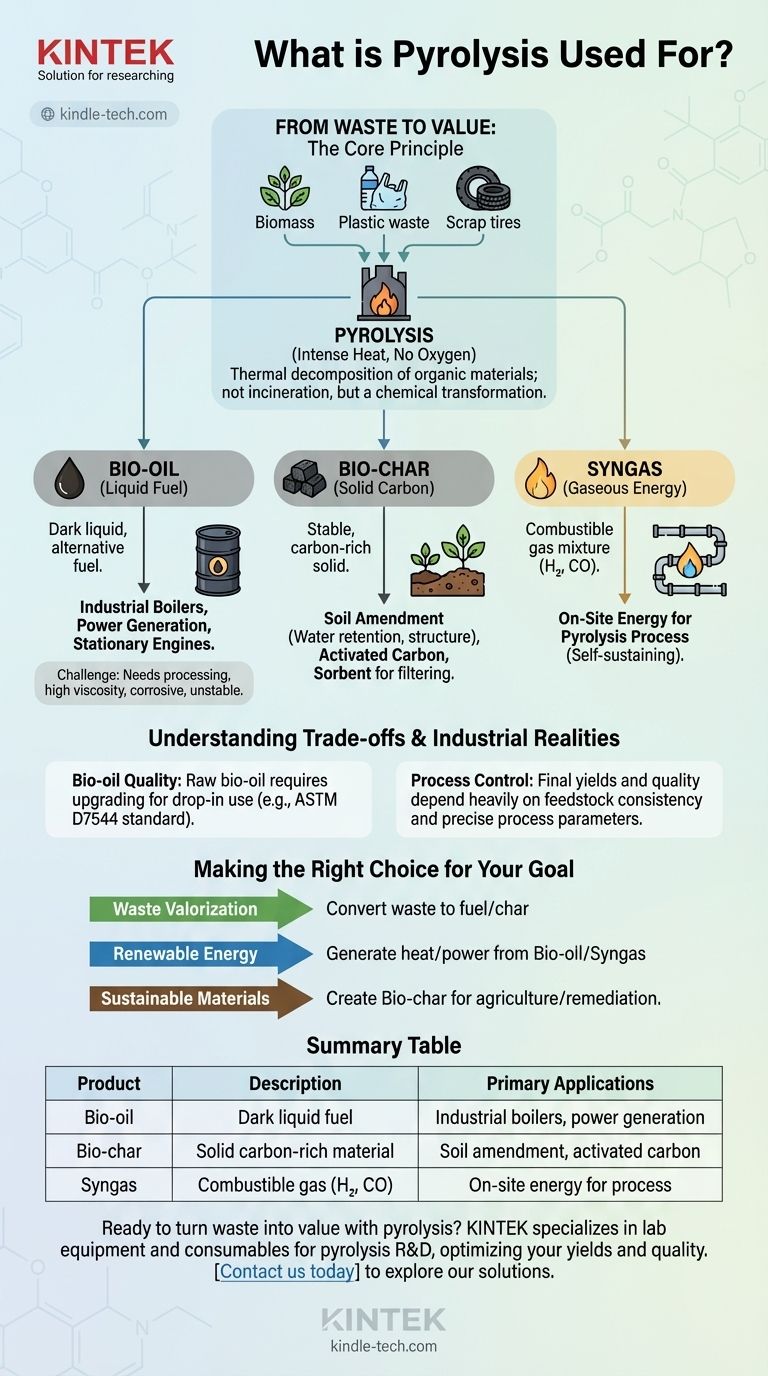
At its core, pyrolysis is used to thermally decompose organic materials like biomass, plastics, or tires in the absence of oxygen. This process transforms what is often considered waste into three valuable outputs: a liquid fuel (bio-oil), a solid carbon-rich material (bio-char), and a combustible gas (syngas).
Pyrolysis is not incineration; it is a chemical transformation. Instead of burning waste to get rid of it, pyrolysis breaks it down into valuable chemical components, creating a pathway for a circular economy by turning low-value materials into fuels, soil enhancers, and industrial feedstocks.

From Waste to Value: The Core Principle
Pyrolysis applies intense heat to organic matter within an oxygen-free environment. Because there is no oxygen, the material does not combust.
Instead, the long-chain polymer molecules that make up materials like wood, crops, or rubber are "cracked" into smaller, more useful molecules. It’s the fundamental process behind charring wood.
The Feedstocks: What Goes In
The process is versatile and can handle a wide range of organic inputs. Common feedstocks include agricultural waste, forestry residues, scrap tires, and certain types of plastic. The specific input material directly influences the properties of the final products.
The Three Key Products and Their Applications
The true value of pyrolysis lies in its distinct outputs. The process reliably separates the initial feedstock into liquid, solid, and gaseous components, each with its own market and use cases.
Bio-oil: The Liquid Fuel Component
Bio-oil, also known as pyrolysis oil, is a dark, dense liquid that can be used as an alternative to conventional fuel oil.
Its primary applications are in stationary engines, industrial boilers, and power generation units to produce heat and electricity. While it can serve as a substitute for fossil fuels, it often requires processing or specialized equipment to use effectively.
Bio-char: The Solid Carbon Component
Bio-char is a stable, carbon-rich solid, similar to charcoal. It has a diverse range of applications far beyond simply being burned for heat.
It is highly valued as a soil amendment to improve soil structure and water retention. Its porous nature also makes it an excellent sorbent for filtering pollutants or a feedstock for producing high-grade activated carbon.
Syngas: The Gaseous Energy Component
Syngas, or synthesis gas, is a mixture of combustible gases (primarily hydrogen and carbon monoxide).
Its most common use is to be captured and combusted on-site to provide the energy needed to run the pyrolysis furnace itself. This creates a more self-sustaining and energy-efficient system.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Industrial Realities
While pyrolysis holds immense promise, it is not a perfect solution. Understanding its practical limitations is critical for evaluating its feasibility for any given project.
The Challenge of Bio-oil Quality
Raw bio-oil has several properties that limit its widespread industrial use as a "drop-in" fuel. It can be highly viscous, corrosive to standard pipes and engines, and chemically unstable over time.
For these reasons, bio-oil often needs to be upgraded in a refinery-like process to produce more conventional hydrocarbon fuels. Standards like ASTM D7544 have been developed to regulate its use in specific stationary applications.
Feedstock and Process Control
The final product yields and quality are highly dependent on the type of feedstock and the precise control of the pyrolysis process (e.g., temperature and heating rate).
Inconsistent waste streams can lead to inconsistent outputs, which presents a significant challenge for producing reliable, market-grade commodities at an industrial scale.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To determine if pyrolysis is the right technology, you must first clarify your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is waste valorization: Pyrolysis is an excellent method for converting low-value organic waste streams into marketable products like fuel oil and bio-char.
- If your primary focus is renewable energy production: The bio-oil and syngas fractions provide a direct path to generating heat and power, helping to displace fossil fuels.
- If your primary focus is creating sustainable materials: Bio-char offers a valuable, carbon-sequestering product for agriculture and environmental remediation applications.
By understanding both its valuable outputs and its practical limitations, you can effectively assess pyrolysis as a key technology for a more sustainable future.
Summary Table:
| Product | Description | Primary Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Bio-oil | Dark liquid fuel from pyrolysis | Industrial boilers, power generation |
| Bio-char | Solid carbon-rich material | Soil amendment, activated carbon production |
| Syngas | Combustible gas (H₂, CO) | On-site energy for pyrolysis process |
Ready to turn waste into value with pyrolysis? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research and development. Whether you're processing biomass, plastics, or other organic materials, our solutions help you optimize product yields and quality. Contact us today to explore how our expertise can advance your sustainable energy or materials project!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
People Also Ask
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What are the products of pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock Bio-Char, Bio-Oil, and Syngas
- Is pyrolysis viable? A Guide to Economic, Technological, and Environmental Success
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs



















