In short, pyrolysis is a powerful thermal process that converts organic materials into valuable products like bio-oil, biochar, and syngas in the absence of oxygen. Its primary advantage is transforming low-value waste into high-value resources while offering significant environmental benefits. However, its primary disadvantages are the high initial investment costs and the technical complexities required to operate it cleanly and efficiently at a commercial scale.
Pyrolysis is not a simple solution, but a sophisticated tool. Its success hinges on a critical trade-off: achieving significant environmental and economic gains requires substantial capital investment and precise operational control to manage costs and prevent secondary pollution.
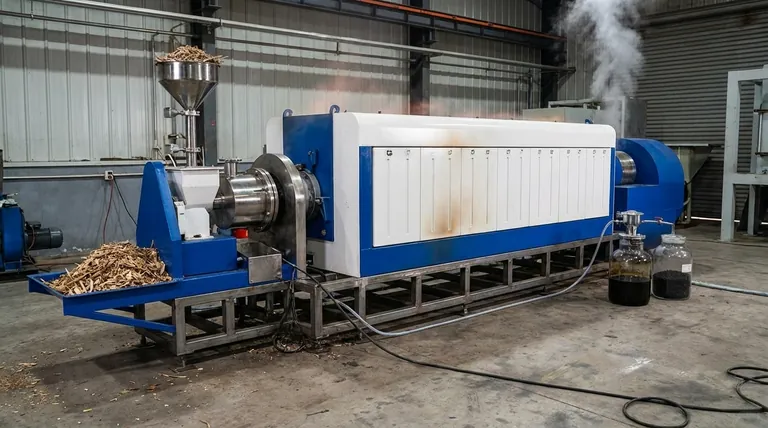

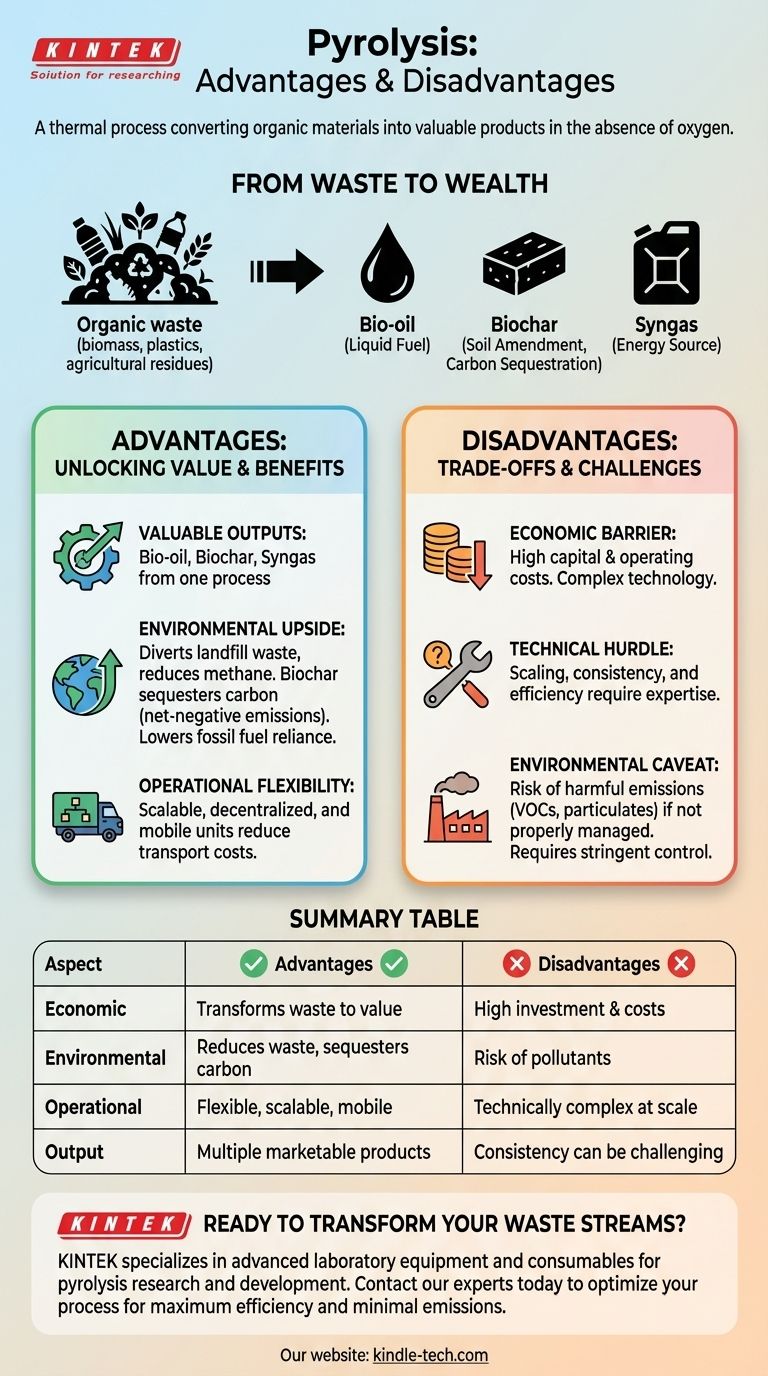
The Core Value Proposition: From Waste to Wealth
Pyrolysis excels at unlocking the stored value in organic materials that would otherwise be considered waste. It effectively deconstructs biomass, plastics, or agricultural residues into a set of useful, marketable products.
H3: Producing Three Valuable Outputs
The process separates organic matter into three distinct streams:
- Bio-oil: A liquid fuel, often called pyrolysis oil, that can be used to generate heat and power or be upgraded into transportation fuels.
- Biochar: A stable, carbon-rich solid that acts as an excellent soil amendment, improving water retention and sequestering carbon for long periods.
- Syngas: A mixture of combustible gases (primarily hydrogen and carbon monoxide) that can be burned on-site to power the pyrolysis process itself, making it more energy-efficient.
H3: Significant Environmental Upside
When implemented correctly, pyrolysis offers compelling environmental advantages. By diverting waste from landfills, it reduces methane emissions, a potent greenhouse gas.
The process can be a net-negative emissions technology. The production of stable biochar sequesters carbon that would have otherwise returned to the atmosphere, effectively removing it from the global carbon cycle.
Furthermore, by creating biofuels, it reduces our dependence on fossil fuels and the associated pollution from their extraction and combustion.
H3: Unmatched Operational Flexibility
Unlike massive, centralized power plants, pyrolysis facilities can be built at a smaller, decentralized scale.
This allows for mobile units that can be brought directly to the source of the waste (e.g., a farm or forest), reducing the high costs associated with transporting bulky biomass. This process converts low-density biomass into high-density, easily transportable bio-oil.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
The theoretical benefits of pyrolysis are clear, but practical implementation presents significant hurdles. Acknowledging these challenges is essential for any realistic evaluation.
H3: The Economic Barrier: High Capital and Operating Costs
Pyrolysis plants are technologically complex and require a significant upfront capital investment. The high temperatures and specialized equipment also lead to considerable ongoing operational and maintenance costs.
This economic reality often makes it difficult to justify for smaller operations without subsidies or a high-value market for the end products.
H3: The Technical Hurdle: Scaling and Consistency
While the basic process is straightforward, achieving high efficiency and consistent product quality at a commercial scale is technically challenging.
Optimizing reactor design, temperature control, and processing time for different types of feedstock requires deep expertise and ongoing research and development to maximize yields and profitability.
H3: The Environmental Caveat: Managing Emissions
This is the most critical trade-off. While pyrolysis can be very clean, it can also produce harmful pollutants if not managed properly.
The high-temperature process can release volatile organic compounds, particulates, and other emissions that impact air quality. Proper furnace design, stringent operational controls, and effective maintenance are non-negotiable to ensure the environmental benefits are actually realized.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Pyrolysis is not a one-size-fits-all solution. Your specific objective will determine if it is the right technology for your needs.
- If your primary focus is large-scale waste management and energy production: Be prepared for high capital costs, but recognize the potential for significant returns by turning a waste liability into a valuable energy asset.
- If your primary focus is carbon sequestration and soil health: The value of biochar is your key driver, making pyrolysis one of the most effective technologies for this specific environmental goal.
- If your primary focus is managing agricultural or forestry residue in remote areas: The flexibility of smaller, mobile pyrolysis units offers a distinct advantage by reducing transportation costs and creating a valuable liquid fuel on-site.
Ultimately, the viability of pyrolysis depends on a clear-eyed assessment of its costs against its powerful potential to create value and solve environmental challenges.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Economic | Transforms low-value waste into high-value products (bio-oil, biochar, syngas) | High initial capital investment and operational costs |
| Environmental | Reduces landfill waste, sequesters carbon (biochar), lowers fossil fuel dependence | Risk of air pollutants (VOCs, particulates) if not properly controlled |
| Operational | Flexible, scalable technology; allows for mobile units to reduce transport costs | Technically complex to operate efficiently at commercial scale |
| Output | Produces multiple marketable outputs from a single process | Product quality and consistency can be challenging to maintain |
Ready to transform your waste streams into valuable resources?
KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research and development. Whether you are scaling up from the lab or optimizing your process for maximum efficiency and minimal emissions, our solutions provide the precision and reliability you need.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our pyrolysis tools can help you achieve your environmental and economic goals.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Mesh belt controlled atmosphere furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas



















