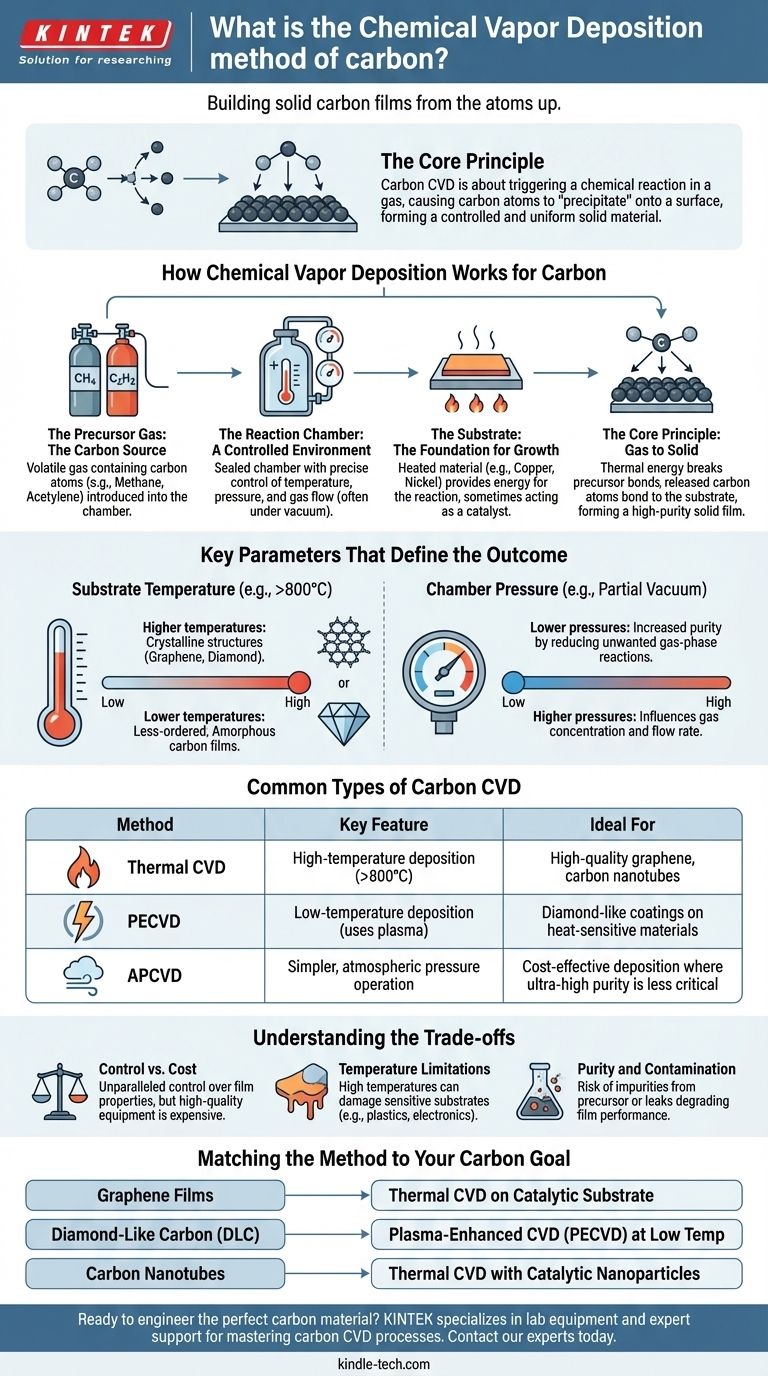
In essence, the chemical vapor deposition (CVD) of carbon is a method for building a solid carbon film or structure from the atoms up. It involves introducing a carbon-containing gas into a reaction chamber, where it decomposes on a heated surface (called a substrate), leaving behind a high-purity layer of solid carbon. This technique is fundamental to creating advanced materials like graphene, diamond films, and carbon nanotubes.
The core principle of carbon CVD is not simply depositing carbon, but triggering a chemical reaction in a gas that causes carbon atoms to "precipitate" onto a surface, forming a highly controlled and uniform solid material. The final product is defined entirely by the process conditions.

How Chemical Vapor Deposition Works for Carbon
To understand the process, it's best to break it down into its essential components. Each part plays a critical role in determining the type and quality of the carbon material being created.
The Core Principle: Gas to Solid
The entire process happens within a sealed chamber. A precursor gas containing carbon atoms is introduced into this chamber, which is typically under a vacuum.
This gas flows over a heated substrate. The thermal energy from the substrate breaks the chemical bonds in the precursor gas, releasing the carbon atoms, which then bond to the substrate surface to form a solid film.
The Precursor Gas: The Carbon Source
The choice of gas is the first critical decision, as it is the source of the carbon atoms. The gas must be volatile and decompose at a manageable temperature.
Common precursors for carbon CVD include methane (CH4), acetylene (C2H2), and ethanol. The type of precursor can influence the growth rate and quality of the final carbon structure.
The Substrate: The Foundation for Growth
The substrate is the material onto which the carbon film grows. Its temperature provides the energy needed to drive the chemical reaction.
The substrate material itself can also act as a catalyst. For example, large-area graphene is commonly grown on copper or nickel foils, which catalyze the decomposition of the precursor and the formation of the graphene lattice.
The Reaction Chamber: A Controlled Environment
The chamber allows for precise control over the growth environment. Key parameters like temperature, pressure, and gas flow rates are carefully managed to achieve the desired outcome.
Key Parameters That Define the Outcome
Slight changes in the CVD process can result in dramatically different forms of carbon. The most important control knobs are temperature and pressure.
Substrate Temperature
Temperature is arguably the most critical parameter. It directly dictates the amount of energy available for breaking the bonds in the precursor gas and for the carbon atoms to arrange themselves on the surface.
Higher temperatures generally lead to more crystalline structures (like graphene or diamond), while lower temperatures might result in less-ordered, amorphous carbon films.
Chamber Pressure
Pressure inside the chamber affects the concentration of the precursor gas and the rate at which it flows across the substrate.
Lower pressures (a partial vacuum) are often used to increase the purity of the film by reducing the chances of unwanted gas-phase reactions and contamination.
Common Types of Carbon CVD
While the core principle remains the same, several variations of CVD exist, each optimized for different needs.
Atmospheric Pressure CVD (APCVD)
As the name implies, this process is conducted at standard atmospheric pressure. It is simpler and less expensive to implement because it doesn't require complex vacuum systems.
However, it can sometimes lead to lower-purity films compared to vacuum-based methods.
Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD)
PECVD uses an electric field to generate a plasma (an ionized gas) within the chamber. This highly energetic plasma helps break down the precursor gas molecules.
The key advantage of PECVD is that it allows deposition to occur at much lower temperatures than traditional thermal CVD, making it suitable for substrates that cannot withstand high heat.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While powerful, CVD is not without its complexities and limitations. Understanding these is key to its successful application.
Control vs. Cost
CVD offers unparalleled control over film thickness, uniformity, and purity. This precision comes at a cost, as high-quality CVD equipment, particularly with vacuum and plasma capabilities, can be expensive.
Temperature Limitations
The high temperatures required for many thermal CVD processes (often >800°C) can damage or melt sensitive substrates, such as plastics or certain electronic components. This is the primary reason techniques like PECVD were developed.
Purity and Contamination
Because it is a chemical process, there is always a risk of impurities from the precursor gas or leaks in the chamber being incorporated into the final carbon film, which can degrade its performance.
Matching the Method to Your Carbon Goal
The right CVD approach depends entirely on the specific carbon material you intend to create.
- If your primary focus is large-area, high-quality graphene films: Thermal CVD using methane on a catalytic copper foil substrate is the dominant and most effective industry standard.
- If your primary focus is hard, diamond-like carbon (DLC) coatings on heat-sensitive materials: Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) is the ideal choice because it enables high-quality deposition at low temperatures.
- If your primary focus is growing arrays of carbon nanotubes: Thermal CVD is typically used with a substrate that has been pre-coated with catalytic nanoparticles (like iron or nickel) to seed the nanotube growth.
By mastering these core principles, you can select and control the CVD process to engineer carbon materials with precisely the properties you need.
Summary Table:
| CVD Method | Key Feature | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal CVD | High-temperature deposition | High-quality graphene, carbon nanotubes |
| PECVD | Low-temperature deposition (uses plasma) | Diamond-like coatings on heat-sensitive materials |
| APCVD | Simpler, atmospheric pressure operation | Cost-effective deposition where ultra-high purity is less critical |
Ready to engineer the perfect carbon material for your application?
The principles of Chemical Vapor Deposition are complex, but achieving your material goals doesn't have to be. KINTEK specializes in providing the lab equipment and expert support you need to master carbon CVD processes, whether you're developing graphene electronics, durable coatings, or advanced composites.
We understand that the right tools and parameters are critical for success. Let us help you select the ideal CVD system for your specific substrate, precursor, and performance requirements.
Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory's innovation in carbon materials.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is PECVD in semiconductor? Enable Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition for ICs
- What are the different types of thin films? A Guide to Optical, Electrical, and Functional Coatings
- What are the methods of deposition? A Guide to PVD and CVD Thin-Film Techniques
- What color diamonds are CVD? Understanding the Process from Brown Tint to Colorless Beauty
- What are the steps of the CVD process? A Guide to Precision Thin Film Deposition



















