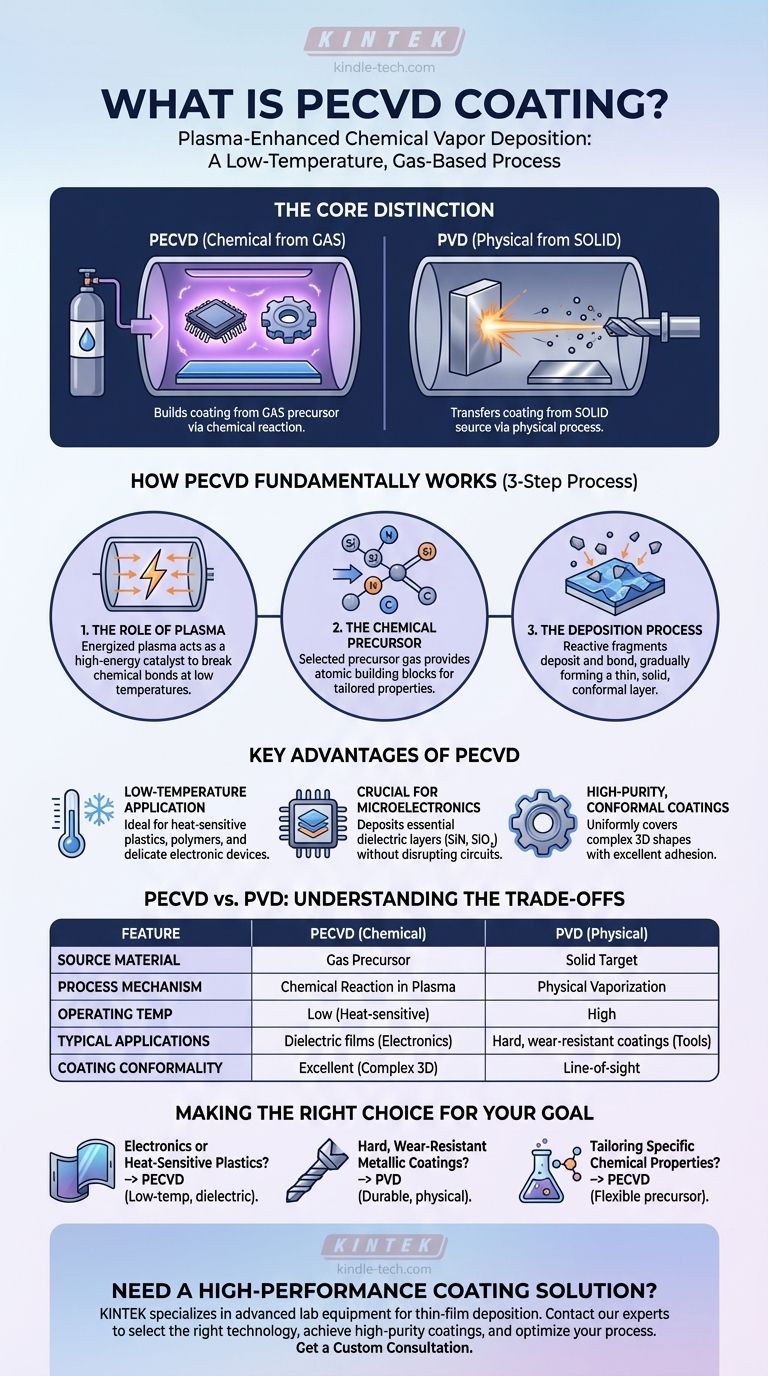
In essence, Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) is a low-temperature process that uses an energized gas, or plasma, to create a thin, solid film on a surface. Unlike methods that require high heat, PECVD initiates a chemical reaction with plasma to break down a precursor gas, allowing its fragments to deposit and build up as a high-performance coating. This makes it ideal for coating heat-sensitive materials like plastics and complex electronic components.
The critical distinction to understand is that PECVD builds a coating from a gas precursor using a plasma-driven chemical reaction. This contrasts with other methods like PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition), which transfers a coating from a solid source material using a physical process. This fundamental difference dictates the ideal applications for each technology.
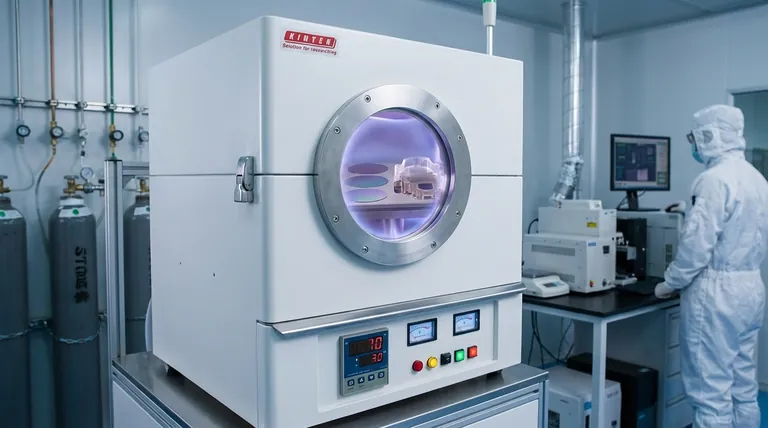

How PECVD Fundamentally Works
The PECVD process can be understood as a controlled, three-step sequence that transforms a gas into a solid layer. It is valued for its precision and its ability to operate without damaging the underlying part.
The Role of Plasma
At the heart of the process is plasma, often called the fourth state of matter. An electrical field is applied to a low-pressure gas inside a vacuum chamber, energizing it until it becomes a reactive plasma. This plasma acts as a high-energy catalyst, capable of breaking down chemical bonds in the precursor gas that would otherwise require extreme heat.
The Chemical Precursor
Unlike processes that start with a solid block of material, PECVD begins with a carefully selected precursor gas or vapor. This gas contains the atomic building blocks needed for the final coating, such as silicon, nitrogen, or carbon. The properties of the final coating are directly inherited from the chemistry of this precursor gas, allowing for highly tailored results.
The Deposition Process
Once the plasma breaks down the precursor gas into reactive fragments, these fragments deposit onto the target substrate inside the chamber. They then bond with the surface and each other, gradually building a thin, uniform, and solid film. The process is carefully controlled to achieve the desired thickness and material properties.
Key Advantages of the PECVD Method
PECVD is not a universal solution, but it offers significant advantages in specific, high-value applications, primarily due to its low-temperature and chemical nature.
Low-Temperature Application
The most significant advantage of PECVD is its low operating temperature. This allows for the coating of temperature-sensitive substrates, such as plastics, polymers, and delicate electronic devices, without causing thermal damage, warping, or diffusion that would destroy their function.
Crucial for Microelectronics
The semiconductor industry relies heavily on PECVD. It is used to deposit essential dielectric layers like silicon nitride (SiN) and silicon oxide (SiO₂). The low temperature prevents the disruption of carefully constructed doping profiles in integrated circuits, a problem that would render the devices useless.
High-Purity, Conformal Coatings
Because the coating is built from a gas, it can uniformly cover complex, three-dimensional shapes. The chemical reaction process results in high-purity films with excellent adhesion and precisely controlled properties.
Understanding the Trade-offs: PECVD vs. PVD
To truly understand PECVD, it is essential to compare it with its common alternative, Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD). The choice between them is dictated by the starting material and the desired outcome.
The Fundamental Difference: Gas vs. Solid
The core distinction is the source material. PECVD is a chemical process that starts with a gas. PVD is a physical process that starts with a solid metal "target" (like titanium or chromium). This target is vaporized by sputtering or an electric arc and then physically deposited onto the substrate.
Deposition Mechanism: Chemical vs. Physical
In PECVD, a true chemical reaction occurs in the plasma, creating new molecular compounds that form the coating. In PVD, the process is physical; atoms from the solid target are simply transported from the source to the substrate without a fundamental chemical change (though they can be reacted with gases like nitrogen).
Typical Applications and Outcomes
This difference in mechanism leads to different applications. PECVD excels at creating dielectric and amorphous films for electronics. PVD excels at depositing very hard, durable, and dense metallic or ceramic coatings, such as Titanium Nitride (TiN), for cutting tools, machine parts, and decorative finishes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct coating technology requires matching the process capabilities to your application's primary requirement.
- If your primary focus is on electronic components or heat-sensitive plastics: PECVD is the definitive choice due to its low-temperature chemical process that deposits essential dielectric layers without damaging the substrate.
- If your primary focus is creating hard, wear-resistant metallic coatings on tools or metal parts: PVD is the industry standard, as its physical process is designed to vaporize solid metals and create exceptionally durable surfaces.
- If your primary focus is tailoring specific chemical properties in the coating: PECVD offers greater flexibility, as the final coating's characteristics can be finely tuned by changing the precursor gas mixture.
Ultimately, choosing the right deposition method begins with understanding whether your goal requires a chemical transformation or a physical transfer of material.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PECVD (Chemical Process) | PVD (Physical Process) |
|---|---|---|
| Source Material | Gas Precursor | Solid Target |
| Process Mechanism | Chemical Reaction in Plasma | Physical Vaporization |
| Operating Temperature | Low (Ideal for heat-sensitive substrates) | High |
| Typical Applications | Dielectric films for electronics (SiN, SiO₂) | Hard, wear-resistant coatings (TiN) |
| Coating Conformality | Excellent for complex 3D shapes | Line-of-sight deposition |
Need a High-Performance Coating Solution?
Choosing between PECVD and PVD is critical for your project's success. KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for thin-film deposition, serving the precise needs of R&D and production laboratories.
We can help you:
- Select the right technology for your specific substrate and application goals.
- Achieve high-purity, uniform coatings on even the most delicate electronic components or complex geometries.
- Optimize your process with reliable equipment and expert support.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your coating capabilities and drive your innovations forward.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How does a one-zone tubular furnace influence SiC coatings? Master CVD Precision & Material Hardness
- What are the advantages of using multi-stage split tube furnaces for heating methane pyrolysis reactors? Boost Efficiency
- What function does a high-temperature tube furnace serve in alkali fusion hydroxide recovery? Precision Thermal Control
- How do high-temperature tube furnaces or rotary furnaces facilitate the regeneration of spent activated carbon?
- How does a temperature-controlled tube furnace influence the performance of biochar adsorbents? Optimize Pore Structure



















