In short, sieve analysis is a foundational method used to determine the particle size distribution of a granular material. The test works by passing a sample through a stack of screens, or sieves, with progressively smaller mesh openings and then weighing the amount of material retained on each sieve. This process physically sorts the sample into different size fractions.
Sieve analysis does not measure individual particles. Instead, it provides a practical, weight-based overview of a material's composition, making it an indispensable tool for quality control in industries dealing with powders and granules.
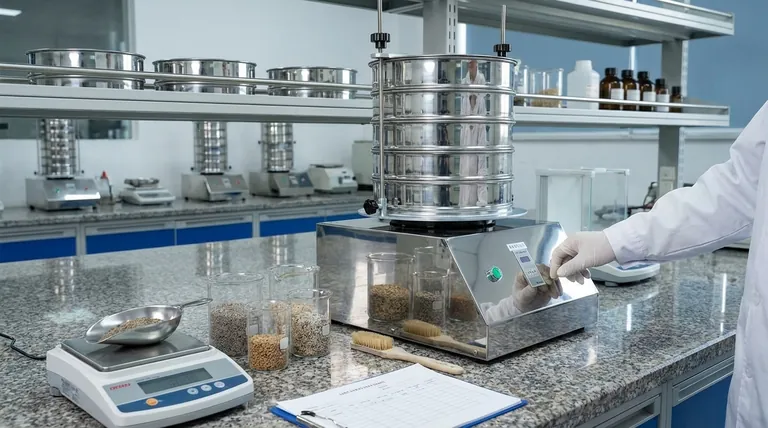

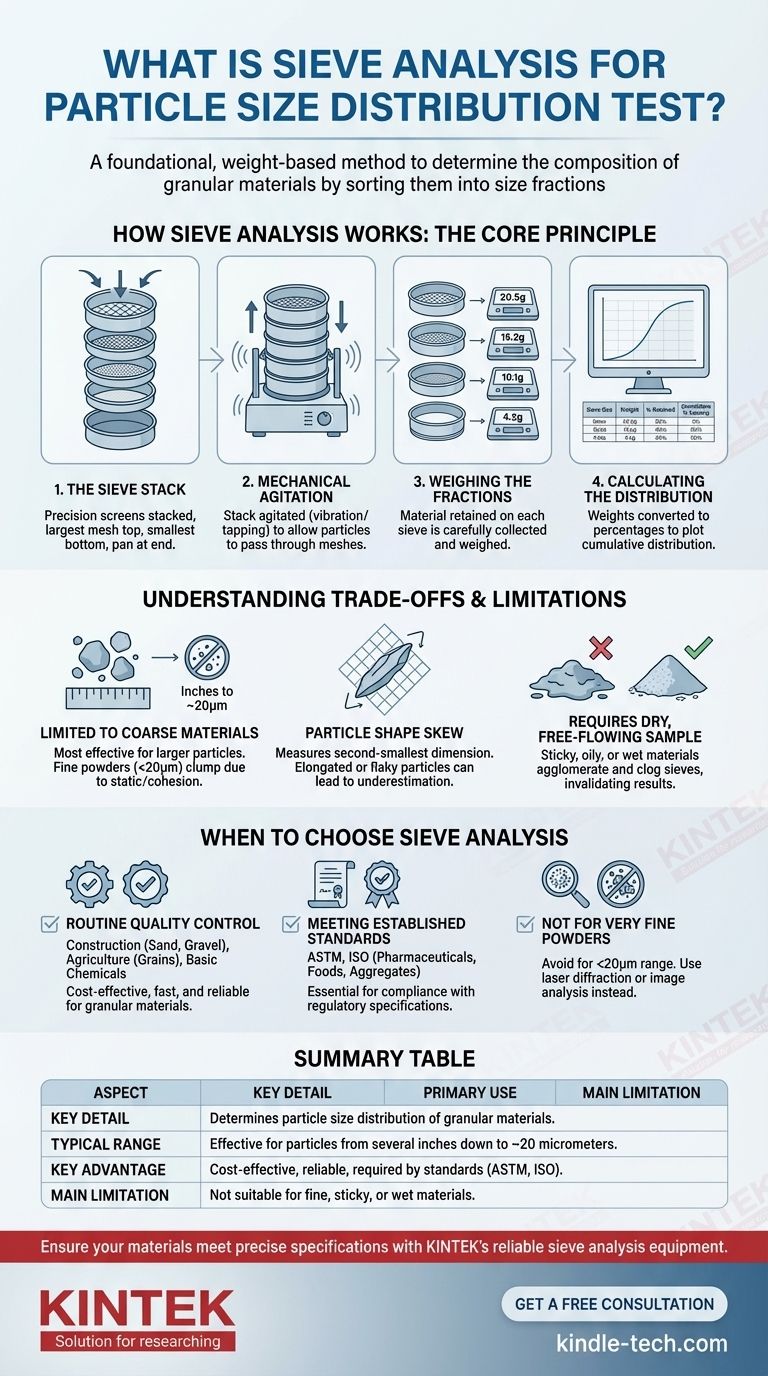
How Sieve Analysis Works: The Core Principle
The elegance of sieve analysis lies in its direct, mechanical approach. The entire process is designed to be a reliable and repeatable way to characterize the physical makeup of a bulk sample.
The Sieve Stack
The core of the test is a set of nested sieves. These are precision-made screens with wire mesh of a specific, certified aperture size.
They are stacked vertically with the largest openings at the top and the smallest at the bottom, ending with a solid pan to collect the finest particles.
Mechanical Agitation
Once the sample is placed on the top sieve, the entire stack is secured in a mechanical shaker.
This shaker agitates the stack, typically with a tapping or vibratory motion, for a set period. This movement ensures particles have the opportunity to find an aperture they can pass through until they are retained by a sieve too small for them to clear.
Weighing the Fractions
After shaking is complete, the stack is disassembled. The material retained on each individual sieve is carefully collected and weighed.
This critical step turns the physical separation into quantitative data. The weight on each sieve represents the total mass of all particles within that specific size range.
Calculating the Distribution
The weights from each sieve are converted into percentages of the total sample weight.
This data is then typically presented in a table or plotted on a graph to show the cumulative particle size distribution, providing a clear picture of the material's composition.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Limitations
While powerful, sieve analysis is not universally applicable. Understanding its limitations is key to using it correctly and interpreting the results.
Limited to Coarser Materials
Sieve analysis is most effective for particles ranging from several inches down to about 20 micrometers.
Below this size, forces like static electricity and cohesion cause fine particles to clump together, preventing them from passing through the fine mesh openings effectively. For these materials, methods like laser diffraction are required.
Particle Shape Can Skew Results
A sieve measures a particle's second-smallest dimension. Elongated or flaky particles may pass through an aperture end-on or diagonally, leading to an underestimation of their true size.
This means the results reflect a particle's ability to pass a square opening, which may not correspond to its actual volume or primary dimension.
Requires a Dry, Free-Flowing Sample
The material being tested must be dry and able to flow freely. Sticky, oily, or wet materials will agglomerate and clog the sieve openings, invalidating the test results.
When to Choose Sieve Analysis
Sieve analysis remains a cornerstone of material characterization because it is the ideal tool for specific, critical applications.
- If your primary focus is routine quality control for granular materials: Sieve analysis is unmatched for its cost-effectiveness, speed, and reliability in industries like construction (sand, gravel), agriculture (grains, seeds), and basic chemicals.
- If your primary focus is meeting established industry standards: Many regulatory specifications (ASTM, ISO) for products like pharmaceuticals, foods, and aggregates explicitly require sieve analysis, making it essential for compliance.
- If your primary focus is characterizing very fine powders or nanoparticles: Sieve analysis is the wrong tool; you must use more advanced methods like light scattering or image analysis designed for the sub-micron range.
Ultimately, sieve analysis is a trusted and indispensable method for understanding the physical character of a wide range of materials.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Primary Use | Determines particle size distribution of granular materials. |
| Typical Range | Effective for particles from several inches down to ~20 micrometers. |
| Key Advantage | Cost-effective, reliable, and required by many industry standards (ASTM, ISO). |
| Main Limitation | Not suitable for fine, sticky, or wet materials that clog sieves. |
Ensure your materials meet precise specifications with KINTEK's reliable sieve analysis equipment.
As a leading supplier of laboratory equipment, KINTEK provides the durable sieves and mechanical shakers you need for accurate, repeatable particle size distribution testing. Our products are trusted for quality control in construction, chemicals, and pharmaceuticals.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect sieve analysis solution for your lab's needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Laboratory Single Horizontal Jar Mill
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulse Vacuum Lifting Sterilizer
People Also Ask
- How are vibratory sieve shakers and standard sieves utilized to analyze the effects of biomass torrefaction? Optimize Grindability
- What are the specifications for test sieves? A Guide to ASTM & ISO Standards for Accurate Particle Analysis
- What are the factors affecting sieving performance and efficiency? Optimize Your Particle Separation Process
- How is a vibratory sieve shaker used in the particle size analysis of mechanically alloyed powders? Expert Guide
- What is the role of standard sieves in gold scrap leaching kinetic studies? Ensure Precision in Particle Classification



















