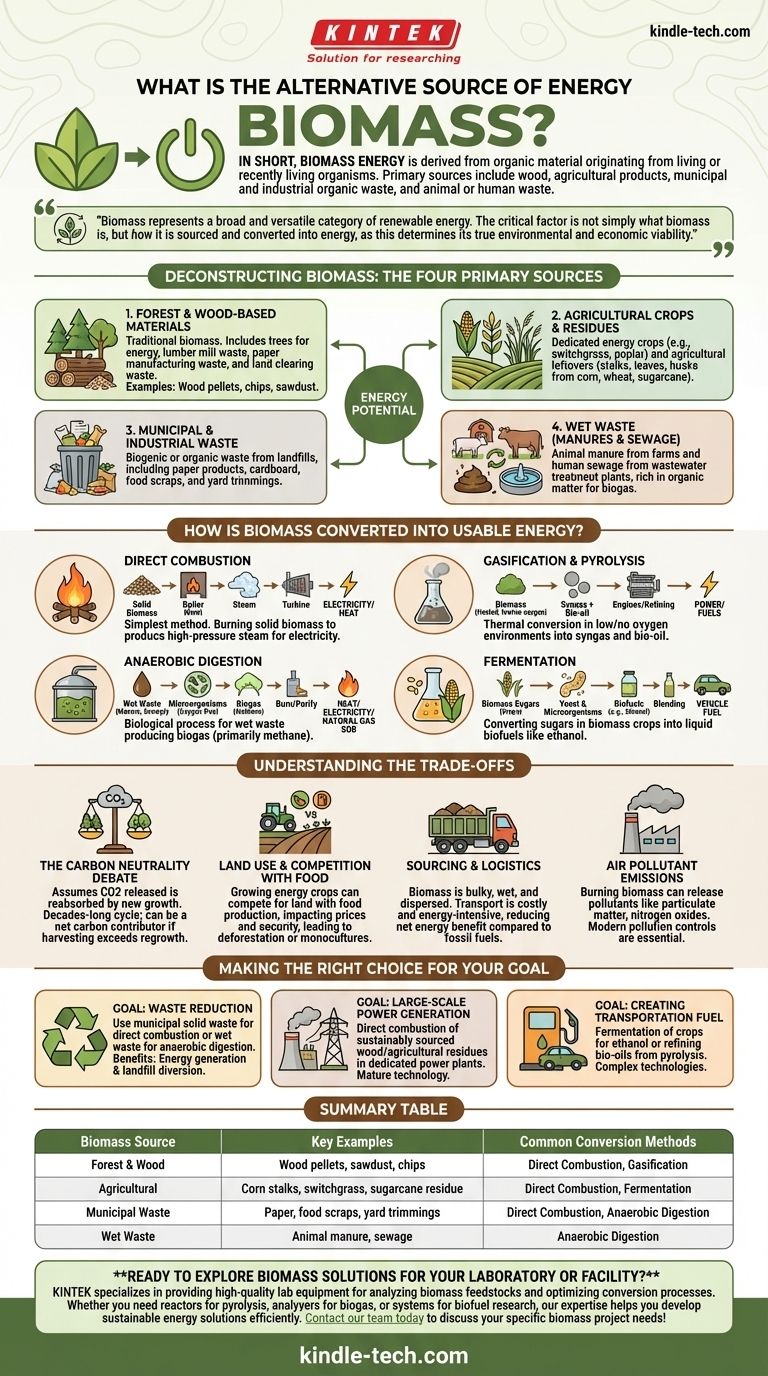
In short, biomass energy is derived from any organic material originating from living or recently living organisms. The primary sources include wood and agricultural products, organic waste from municipalities and industries, and animal or human waste.
Biomass represents a broad and versatile category of renewable energy. The critical factor is not simply what biomass is, but how it is sourced and converted into energy, as this determines its true environmental and economic viability.
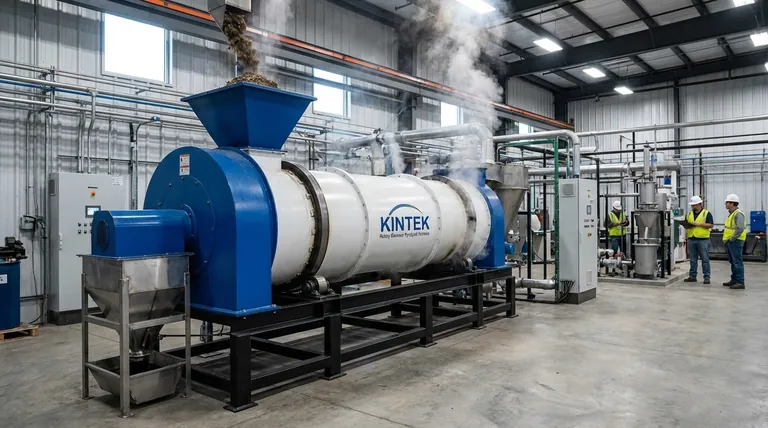

Deconstructing Biomass: The Four Primary Sources
Biomass is not a single fuel but a collection of different organic materials, each with unique properties and potential uses. Understanding these categories is the first step to evaluating its potential.
1. Forest and Wood-Based Materials
This is the most traditional form of biomass energy. It includes everything from whole trees harvested specifically for energy to the waste products from lumber mills, paper manufacturing, and land clearing. Examples include wood pellets, chips, and sawdust.
2. Agricultural Crops and Residues
This category is twofold. It includes dedicated energy crops like switchgrass or poplar trees grown solely for fuel. It also includes agricultural residues—the leftover stalks, leaves, and husks from crops like corn, wheat, and sugarcane after the primary food component has been harvested.
3. Municipal and Industrial Waste
A significant portion of the waste we send to landfills is biogenic, or organic. This includes paper products, cardboard, food scraps, and yard trimmings. Capturing this "waste stream" for energy production turns a disposal problem into an energy resource.
4. Wet Waste (Manures and Sewage)
Animal manure from farms and human sewage from wastewater treatment plants are rich in organic matter. Rather than being treated solely as waste, these materials can be processed to produce biogas, a renewable form of natural gas.
How Is Biomass Converted into Usable Energy?
The source material dictates the best conversion method. There are four primary pathways for turning raw biomass into electricity, heat, or fuel.
Direct Combustion
This is the simplest and most common method. Solid biomass, such as wood pellets or agricultural waste, is burned in a boiler to produce high-pressure steam. This steam then drives a turbine connected to a generator to create electricity.
Gasification and Pyrolysis
These are thermal conversion processes that heat biomass in low-oxygen or no-oxygen environments. Instead of burning, the material breaks down into a mixture of gases (syngas) and liquids (bio-oil), which can then be used to power engines or be refined into other fuels.
Anaerobic Digestion
This biological process is ideal for wet waste like manure and sewage. In an oxygen-free environment, microorganisms break down the organic matter, producing biogas (primarily methane). This biogas can be burned for heat and electricity or purified to be used as a natural gas substitute.
Fermentation
This process uses yeast and other microorganisms to convert the sugars in certain biomass crops (like corn, sugarcane, or cellulosic material) into liquid biofuels. The most well-known product of fermentation is ethanol, which is blended with gasoline for use in vehicles.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While renewable, biomass is not without its complexities and challenges. An objective assessment requires acknowledging the potential downsides.
The Carbon Neutrality Debate
The idea that biomass is carbon neutral rests on the assumption that the carbon dioxide released during combustion is reabsorbed by new plant growth. However, this cycle can take decades, especially for forests. If the rate of harvesting exceeds the rate of regrowth, biomass can be a net contributor to atmospheric carbon.
Land Use and Competition with Food
Growing dedicated energy crops on a large scale raises significant concerns. It can compete with land needed for food production, potentially impacting food prices and security. It can also lead to deforestation or the conversion of natural habitats into monoculture farms.
Sourcing and Logistics
Biomass is often bulky, wet, and geographically dispersed. Unlike fossil fuels, which are energy-dense, transporting biomass from its source to a power plant can be costly and energy-intensive, reducing its overall net energy benefit.
Air Pollutant Emissions
Burning biomass, especially in older or less advanced facilities, can release air pollutants like particulate matter, nitrogen oxides, and other volatile organic compounds. Modern pollution controls are essential to mitigate these health and environmental impacts.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The best application of biomass depends entirely on your specific objective.
- If your primary focus is waste reduction: Using municipal solid waste for direct combustion or wet waste for anaerobic digestion offers a dual benefit of generating energy and diverting materials from landfills.
- If your primary focus is large-scale power generation: Direct combustion of sustainably sourced wood products or agricultural residues in dedicated power plants is the most established and technologically mature path.
- If your primary focus is creating transportation fuel: Fermentation of crops to produce ethanol or the refinement of bio-oils from pyrolysis are the relevant, though complex, technologies.
Understanding these sources, conversion pathways, and their inherent trade-offs is the first step toward leveraging biomass responsibly in a diversified energy portfolio.
Summary Table:
| Biomass Source | Key Examples | Common Conversion Methods |
|---|---|---|
| Forest & Wood | Wood pellets, sawdust, chips | Direct Combustion, Gasification |
| Agricultural | Corn stalks, switchgrass, sugarcane residue | Direct Combustion, Fermentation |
| Municipal Waste | Paper, food scraps, yard trimmings | Direct Combustion, Anaerobic Digestion |
| Wet Waste | Animal manure, sewage | Anaerobic Digestion |
Ready to explore biomass solutions for your laboratory or facility? KINTEK specializes in providing high-quality lab equipment for analyzing biomass feedstocks and optimizing conversion processes. Whether you need reactors for pyrolysis, analyzers for biogas, or systems for biofuel research, our expertise helps you develop sustainable energy solutions efficiently. Contact our team today to discuss your specific biomass project needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- High Purity Pure Graphite Crucible for Electron Beam Evaporation
People Also Ask
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time
- What are the reactions involved in pyrolysis of biomass? Unlock the Chemistry for Tailored Bio-Products
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs





