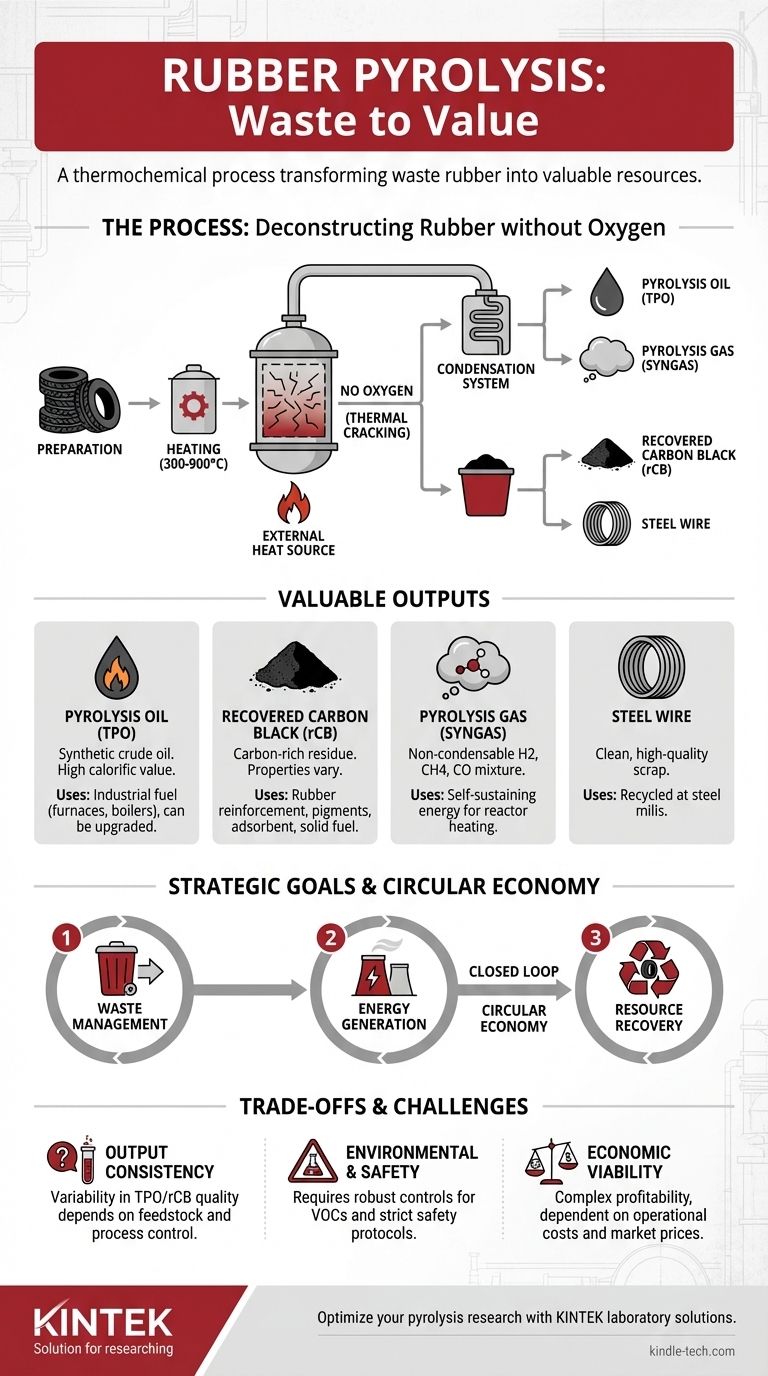
In essence, rubber pyrolysis is a thermochemical process that breaks down waste rubber, most commonly end-of-life tires, into valuable raw materials. It achieves this by heating the shredded rubber to high temperatures (typically 300-900°C) in a sealed, oxygen-free environment. The absence of oxygen is critical, as it prevents the rubber from burning and instead causes its long polymer chains to break apart into smaller, more useful molecules.
Rubber pyrolysis is not waste incineration; it is a resource recovery technology. It transforms a problematic waste stream into valuable commodities—namely synthetic oil, carbon black, syngas, and steel—effectively closing the loop in a circular economy.

The Pyrolysis Process: Deconstructing Rubber at the Molecular Level
To understand the value of pyrolysis, you must first understand the mechanism. It is a controlled deconstruction process, not a simple disposal method.
The Core Principle: Thermal Decomposition without Oxygen
The heart of pyrolysis is heating material without oxygen. When rubber is heated with oxygen, it combusts, releasing energy and producing ash and flue gases like CO2.
By removing oxygen, we change the chemical pathway. Instead of burning, the intense heat provides the energy needed to sever the strong chemical bonds holding the rubber polymers together, a process known as thermal cracking.
The Key Process Stages
A typical rubber pyrolysis plant operates in a continuous or batch sequence:
- Preparation: Whole tires are shredded into smaller, more uniform pieces (typically 1-2 inches). This increases the surface area for more efficient heat transfer.
- Feeding: The shredded rubber is fed into the pyrolysis reactor through an air-tight system to prevent oxygen from entering.
- Heating: The reactor is heated externally. As the internal temperature rises, the rubber decomposes, turning into a mixture of hot vapors and solid residue.
- Separation: The hot vapors are channeled out of the reactor and into a condensation system. The condensable portion cools into liquid oil, while the non-condensable gases are separated. The solid residue (carbon black and steel) remains in the reactor.
The Valuable Outputs of Rubber Pyrolysis
The economic viability of pyrolysis hinges on the quality and marketability of its four primary products.
Pyrolysis Oil (Tire Pyrolysis Oil - TPO)
This liquid fraction is a type of synthetic crude oil. It has a high calorific value and can be used directly as an industrial fuel in furnaces, boilers, or generators.
With further refining (such as distillation and desulfurization), TPO can be upgraded into more valuable products like diesel fuel, but this adds complexity and cost to the operation.
Recovered Carbon Black (rCB)
This is the solid, carbon-rich powder left behind after the process. Its properties can vary significantly based on the original tire composition and the process parameters.
High-quality rCB can be used as a reinforcing agent in new rubber products, a pigment in plastics and inks, or as an adsorbent. Lower-grade rCB is often used as a solid fuel. The market value of rCB is a critical factor in a plant's profitability.
Pyrolysis Gas (Syngas)
This non-condensable gas mixture is rich in hydrogen, methane, and carbon monoxide. It has a good calorific value.
Most modern pyrolysis plants use this gas to fuel the burners that heat the reactor. This creates a self-sustaining energy loop, significantly reducing the plant's external energy consumption and operational costs.
Steel Wire
The steel belts and beads within tires do not decompose. They are recovered from the reactor as clean, high-quality steel scrap. This scrap has immediate value and is easily sold to steel mills for recycling.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
While promising, rubber pyrolysis is not a silver bullet. A clear-eyed assessment of its challenges is essential for any serious consideration.
Output Quality and Consistency
The single greatest challenge is the variability of the end products. The quality of the pyrolysis oil (e.g., sulfur content) and especially the recovered carbon black depends heavily on the feedstock (type and age of tires) and precise control over process temperature and time.
Inconsistent rCB quality can make it difficult to sell into high-value markets, relegating it to use as a low-cost fuel.
Environmental and Safety Concerns
While far superior to burning tires in the open, pyrolysis plants must be engineered with robust environmental controls. Improperly sealed systems can release volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
Additionally, the process handles flammable liquids and gases at high temperatures, demanding strict adherence to industrial safety protocols to prevent accidents.
Economic Viability
The profitability of a pyrolysis plant is a complex equation. It depends on the cost of acquiring and shredding tires, the operational cost (energy, labor), maintenance, and the fluctuating market prices for oil, carbon black, and steel scrap. A thorough feasibility study is non-negotiable.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Adopting pyrolysis technology should be driven by a clear strategic objective.
- If your primary focus is waste management: Pyrolysis is an advanced and environmentally responsible solution to divert millions of tires from landfills and illegal dumps.
- If your primary focus is energy generation: The process creates a synthetic fuel from waste, offering a localized energy source that can reduce dependence on virgin fossil fuels.
- If your primary focus is resource recovery: Pyrolysis embodies the principles of a circular economy by reclaiming steel, carbon, and hydrocarbon molecules to be used in new manufacturing cycles.
Ultimately, rubber pyrolysis represents a powerful shift from viewing waste tires as an environmental burden to recognizing them as a valuable industrial feedstock.
Summary Table:
| Product | Description | Common Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Pyrolysis Oil (TPO) | Synthetic crude oil from condensed vapors | Industrial fuel for furnaces, boilers, generators |
| Recovered Carbon Black (rCB) | Carbon-rich powder residue | Rubber reinforcement, plastics, inks, adsorbent |
| Pyrolysis Gas (Syngas) | Non-condensable gas (H2, CH4, CO) | Fuel for self-sustaining reactor heating |
| Steel Wire | Recovered steel belts/beads from tires | Scrap for steel mill recycling |
Ready to turn waste tires into profit? KINTEK specializes in advanced lab equipment and consumables for pyrolysis research and development. Whether you're optimizing process parameters, analyzing output quality, or scaling up your operation, our precision instruments ensure accurate temperature control, efficient material handling, and reliable data. Enhance your pyrolysis efficiency and product consistency—contact our experts today to find the right solutions for your laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Customizable High Pressure Reactors for Advanced Scientific and Industrial Applications
People Also Ask
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process



















