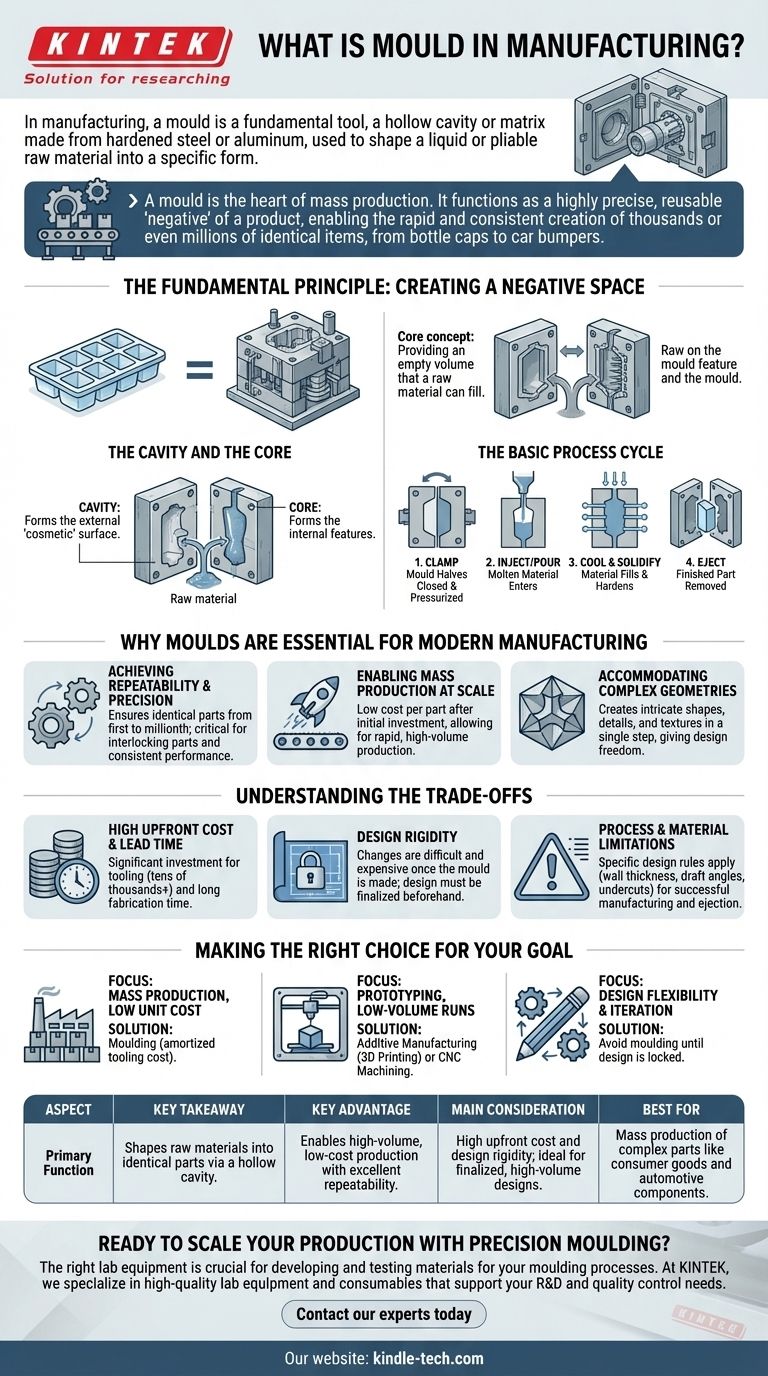
In manufacturing, a mould is a fundamental tool. It is a hollow cavity or matrix, typically made from hardened steel or aluminum, that is used to shape a liquid or pliable raw material—such as molten plastic, metal, or glass—into a specific, desired form. The material is injected or poured into the mould, where it cools and solidifies, taking on the inverse shape of the cavity to create a finished part.
A mould is the heart of mass production. It functions as a highly precise, reusable "negative" of a product, enabling the rapid and consistent creation of thousands or even millions of identical items, from bottle caps to car bumpers.
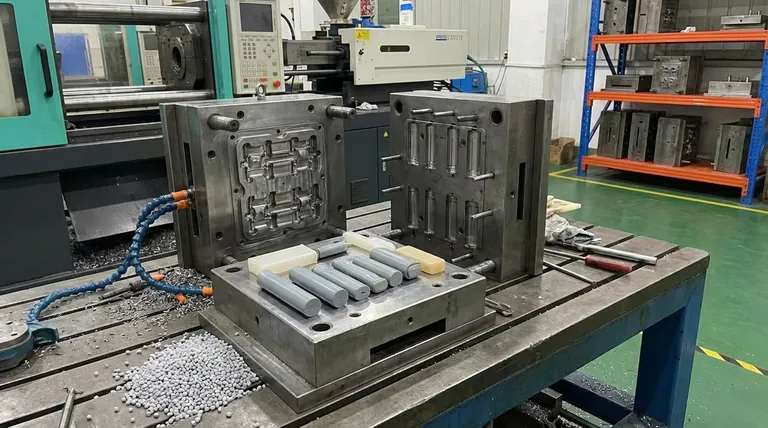

The Fundamental Principle: Creating a Negative Space
At its core, a mould works by providing an empty volume that a raw material can fill. Think of a simple ice cube tray: the tray is the mould, the water is the raw material, and the frozen ice cubes are the finished products. Manufacturing moulds operate on the same principle but with far greater complexity and precision.
The Cavity and the Core
Most industrial moulds are made of at least two halves. The cavity is the part of the mould that typically forms the external, "cosmetic" surface of the product. The core is the other half that forms the internal features of the product. When the two halves are clamped together, the space between the cavity and the core creates the exact shape of the part to be produced.
The Basic Process Cycle
While specific techniques vary, the general cycle is consistent. First, the two halves of the mould are closed and held together under immense pressure. Then, the molten raw material is injected or poured into the closed mould. The material fills the cavity, solidifies as it cools, and finally, the mould opens and the finished part is ejected.
Why Moulds are Essential for Modern Manufacturing
Moulds are not just tools; they are the enabling technology behind the scale and consistency of the modern world. Their use is driven by several key advantages.
Achieving Repeatability and Precision
A well-made mould ensures that the first part produced is virtually identical to the millionth. This level of repeatability is critical for products with interlocking parts, tight tolerances, and consistent performance requirements.
Enabling Mass Production at Scale
While making the initial mould is time-consuming and expensive, the cost per part becomes extremely low once it is in operation. This allows for the mass production of goods at a speed and cost that would be impossible with other methods like machining.
Accommodating Complex Geometries
Moulding processes can create incredibly complex shapes, intricate details, and varied textures in a single step. This gives designers immense freedom to create functional and aesthetically pleasing products that would be difficult or cost-prohibitive to manufacture otherwise.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Despite their advantages, choosing a mould-based manufacturing process involves significant considerations and is not suitable for every application.
High Upfront Cost and Lead Time
The primary disadvantage is the initial investment. Designing and fabricating a high-quality steel mould, often called tooling, can cost tens of thousands to hundreds of thousands of dollars and take weeks or months to complete.
Design Rigidity
Once a mould is machined from hardened steel, making changes to the product design is extremely difficult and expensive. This design rigidity means that the product design must be completely finalized and validated before the mould is created. A mistake found later can be a catastrophic cost.
Process and Material Limitations
The choice of moulding process (e.g., injection moulding for plastics, die casting for metals) imposes specific design rules. Features like wall thickness, draft angles (slight tapers to allow part ejection), and undercuts must be carefully designed to ensure the part can be manufactured successfully and ejected from the mould.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the role of a mould is about understanding the economics of production. Your decision to use a mould-based process should be based on your project's volume, budget, and design maturity.
- If your primary focus is mass production and low unit cost: Moulding is the definitive solution once the high initial tooling cost can be amortized over a large number of parts.
- If your primary focus is prototyping or low-volume runs: The high cost of tooling makes moulding impractical; consider additive manufacturing (3D printing) or CNC machining instead.
- If your primary focus is design flexibility and iteration: Avoid committing to a mould until your design is fully tested and locked, as changes are costly and time-consuming.
Grasping the concept of the mould is fundamental to understanding how the vast majority of physical products in our world are brought to life.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Takeaway |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Shapes raw materials into identical parts via a hollow cavity. |
| Key Advantage | Enables high-volume, low-cost production with excellent repeatability. |
| Main Consideration | High upfront cost and design rigidity; ideal for finalized, high-volume designs. |
| Best For | Mass production of complex parts like consumer goods and automotive components. |
Ready to Scale Your Production with Precision Moulding?
The right lab equipment is crucial for developing and testing materials for your moulding processes. At KINTEK, we specialize in high-quality lab equipment and consumables that support your R&D and quality control needs.
Whether you're testing polymer flow properties, analyzing material durability, or ensuring consistent quality for mass production, our solutions help you achieve reliable results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK can equip your lab for manufacturing success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Isostatic Molding Pressing Molds for Lab
- High-Purity Titanium Foil and Sheet for Industrial Applications
- Custom PTFE Wafer Holders for Lab and Semiconductor Processing
- Zirconia Ceramic Gasket Insulating Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Vacuum Cold Trap Direct Cold Trap Chiller
People Also Ask
- How do steel molds and hydraulic equipment collaborate for high-density molding? Optimize WC/Cu FGM Green Body Prep
- Why is a Cold Isostatic Press (CIP) Required for NaSICON? Achieve Maximum Green Density and Ionic Conductivity
- What is the function of high-strength pressure molds for nanostructured copper powders? Achieve High Purity Densification
- What are molds used for? Unlock Mass Production of Precision Parts
- What are the factors affecting molding? Master the 4 Keys to Perfect Plastic Parts











