While a powerful manufacturing process, powder metallurgy (PM) is not a universal solution. Its primary disadvantages are inherent limitations on part size, lower mechanical properties such as strength and ductility when compared to forged or cast materials, and constraints on certain types of geometric complexity. These factors arise directly from the physics of compacting and sintering metal powders.
Powder metallurgy's core trade-off is sacrificing ultimate part size and strength for exceptional material efficiency and the ability to produce complex, net-shape parts at high production volumes. Understanding this balance is key to deciding if it's the right process for your application.
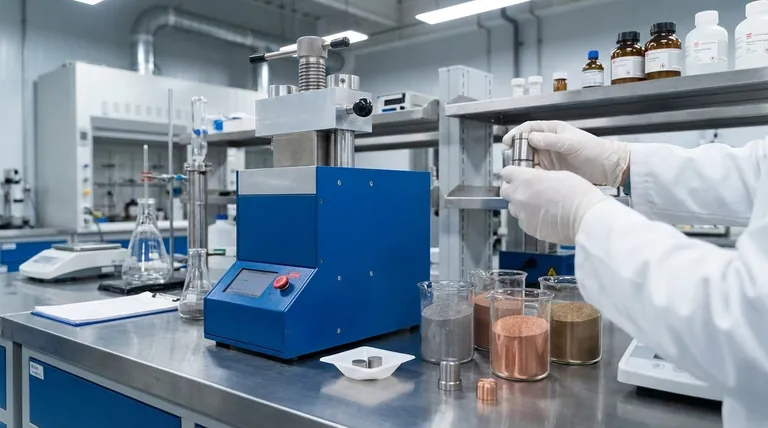

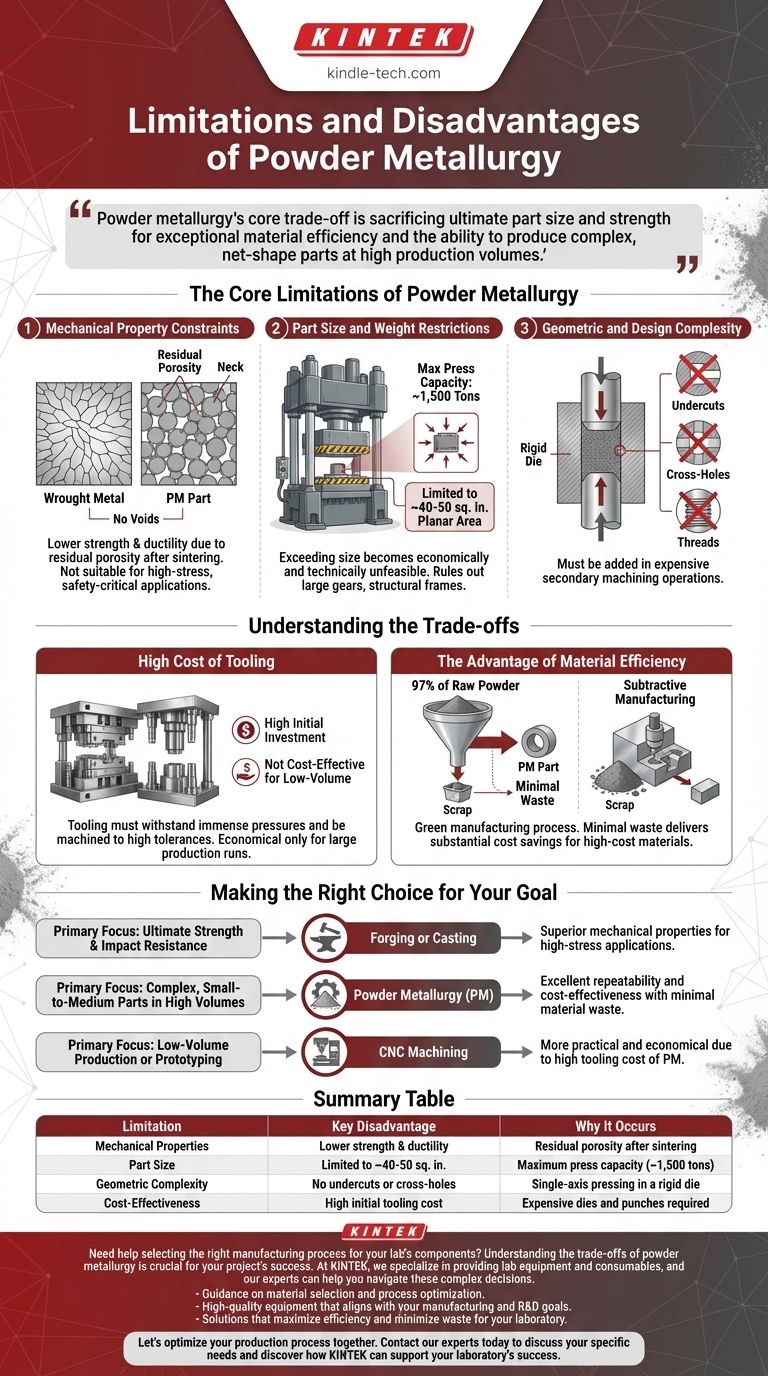
The Core Limitations of Powder Metallurgy
To select the right manufacturing process, you must understand not just what the limitations are, but why they exist. The drawbacks of PM are rooted in the tooling and physics of the process itself.
Mechanical Property Constraints
The defining characteristic of a PM part is its internal porosity. While the sintering process—heating the compacted powder below its melting point—creates metallurgical bonds between particles through a process called necking, it rarely eliminates all voids.
This residual porosity means PM parts are generally not as strong or ductile as components made from wrought metals or through casting. They have lower resistance to fatigue and impact, making them unsuitable for many high-stress, safety-critical applications where maximum material integrity is required.
Part Size and Weight Restrictions
The PM process relies on massive presses to compact the metal powder into its initial "green" state. The force required is directly proportional to the cross-sectional area of the part.
The industry's largest presses are typically around 1,500 tons. This practical reality limits the planar area of a component to roughly 40-50 square inches. Exceeding this size becomes economically and technically unfeasible, ruling PM out for large gears, structural frames, or engine blocks.
Geometric and Design Complexity
While PM is excellent at creating intricate net-shape parts, it has specific geometric limitations. The process involves pressing powder in a rigid die along a single axis.
This means features like undercuts, cross-holes (holes perpendicular to the pressing direction), or threads cannot be molded directly into the part. Such features must be added in more expensive secondary machining operations, which can negate the cost-effectiveness of the PM process.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a manufacturing method is about balancing pros and cons. The disadvantages of powder metallurgy are weighed against one of its most compelling advantages.
The High Cost of Tooling
The dies and punches used for powder compaction must withstand immense pressures and be machined to extremely high tolerances. This tooling is expensive to design and create.
Because of this high initial investment, PM is generally not cost-effective for low-volume production or prototyping. The process only becomes economical when the tooling cost can be amortized over a large production run of many thousands or millions of parts.
The Advantage of Material Efficiency
Powder metallurgy is considered a green manufacturing process for a reason. Approximately 97% of the raw powder that enters the process becomes part of the finished component.
This is a stark contrast to subtractive manufacturing like machining, where a significant portion of the expensive raw material is cut away and becomes scrap. For high-cost materials, PM's minimal waste can deliver substantial cost savings and environmental benefits that outweigh its mechanical limitations.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting powder metallurgy depends entirely on your project's priorities. You must weigh the need for performance and volume against the constraints of the process.
- If your primary focus is ultimate strength and impact resistance: Forging or casting will provide the superior mechanical properties required for high-stress applications.
- If your primary focus is producing complex, small-to-medium parts in high volumes: PM is an outstanding choice, offering excellent repeatability and cost-effectiveness with minimal material waste.
- If your primary focus is low-volume production or prototyping: The high tooling cost of PM makes other methods, such as CNC machining, a more practical and economical solution.
Ultimately, choosing powder metallurgy is a strategic decision that hinges on balancing your performance requirements against your production volume and cost targets.
Summary Table:
| Limitation | Key Disadvantage | Why It Occurs |
|---|---|---|
| Mechanical Properties | Lower strength & ductility | Residual porosity after sintering |
| Part Size | Limited to ~40-50 sq. in. | Maximum press capacity (~1,500 tons) |
| Geometric Complexity | No undercuts or cross-holes | Single-axis pressing in a rigid die |
| Cost-Effectiveness | High initial tooling cost | Expensive dies and punches required |
Need help selecting the right manufacturing process for your lab's components?
Understanding the trade-offs of powder metallurgy is crucial for your project's success. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing lab equipment and consumables, and our experts can help you navigate these complex decisions.
We offer:
- Guidance on material selection and process optimization.
- High-quality equipment that aligns with your manufacturing and R&D goals.
- Solutions that maximize efficiency and minimize waste for your laboratory.
Let's optimize your production process together. Contact our experts today to discuss your specific needs and discover how KINTEK can support your laboratory's success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Automatic Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Electric Lab Cold Isostatic Press CIP Machine for Cold Isostatic Pressing
- Manual Cold Isostatic Pressing Machine CIP Pellet Press
- Manual High Temperature Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Lab
- Manual Heated Hydraulic Press Machine with Heated Plates for Laboratory Hot Press
People Also Ask
- What transfer is sputtering based on? Momentum Transfer for Superior Thin Film Deposition
- What is the process of calcination? A Guide to Purification & Thermal Transformation
- What is the process of DC sputtering? A Step-by-Step Guide to Thin Film Deposition
- What are the different types of ash analysis? Dry vs. Wet Ashing Methods Explained
- How many types of hardening techniques are there? A Multi-Layered Security Strategy Explained
- What is the DC sputtering mechanism? A Guide to Physical Vapor Deposition for Thin Films
- What is magnetron plasma? A Guide to High-Efficiency Thin-Film Deposition
- Why is ultrasonic treatment essential for PAAMP-b-PVK synthesis? Achieve Surfactant-Free Emulsion Polymerization



















