In the pharmaceutical industry, a roller mill is a critical piece of equipment used primarily for dry granulation. Its function is to take fine, often poorly flowing powders and compact them into dense sheets or "ribbons," which are then milled into uniform, free-flowing granules. This process, also known as roller compaction, is essential for preparing materials for tablet manufacturing and capsule filling.
The core value of a roller mill is its ability to densify powders and improve their handling characteristics without using liquid binders or high heat. This makes it an indispensable tool for processing drug formulations that are sensitive to moisture or temperature.

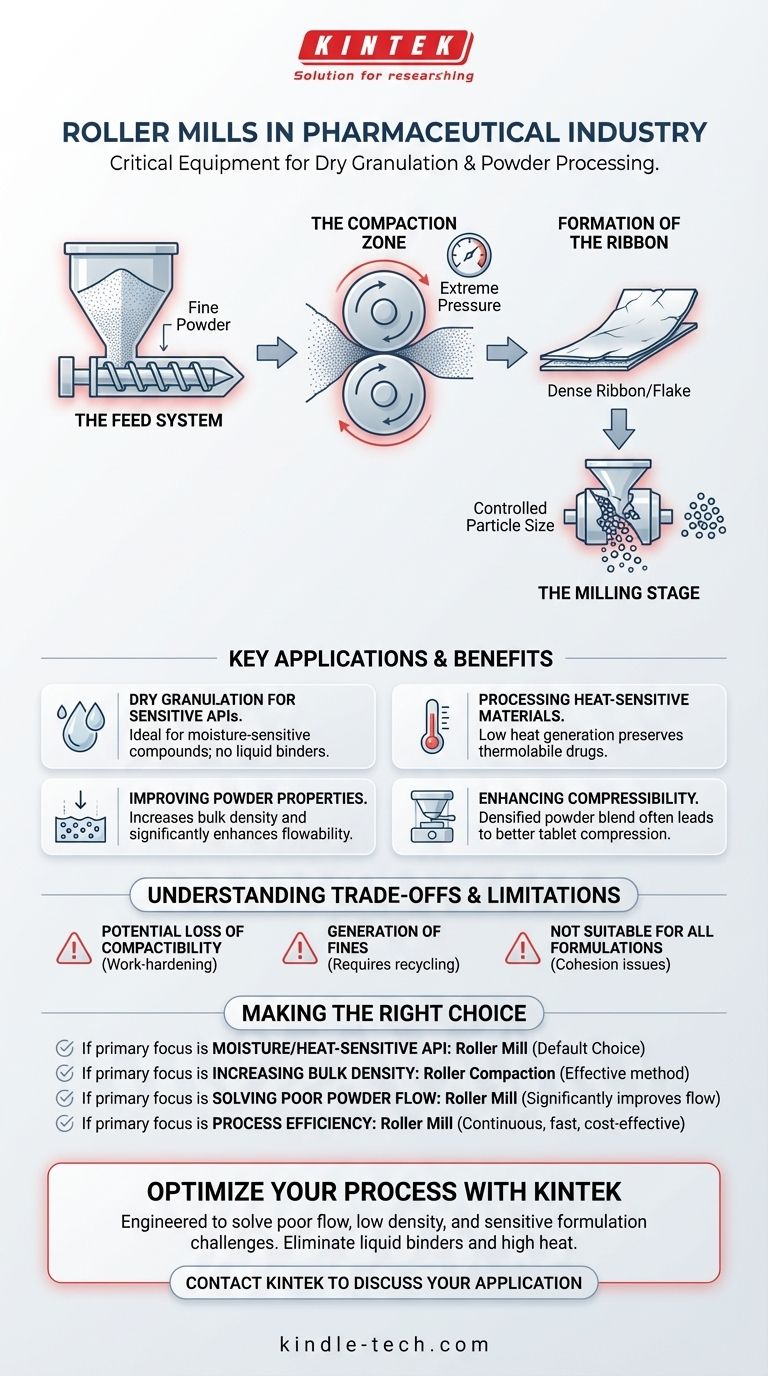
The Core Principle: How a Roller Mill Works
A roller mill, more accurately called a roller compactor in this context, operates on a straightforward mechanical principle. The process can be broken down into a few key stages.
The Feed System
A screw-feeding mechanism precisely meters fine powder from a hopper into the system. This ensures a consistent and uniform flow of material, which is critical for the quality of the final product.
The Compaction Zone
The powder is then drawn between two counter-rotating rollers. These rollers apply extreme mechanical pressure, forcing the individual powder particles into close, intimate contact.
Formation of the Ribbon
This intense pressure compacts the powder into a solid, brittle sheet known as a ribbon or flake. The air between the particles is forced out, significantly increasing the material's bulk density.
The Milling Stage
Finally, this dense ribbon is fed into an integrated low-shear milling unit. This mill gently breaks the ribbon apart and sizes it into granules of a specific, controlled particle size distribution.
Key Applications in Pharmaceutical Manufacturing
The dry granulation process enabled by roller mills solves several common challenges in pharmaceutical production, making it a preferred method for many types of formulations.
Dry Granulation for Sensitive APIs
This is the primary application. It provides a method for granulation when the active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) or excipients are sensitive to moisture and would be damaged or degraded by traditional wet granulation processes.
Processing Heat-Sensitive Materials
The compaction process generates very little heat compared to other high-energy milling techniques. This makes it ideal for thermolabile compounds that cannot withstand the heat generated during wet granulation's drying step.
Improving Powder Properties
Many raw pharmaceutical powders are fluffy, have low density, and do not flow well. Roller compaction dramatically increases the bulk density and creates uniform, spherical granules that exhibit excellent flowability, which is crucial for consistent die filling on a tablet press.
Enhancing Compressibility
By densifying the powder blend, roller compaction creates a material that is often more suitable for compression into a durable, high-quality tablet.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, roller compaction is not a universal solution. It's essential to understand its potential drawbacks to determine if it's the right choice for a specific formulation.
Potential Loss of Compactibility
A primary concern is that the intense pressure of compaction can "work-harden" the particles. This can sometimes make the resulting granules less compressible during the final tableting stage, leading to weaker tablets. This phenomenon is often called "loss of reworkability."
Generation of Fines
The milling of the compacted ribbon is not a perfect process. It inevitably creates a certain percentage of fine powder that must be sieved out and potentially recycled back into the feeder, adding complexity to the process.
Not Suitable for All Formulations
Some materials lack the necessary cohesiveness to form a proper ribbon under pressure. Others might be too elastic, deforming under pressure but failing to bind together once the pressure is released.
Making the Right Choice for Your Formulation
Choosing the correct granulation method is a critical decision in drug product development. The unique advantages of the roller mill make it the optimal choice for specific goals.
- If your primary focus is handling a moisture- or heat-sensitive API: A roller mill is the default choice, as it completely avoids the use of liquids and high-temperature drying steps.
- If your primary focus is increasing the bulk density of a fluffy powder: Roller compaction is one of the most effective methods for densifying materials, improving both handling and downstream processing efficiency.
- If your primary focus is solving poor powder flow: The uniform, dense granules produced by a roller mill will significantly improve flowability, ensuring consistent tablet weights and content uniformity.
- If your primary focus is process efficiency and cost-reduction: A roller mill offers a continuous manufacturing process that is often faster and requires less energy and factory space than multi-step wet granulation.
Ultimately, the roller mill is a powerful tool for simplifying processes and enabling the manufacture of challenging drug formulations.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Information |
|---|---|
| Primary Function | Dry granulation via compaction and milling |
| Main Application | Processing moisture- and heat-sensitive APIs |
| Key Benefits | No liquid binders, improved powder flow and density |
| Key Limitation | Potential loss of compactibility (work-hardening) |
Optimize Your Pharmaceutical Manufacturing Process with KINTEK
Are you developing a formulation with a moisture- or heat-sensitive API? Struggling with poor powder flow or low bulk density? KINTEK's roller mills (roller compactors) are engineered to solve these exact challenges. Our equipment provides a reliable, continuous dry granulation process that eliminates the need for liquid binders and high-temperature drying, preserving the integrity of your sensitive compounds.
We specialize in providing robust lab equipment and consumables tailored to the precise needs of pharmaceutical R&D and production. Let our experts help you enhance your process efficiency and product quality.
Contact our team today to discuss how a KINTEK roller mill can benefit your specific application.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
- High-Energy Omnidirectional Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Milling Machine for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What is a punch tablet press? Precision Tableting for R&D and Small Batches
- What is the pressed pellet technique? A Guide to Creating Uniform Solid Samples from Powder
- What are advantages of single punch tablet press machine? Maximize R&D Efficiency with Minimal Material
- What are the advantages of press working operation? Unlock High-Speed, Low-Cost Mass Production
- What is the difference between single punch and rotary tablet press? Choose the Right Machine for Your Lab or Production



















