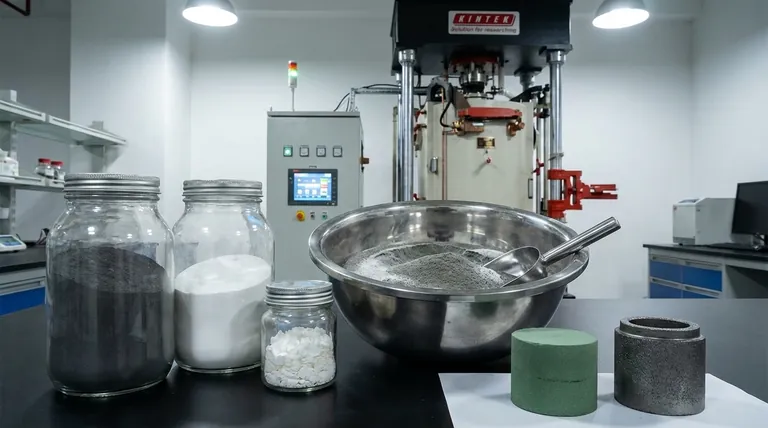
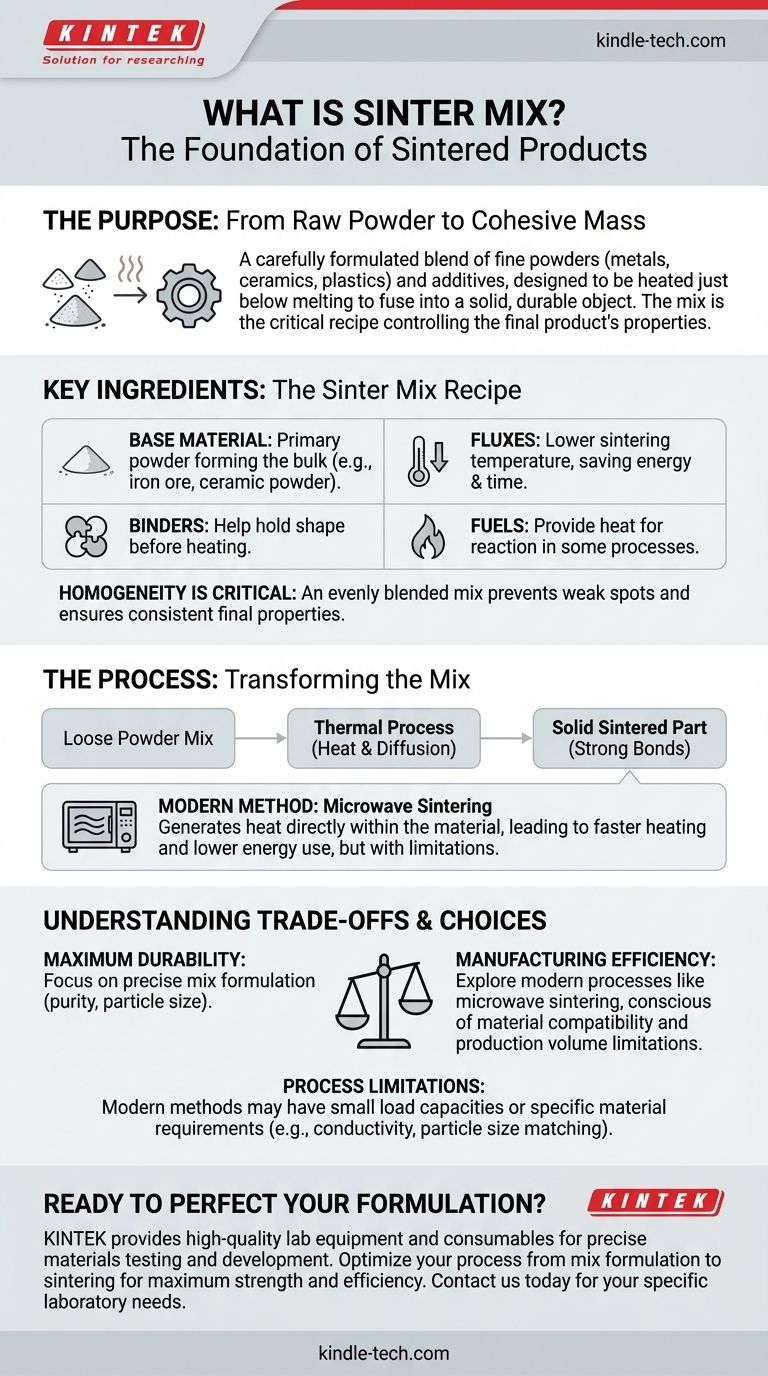
In materials science, a sinter mix is a carefully formulated blend of raw materials designed to be processed through sintering. This mixture typically consists of fine powders—such as metal ores, ceramics, or plastics—along with additives like fluxes, binders, and sometimes a solid fuel. The purpose of this mix is to be heated to a high temperature, just below the melting point, causing the particles to fuse together into a solid, durable mass.
The final properties of a sintered product, such as its strength and durability, are not just a result of the heating process itself. They are fundamentally determined by the precise composition, particle size, and homogeneity of the initial sinter mix.

The Purpose of a Sinter Mix
A sinter mix is the foundational "recipe" for creating a sintered part. The careful preparation of this mix is the first and most critical step in controlling the outcome of the entire manufacturing process.
From Raw Powder to a Cohesive Mass
The fundamental goal of sintering is to turn loose powders into a strong, solid object without melting the material. The sinter mix provides the necessary ingredients in the correct proportions to achieve this transformation efficiently.
Key Ingredients
While the exact composition varies widely by application, most sinter mixes include:
- Base Material: The primary powder that will form the bulk of the final product (e.g., iron ore fines, alumina ceramic powder).
- Fluxes: Additives that lower the temperature required for sintering to begin, saving energy and time.
- Binders: Organic or inorganic agents that help the powder hold a specific shape (e.g., in a pressed compact) before it is heated.
- Fuels: In some large-scale processes like iron ore sintering, a fuel like coke breeze is mixed in to provide the heat for the reaction.
Why Homogeneity is Critical
A thoroughly blended, homogenous sinter mix is essential. If the ingredients are not distributed evenly, the final product will have inconsistent properties, such as weak spots, uneven density, or poor dimensional accuracy.
The Sintering Process: Transforming the Mix
Once prepared, the sinter mix is subjected to a thermal process that bonds the particles together. The method of heating has a significant impact on the final product.
The Role of Heat
Heat provides the energy for a process called diffusion, where atoms move across the boundaries of the particles, creating strong bonds or "necks" between them. This is what turns the loose powder mix into a solid piece.
An Example: Microwave Sintering
One modern method for heating a sinter mix is microwave sintering. Unlike conventional ovens that heat from the outside-in, microwaves generate heat directly within the material itself. This can lead to faster heating, lower energy use, and improved final properties.
Final Product Characteristics
After the process is complete, the transformed sinter mix becomes a final product. As seen in sintered ceramics, this material can be exceptionally durable and resistant to scratches, extreme temperatures, water, stains, and UV rays.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No single sintering process is perfect for every type of sinter mix. The chosen method must be compatible with the materials being used.
Process Limitations
While efficient, methods like microwave sintering are often best suited for small production loads. The equipment typically sinters only one component at a time, which can be a bottleneck for mass production.
Material Compatibility Issues
The composition of the sinter mix dictates which process can be used. For example, microwaves only penetrate a short distance in highly conductive materials. The powder particle size in the mix must be carefully matched to the microwave penetration depth for the process to be effective.
Risk of Failure
Some materials within a sinter mix may fail to "couple" with microwave energy, meaning they won't heat up. Others can exhibit "thermal runaway," where they heat up too quickly, leading to defects or damage. This highlights the importance of matching the mix to the process.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The composition of the sinter mix and the choice of sintering process are deeply interconnected. Your final objective determines how you should approach both.
- If your primary focus is achieving maximum durability and specific material properties: Concentrate on the precise formulation of the sinter mix, including base material purity, particle size, and the selection of appropriate additives.
- If your primary focus is manufacturing efficiency and energy savings: Explore modern processes like microwave sintering, but remain conscious of their limitations regarding the material composition of your mix and the required production volume.
Ultimately, mastering the final product begins with a fundamental understanding of its starting point: the sinter mix.
Summary Table:
| Component | Role in the Sinter Mix |
|---|---|
| Base Material | Primary powder forming the bulk of the final product (e.g., iron ore, ceramic powder). |
| Fluxes | Lower the sintering temperature, saving energy and time. |
| Binders | Help the powder hold its shape before heating. |
| Fuels | Provide heat for the sintering reaction in some processes. |
Ready to perfect your sinter mix formulation and achieve superior material properties?
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables necessary for precise materials testing and development. Whether you are working with metal powders, ceramics, or other materials, our solutions support your entire R&D process—from mix formulation to sintering.
Let our expertise help you optimize your sintering process for maximum strength, durability, and efficiency. Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific laboratory needs and discover the right equipment for your projects.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Pressure Sintering Furnace for High Temperature Applications
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Pulsating Vacuum Desktop Steam Sterilizer
- Desktop Fast Laboratory Autoclave Sterilizer 20L 24L for Lab Use
- Laboratory Vibratory Sieve Shaker Machine Slap Vibrating Sieve
- Large Vertical Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of a high-temperature furnace in thermal stability testing? Ensure Inhibitor Performance
- What is the step by step process of case hardening? A Guide to Creating Durable, Wear-Resistant Parts
- What role does a high-temperature vacuum furnace play in the pyrolysis stage of C/C-SiC composite manufacturing?
- What temperature do metal furnaces operate at? Master Metal Melting and Heat Treatment
- Should I braze or weld aluminum? Choosing the Right Method for Your Project's Success
- What temperature is copper brazing in Celsius? Get the Right Heat for Strong Joints
- What is the difference between resistance and induction furnace? Choose the Right Heating Technology
- What is the necessity of de-binding for LLZO ceramic membranes? Ensure Integrity with KINTEK Thermal Solutions






