At its core, the ball mill method is a mechanical technique used to grind and mix materials into an extremely fine powder. The process involves placing the substance into a rotating cylinder, known as a mill or jar, along with grinding media such as steel or ceramic balls. As the cylinder rotates, the balls continuously tumble and cascade, crushing and grinding the material through repeated impacts.
The ball mill method is not just about simple crushing; it's a controlled process of size reduction that leverages the dual forces of impact and attrition. This allows it to reliably produce fine, homogenous powders from a wide variety of coarse or abrasive materials.
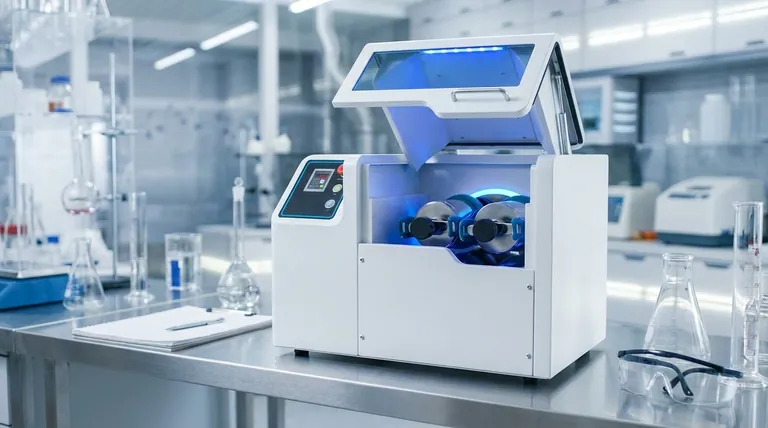

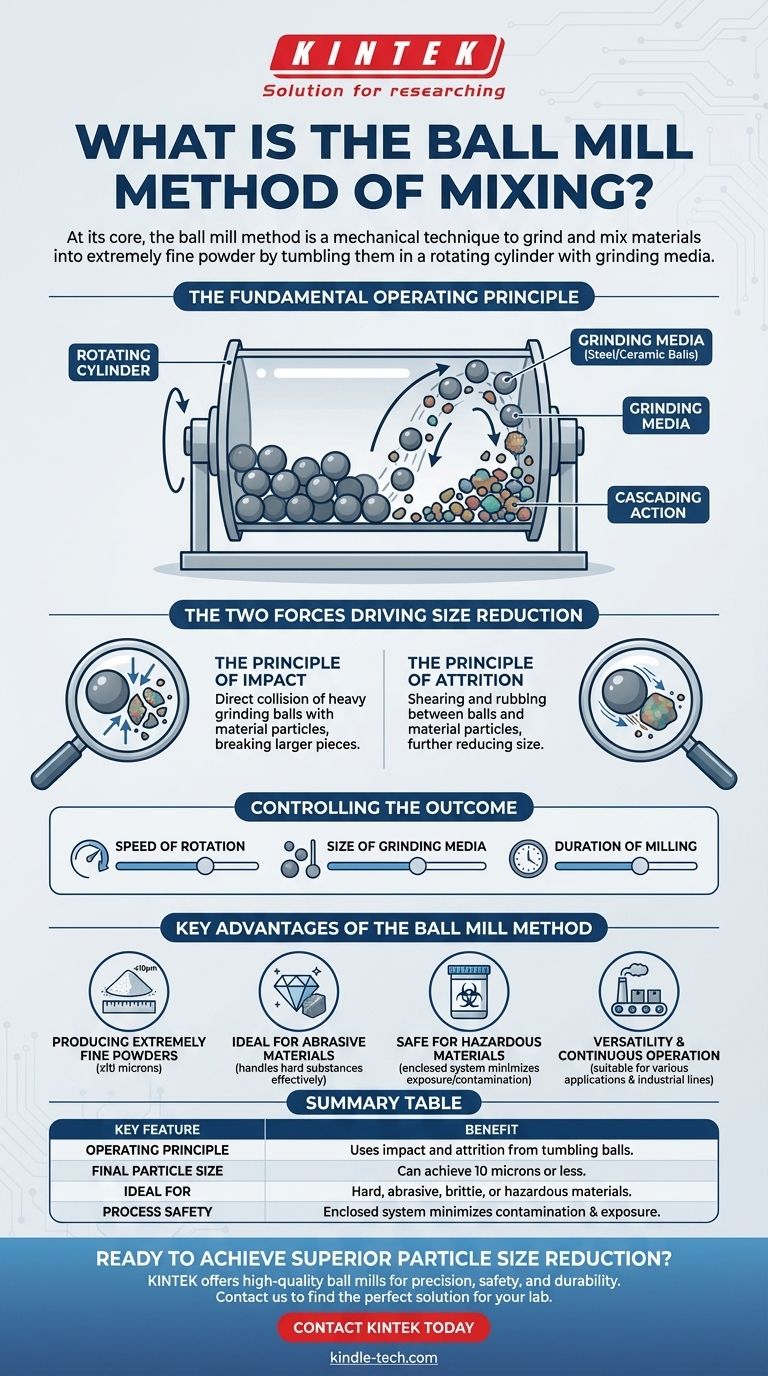
The Fundamental Operating Principle
The Rotating Cylinder
A ball mill consists of a hollow cylinder mounted on a frame that allows it to rotate along its longitudinal axis. This cylinder serves as the container for both the material being processed and the grinding media.
The Role of Grinding Media
Inside the cylinder are the grinding media—typically hard balls made of steel, ceramic, or another durable material. The size of these balls is chosen based on the starting material and the desired final particle size.
Cascading and Crushing
As the cylinder rotates, the balls are lifted up the side of the inner wall and then fall back down, striking the material below. This continuous tumbling, or cascading, is the primary mechanical action that drives the grinding process.
The Two Forces Driving Size Reduction
The Principle of Impact
Impact is the primary force at play. It refers to the direct, forceful collision of the heavy grinding balls with the material particles. This action is responsible for breaking down larger, coarser pieces into smaller fragments.
The Principle of Attrition
Attrition is the secondary force. It is the shearing and rubbing that occurs as the balls and material particles slide against each other. This friction further reduces the size of the particles, grinding them into a fine powder.
Controlling the Outcome
The final particle size of the powder is not left to chance. It can be precisely controlled by adjusting key variables, such as the speed of rotation, the size of the grinding media, and the duration of the milling process.
Key Advantages of the Ball Mill Method
Producing Extremely Fine Powders
One of the most significant advantages is the method's ability to produce very fine powders. It can consistently achieve a final particle size of 10 microns or less, which is critical for many industrial and laboratory applications.
Ideal for Abrasive Materials
The robust mechanical action of a ball mill makes it exceptionally effective for grinding hard and abrasive materials that would quickly wear down other types of equipment.
Safe for Hazardous Materials
Because the entire process occurs within a sealed cylinder, ball mills are highly suitable for safely processing toxic or hazardous materials. This enclosed design minimizes operator exposure and prevents contamination of the surrounding environment.
Versatility and Continuous Operation
This method is incredibly versatile, with applications ranging from ceramics and paints to ores and chemicals. Many industrial-scale ball mills are designed for continuous operation, making them a reliable component of a larger production line.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Deciding if a ball mill is the right tool depends entirely on your material and desired outcome.
- If your primary focus is achieving an extremely fine powder: The ball mill's ability to reduce materials to 10 microns or less through controlled impact and attrition is its key strength.
- If your primary focus is processing hard, brittle, or abrasive materials: A ball mill is an excellent choice, as its powerful mechanical action is specifically designed to handle such substances effectively.
- If your primary focus is safety when handling toxic or sensitive materials: The enclosed nature of the ball mill system provides a secure environment that minimizes both contamination and operator exposure.
Ultimately, the ball mill method offers a powerful and predictable solution for precise particle size reduction across a vast range of materials.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Benefit |
|---|---|
| Operating Principle | Uses impact and attrition from tumbling balls for size reduction. |
| Final Particle Size | Can achieve 10 microns or less. |
| Ideal For | Hard, abrasive, brittle, or hazardous materials. |
| Process Safety | Enclosed system minimizes contamination and operator exposure. |
Ready to achieve superior particle size reduction in your lab?
The ball mill method is a cornerstone of material processing for a reason. If you need to reliably produce fine, homogenous powders from hard, abrasive, or sensitive materials, KINTEK has the right solution for you.
We specialize in high-quality lab equipment, including robust ball mills designed for precision, safety, and durability. Let our experts help you select the perfect mill to meet your specific grinding goals.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your application and find the ideal ball mill for your laboratory needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Horizontal Tank Type
- Mini Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Milling
- Liquid Nitrogen Cryogenic Grinder Mill Cryomill Airflow Ultrafine Pulverizer
- Small Injection Molding Machine for Lab Use
- Single Punch Electric Tablet Press Machine Laboratory Powder Tablet Punching TDP Tablet Press
People Also Ask
- What is the role of a planetary ball mill in the preparation of NiCr-Al2O3-SrCO3 composite powders? Enhanced Homogeneity
- What is the role of a planetary ball mill in the synthesis of Li2S–P2S5 sulfide solid-state electrolytes?
- How does a planetary high-energy ball mill contribute to the top-down preparation of layered materials? Optimize Yield
- How does a planetary ball mill enhance the electrocatalytic activity of La0.6Sr0.4CoO3-δ? Boost Your Catalyst Performance
- What role does a planetary ball mill play in SHS? Optimize Powder Activation for Superior Alloy Synthesis



















