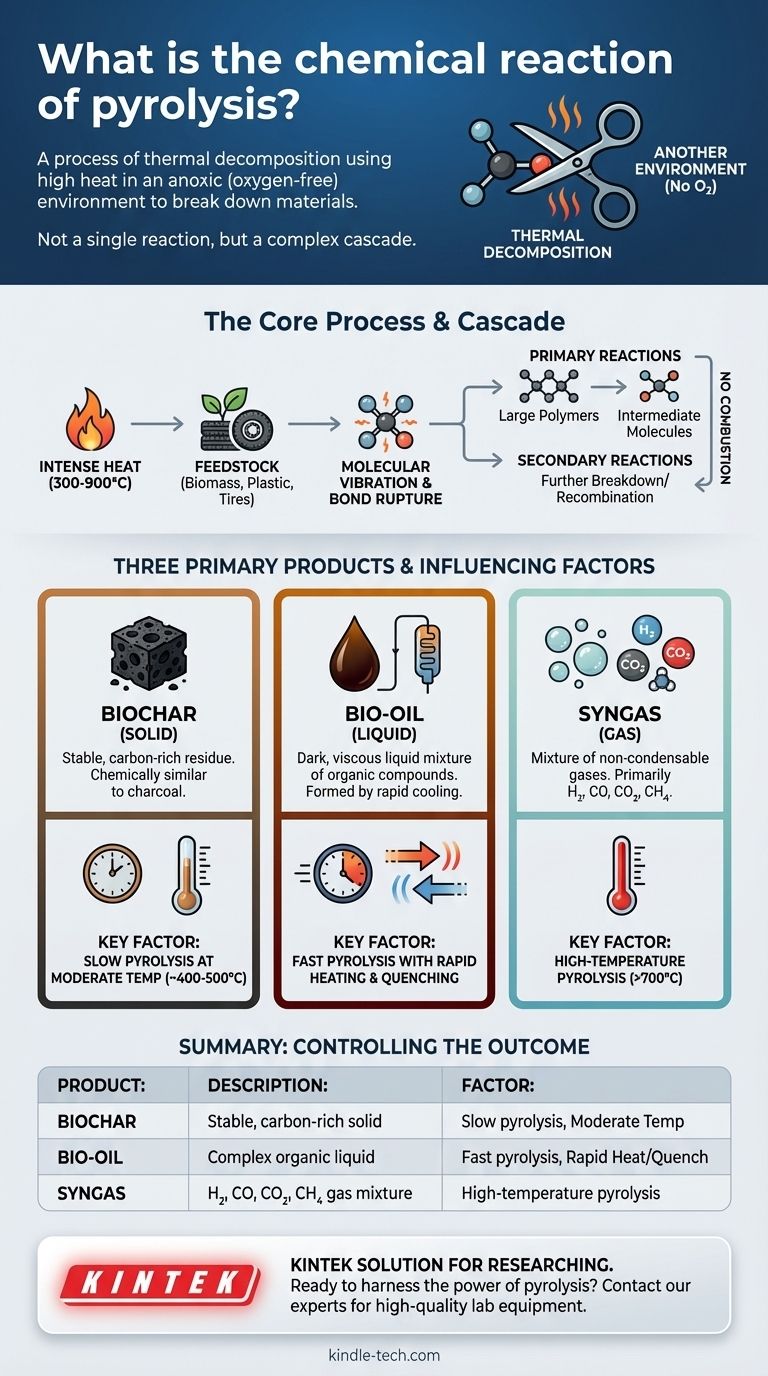
At its core, pyrolysis is a process of thermal decomposition. It uses high heat to break down materials in an environment that is completely or almost completely free of oxygen, preventing the material from simply catching fire and burning.
Pyrolysis is not a single chemical reaction, but rather a complex sequence of reactions. The fundamental principle is using heat as a form of "molecular scissors" to break large, complex molecules into smaller, often more valuable ones, without the presence of oxygen to enable combustion.

What is Pyrolysis at the Molecular Level?
To truly understand pyrolysis, you must look beyond a single chemical formula. It is a dynamic process defined by its conditions and mechanisms.
The Core Principle: Thermal Decomposition
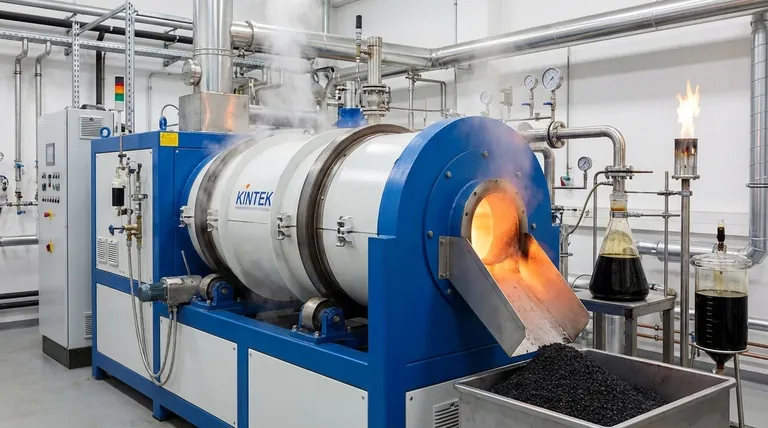
The process begins by applying intense heat (typically 300-900°C or higher) to a feedstock, such as biomass, plastics, or tires.
This thermal energy is absorbed by the molecules, causing their atoms to vibrate violently. When the vibration energy exceeds the strength of the chemical bonds holding the molecule together, those bonds rupture.
The Critical Condition: An Anoxic Environment
This decomposition happens in an anoxic (oxygen-free) or anaerobic environment. This is the single most important factor that distinguishes pyrolysis from combustion.
Without oxygen, the material cannot burn to form carbon dioxide and water. Instead, the fragmented molecules recombine into new, smaller, and more stable solid, liquid, and gaseous products.
Not One Reaction, But a Cascade
Pyrolysis rarely involves a single A → B reaction. It is a cascade of primary and secondary reactions.
First, large polymers (like cellulose in wood or polyethylene in plastic) break into smaller, volatile intermediate molecules. These intermediates can then break down further or react with each other in the gas phase before they are collected.
The Three Primary Products of Pyrolysis
The output of pyrolysis is almost always a mixture of three distinct product types. The ratio of these products is not random; it is controlled by the process conditions.
Biochar (Solid)
Biochar is the stable, carbon-rich solid residue that remains after all volatile components have been driven off. It is chemically similar to charcoal.
Bio-oil (Liquid)
Also known as pyrolysis oil or tar, bio-oil is a dark, viscous liquid. It forms when the hot gases produced during decomposition are rapidly cooled and condensed. It is a complex mixture of hundreds of different organic compounds.
Syngas (Gas)
Syngas, or synthesis gas, is the collection of non-condensable gases that remain after the bio-oil has been separated. It primarily consists of hydrogen (H₂), carbon monoxide (CO), carbon dioxide (CO₂), and methane (CH₄).
Understanding the Trade-offs: Key Influencing Factors
You cannot understand the "reaction" of pyrolysis without understanding the factors that control its outcome. Tweaking these parameters is how operators determine the final product yields.
The Role of Temperature
Temperature directly impacts the extent of molecular breakdown. Lower temperatures (300-500°C) tend to favor the production of solid biochar. Extremely high temperatures (>700°C) crack molecules more thoroughly, maximizing the yield of syngas.
The Impact of Heating Rate
The speed at which the feedstock is heated is critical.
- Slow pyrolysis (long heating times) maximizes the yield of biochar.
- Fast pyrolysis (heating in seconds) minimizes char formation and maximizes the yield of liquid bio-oil.
The Influence of Feedstock
The chemical makeup of the starting material directly dictates the composition of the products. Pyrolyzing wood (rich in cellulose and lignin) will produce a different bio-oil and syngas than pyrolyzing plastic (rich in hydrocarbons).
How to Control Pyrolysis for Your Goal
The key to pyrolysis is understanding that you can steer the chemical outcomes based on your desired product.
- If your primary focus is maximizing solid biochar (for soil amendment or carbon sequestration): Employ slow pyrolysis at moderate temperatures (around 400-500°C) to allow for the gradual release of volatiles and the formation of a stable carbon structure.
- If your primary focus is maximizing liquid bio-oil (for biofuel or chemical production): Use fast pyrolysis with a very high heating rate and short vapor residence time, followed by rapid quenching to capture the liquid before it breaks down further.
- If your primary focus is maximizing syngas (for energy generation): Utilize high-temperature pyrolysis (>700°C) with a longer residence time to ensure complete thermal cracking of larger molecules into simple gases.
By mastering these conditions, you can transform pyrolysis from a simple decomposition process into a precise tool for chemical manufacturing.
Summary Table:
| Product | Description | Key Influencing Factor |
|---|---|---|
| Biochar (Solid) | Stable, carbon-rich solid residue | Slow pyrolysis at moderate temperatures (~400-500°C) |
| Bio-oil (Liquid) | Complex mixture of organic compounds | Fast pyrolysis with rapid heating and quenching |
| Syngas (Gas) | Mixture of H₂, CO, CO₂, CH₄ | High-temperature pyrolysis (>700°C) |
Ready to harness the power of pyrolysis in your lab?
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment, including pyrolysis systems, to help you precisely control thermal decomposition for your research and material processing needs. Whether your goal is to produce biochar, bio-oil, or syngas, our solutions are designed for accuracy and efficiency.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's specific pyrolysis applications!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the different types of pyrolysis machines? Choose the Right System for Your Output



















