optics, film thickness directly controls properties like color, reflectivity, and anti-reflection. A non-uniform coating on a lens will result in distorted optical performance.
In semiconductors, the thickness of gate oxides, conductors, and dielectric layers determines electrical characteristics like capacitance and resistance. Non-uniformity leads to devices that operate outside of their required specifications.
Manufacturing Yield and Cost
Every substrate that fails to meet thickness uniformity standards is a loss of time, materials, and money.
High uniformity translates directly to high manufacturing yield—the percentage of usable devices produced from a single substrate or batch. Increasing uniformity from 90% to 95% across a substrate can mean a significant increase in the number of viable chips or components, drastically lowering the cost per unit.
Defining the "Usable Area"
The "uniform area" is the portion of the substrate where the film meets the required thickness tolerance.
For practical purposes, this is the only part of the substrate that can be used to fabricate functional devices. The goal of process engineering is to maximize this usable area, pushing the uniform zone as close to the physical edge of the substrate as possible.
Key Techniques for Achieving Uniformity
Engineers use several well-established methods to control the deposition process and create highly uniform films. These techniques are designed to average out the natural inconsistencies of a deposition source.
Substrate Rotation
This is the most common and effective method for improving uniformity. By rotating the substrate during deposition, you ensure that every point on its surface passes through different regions of the deposition plume.
This movement averages out any "hot spots" or areas of lower flux from the source, resulting in a much more even coating than would be possible with a static substrate.
Strategic Source Geometry
The positioning of the deposition source relative to the substrate is critical. In processes like confocal sputtering, cathodes are intentionally tilted at an angle.
This, combined with substrate rotation, ensures that both the center and the outer edges of the substrate receive a comparable amount of deposited material over the course of the process. The exact tilt angle and target-to-substrate distance are carefully optimized to achieve uniformity often better than ±5%.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Pursuing perfect uniformity often involves balancing competing factors. There is no single "best" setup for all applications; there are only optimal solutions for specific goals.
Uniformity vs. Deposition Rate
Techniques that improve uniformity, such as increasing the distance between the source and the substrate, often reduce the deposition rate. This means the process takes longer, lowering throughput. A key engineering challenge is to find the sweet spot that provides acceptable uniformity without making the process time prohibitively long.
Uniformity vs. Equipment Cost
Achieving the highest levels of uniformity requires sophisticated equipment. Systems with planetary rotation, multiple sources, or complex magnetic field shaping are significantly more expensive to purchase and maintain than simpler, static systems. The required level of uniformity must justify the capital investment.
Edge Effects and Material Waste
It is nearly impossible to achieve perfect uniformity all the way to the physical edge of a substrate. This "edge exclusion" zone results in some wasted material and unusable substrate area. Minimizing this effect is a constant focus, but it can rarely be eliminated entirely.
Making the Right Choice for Your Process
Your approach to film thickness uniformity should be dictated by your end goal. Whether you prioritize absolute precision or manufacturing efficiency will determine your optimal process parameters.
- If your primary focus is research and development: Prioritize achieving the highest possible uniformity to ensure your experimental results are repeatable and that material properties are the only changing variable.
- If your primary focus is high-volume manufacturing: Aim for the most cost-effective balance between uniformity (to maximize device yield) and deposition rate (to maximize throughput).
Ultimately, mastering film thickness uniformity is about taking direct control over the quality and performance of your final product.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Importance | Typical Target |
|---|---|---|
| Device Performance | Determines electrical/optical properties | < ±5% variation |
| Manufacturing Yield | Increases usable devices per substrate | Maximize uniform area |
| Cost Control | Reduces material waste and failed batches | Optimize uniformity vs. rate |
Ready to optimize your thin film deposition process? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for precise thin film applications. Our expertise helps laboratories achieve superior film thickness uniformity, ensuring predictable device performance and higher manufacturing yields. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your research or production efficiency!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- CVD Diamond Cutting Tool Blanks for Precision Machining
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Anti-Cracking Press Mold for Lab Use
People Also Ask
- What is microwave plasma CVD? A Guide to High-Purity Diamond and Material Synthesis
- What is the role of the HF-CVD system in preparing BDD electrodes? Scalable Solutions for Boron-Doped Diamond Production
- What are the advantages of using HFCVD for BDD electrodes? Scaling Industrial Diamond Production Efficiently
- What is the specific function of the metal filament in HF-CVD? Key Roles in Diamond Growth
- How is something diamond coated? A Guide to CVD Growth vs. Plating Methods



















