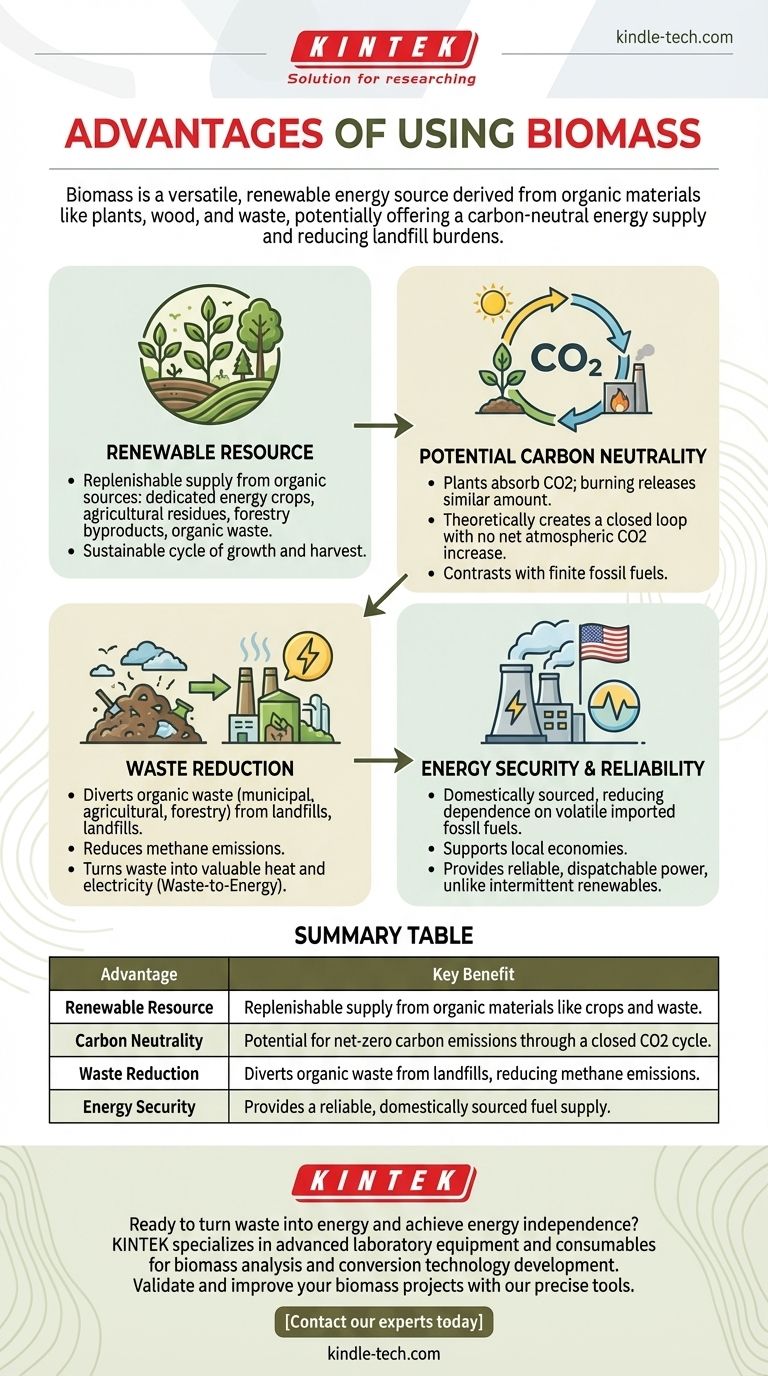
In short, the primary advantage of using biomass is its status as a versatile, renewable energy source that can be carbon-neutral. Derived from organic materials like plants, wood, and waste, it helps reduce landfill burdens and creates a more reliable, domestically-sourced energy supply compared to finite fossil fuels.
The true strength of biomass lies not just in being a renewable fuel, but in its unique ability to integrate energy production with waste management and agricultural systems. However, its environmental and economic viability depends entirely on sustainable sourcing and efficient conversion technology.

The Core Advantages of Biomass Energy
Biomass energy is generated from the combustion or conversion of organic matter. Understanding its benefits requires looking at its role within a larger ecological and economic system.
It's a Renewable Resource
Unlike coal, oil, and natural gas, which are finite, biomass is a renewable resource. The sources—such as dedicated energy crops, agricultural residues, forestry byproducts, and organic waste—can be replenished in a relatively short time frame. This cycle of growth and harvest provides a sustainable fuel stream when managed correctly.
Potential for Carbon Neutrality
The concept of carbon neutrality is a key advantage. As plants grow, they absorb carbon dioxide (CO2) from the atmosphere through photosynthesis. When this biomass is used for energy, it releases a similar amount of CO2 back into the atmosphere.
In theory, this creates a closed loop where emissions are balanced by absorption, resulting in no net increase in atmospheric CO2. This stands in stark contrast to fossil fuels, which release carbon that has been locked away for millions of years.
Reduces Landfill Waste
A significant portion of municipal solid waste is organic. Instead of decomposing in landfills and releasing methane—a greenhouse gas far more potent than CO2—this waste can be diverted to biomass facilities.
This "waste-to-energy" approach solves two problems at once: it reduces the environmental impact of landfills and generates valuable heat or electricity. The same principle applies to agricultural and forestry residues that might otherwise be left to rot or be burned in the open.
Creates a Domestic, Reliable Energy Supply
Biomass is typically sourced locally or regionally. This strengthens a nation's energy security by reducing its dependence on imported fossil fuels, which are often subject to price volatility and geopolitical instability.
Furthermore, it supports local economies by creating jobs in agriculture, forestry, transportation, and power plant operation. Because biomass can be stored and used on demand, it provides a reliable and dispatchable power source, unlike intermittent renewables like solar and wind.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Challenges
No energy source is without its drawbacks. An objective assessment of biomass requires acknowledging its significant challenges, which must be managed to realize its benefits.
The Sustainability Question: Sourcing is Everything
The carbon neutrality of biomass hinges entirely on sustainable sourcing. If forests are clear-cut and not replanted, or if land use changes result in a net loss of carbon-storing ecosystems, the climate benefit disappears.
"Renewable" does not automatically mean "sustainable." Poor harvesting practices can lead to deforestation, soil degradation, and loss of biodiversity. True sustainability requires careful management to ensure the rate of harvest does not exceed the rate of regrowth.
Land and Water Use Competition
Growing crops specifically for energy (like switchgrass or corn for ethanol) can compete with food production for arable land and water resources. This can potentially lead to increased food prices and raise complex ethical questions about resource allocation.
The most sustainable biomass models prioritize the use of residues and waste products over dedicated energy crops to avoid this conflict.
Air Quality Concerns
Burning any solid fuel, including biomass, can release air pollutants if not properly controlled. These include particulate matter (PM2.5), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and other compounds that can harm human health and the environment.
Modern biomass facilities use advanced combustion technologies, scrubbers, and filters to capture the vast majority of these pollutants, but older or smaller-scale systems may pose a risk to local air quality.
Logistical and Cost Hurdles
Biomass generally has a lower energy density than fossil fuels. This means it is bulkier and more expensive to collect, transport, and store per unit of energy produced. The initial capital investment for building a biomass power plant can also be higher than for a comparable natural gas plant.
How to Apply This to Your Goal
The viability of biomass depends entirely on your strategic goals and how you plan to mitigate its inherent challenges.
- If your primary focus is waste management and the circular economy: Biomass is an exceptional choice for converting agricultural residues, forestry byproducts, and municipal solid waste into valuable energy.
- If your primary focus is energy independence and local economic support: Locally sourced biomass provides a stable, domestic fuel supply that is less vulnerable to global market fluctuations.
- If your primary focus is large-scale carbon reduction: Biomass can be a powerful tool, but only if you can guarantee genuinely sustainable sourcing practices and use efficient, low-emission conversion technology.
Ultimately, leveraging biomass effectively is a matter of strategic implementation, turning potential environmental liabilities into a reliable energy asset.
Summary Table:
| Advantage | Key Benefit |
|---|---|
| Renewable Resource | Replenishable supply from organic materials like crops and waste. |
| Carbon Neutrality | Potential for net-zero carbon emissions through a closed CO2 cycle. |
| Waste Reduction | Diverts organic waste from landfills, reducing methane emissions. |
| Energy Security | Provides a reliable, domestically sourced fuel supply. |
Ready to turn waste into energy and achieve energy independence?
KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory equipment and consumables for biomass analysis and conversion technology development. Whether you're researching sustainable sourcing, optimizing conversion processes, or analyzing emissions, our precise tools help you validate and improve your biomass projects.
Contact our experts today to find the right equipment for your lab and ensure your biomass solutions are both efficient and sustainable.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Small Vacuum Heat Treat and Tungsten Wire Sintering Furnace
- Laboratory Test Sieves and Sieving Machines
People Also Ask
- What is the role of corundum tubes in oxygen permeation testing? Ensure Integrity for Bi-doped Membranes
- What is the ceramic tube high temperature? From 1100°C to 1800°C, Choose the Right Material
- What factors influence the general design of a tube furnace? Match Your Process with the Perfect System
- How do you clean a tube furnace tube? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe and Effective Cleaning
- Why is a horizontal alumina tube furnace ideal for mixed gas corrosion at 650 °C? Ensure Pure Experimental Integrity


















