At its core, Molybdenum Disilicide (MoSi2) possesses a specific and highly ordered atomic arrangement. It crystallizes in the tetragonal crystal system, belonging to the I4/mmm space group. This structure, often referred to as the C11b prototype, is the fundamental reason for its unique combination of properties, making it an exceptional material for high-temperature applications.
The tetragonal structure of MoSi2 is not just a classification; it is the direct cause of its most valued characteristic—excellent stability at high temperatures—and its most significant drawback—brittleness at room temperature.
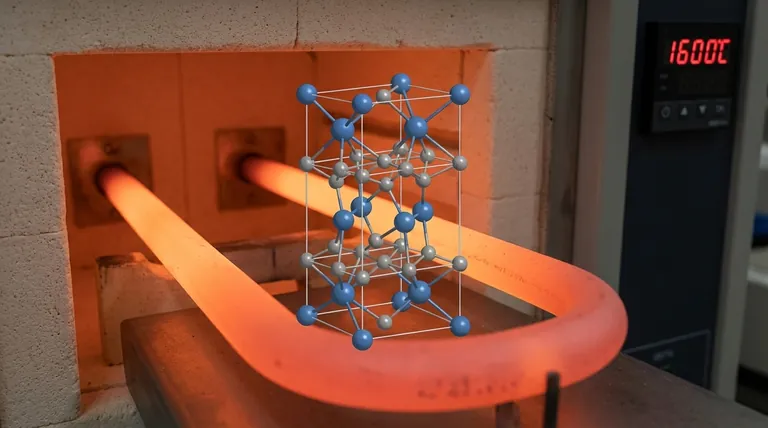
Deconstructing the MoSi2 Crystal Structure
To understand MoSi2's behavior, we must first understand its atomic architecture. The "I4/mmm" designation is a precise shorthand that describes this arrangement.
The Tetragonal System
The term tetragonal means the unit cell, the basic repeating block of the crystal, has a square base but a different height. Imagine a rectangular box where the length and width are equal, but the height is not (a = b ≠ c). This deviation from a perfect cube is a source of anisotropy, meaning properties can differ along different directions in the crystal.
The I4/mmm Space Group
This code provides more detail. The "I" signifies that the structure is body-centered, meaning there is an atom at the center of the tetragonal cell in addition to the atoms at the corners. The "4/mmm" describes the crystal's high degree of symmetry, including a four-fold rotational axis and multiple mirror planes. This high symmetry contributes to the structure's stability.
The C11b Prototype
MoSi2 is the classic example of the C11b crystal structure. In this arrangement, atoms are stacked in distinct layers along the taller 'c' axis. This layered nature—a plane of molybdenum atoms followed by two planes of silicon atoms—is a key feature that influences how the material deforms and fractures.
How Structure Dictates MoSi2's Properties
A material's crystal structure is its blueprint, directly defining its mechanical and chemical behavior. For MoSi2, this link is especially clear.
High-Temperature Strength and Stability
The combination of strong, covalent Mo-Si bonds and the highly ordered, symmetric crystal structure makes it very difficult for atoms to shift or dislocate at high temperatures. This resistance to deformation is what gives MoSi2 its exceptional strength and creep resistance when heated, making it ideal for furnace heating elements and aerospace components.
Inherent Low-Temperature Brittleness
The same complex, ordered structure that provides high-temperature strength also severely restricts atomic movement at low temperatures. The material has very few "slip systems"—planes along which atoms can easily slide past one another. When stress is applied at room temperature, the crystal cannot deform plastically and instead fractures in a brittle manner.
Excellent Oxidation Resistance
When exposed to oxygen at high temperatures, MoSi2 forms a thin, self-healing, and continuous layer of silica (SiO2) on its surface. This glassy layer is highly stable and acts as a barrier, protecting the underlying material from further oxidation and degradation.
Understanding the Trade-offs
No material is perfect. The properties that make MoSi2 valuable in one context create challenges in another.
The Stability vs. Ductility Dilemma
The core trade-off for MoSi2 is clear: its structural and chemical stability comes at the cost of ductility. The very atomic arrangement that prevents it from deforming at 1500°C is what causes it to shatter like glass if dropped at room temperature.
The Brittle-to-Ductile Transition
MoSi2 is not brittle at all temperatures. It undergoes a brittle-to-ductile transition at approximately 900–1000°C. Above this temperature, atoms have enough thermal energy to move, activating more slip systems and allowing the material to deform plastically rather than fracture. This transition temperature is a critical parameter for any manufacturing or forming process.
Challenges in Fabrication
The room-temperature brittleness makes MoSi2 extremely difficult to machine or form using conventional metalworking techniques. It is typically processed using powder metallurgy methods, where MoSi2 powder is compacted and sintered at high temperatures to form a solid part.
Applying This Knowledge to Your Application
Understanding the link between MoSi2's structure and its properties is key to using it effectively. Your design and processing choices must account for its fundamental nature.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature structural components: Leverage the stability of the tetragonal phase, but design components to minimize mechanical shock and tensile stress, especially during heat-up and cool-down cycles.
- If your primary focus is composite materials: Use MoSi2 as a reinforcing matrix to impart high-temperature strength and oxidation resistance to another material that may improve overall toughness.
- If your primary focus is material processing and fabrication: Be aware that the brittle-to-ductile transition temperature is the critical window for any forming or shaping operations.
By understanding its atomic architecture, you can engineer around its limitations and fully exploit its remarkable strengths.
Summary Table:
| Key Feature | Description | Impact on Properties |
|---|---|---|
| Crystal System | Tetragonal (a = b ≠ c) | Causes anisotropy; properties vary with direction. |
| Space Group | I4/mmm (Body-centered) | High symmetry contributes to thermal stability. |
| Structure Type | C11b Prototype | Layered arrangement (Mo-Si-Si) influences deformation. |
| Brittle-to-Ductile Transition | ~900–1000°C | Material changes from brittle to plastic above this temperature. |
Need High-Performance Lab Equipment for Advanced Materials Like MoSi2?
Understanding material properties is just the first step. KINTEK specializes in providing the robust lab equipment and consumables you need to research, process, and test high-temperature materials effectively. From furnace systems that can handle MoSi2's operational range to precision tools for sample preparation, we support your laboratory's innovation.
Contact our experts today to find the perfect solution for your materials science challenges and enhance your lab's capabilities.
Visual Guide

Related Products
- Conductive Carbon Cloth Carbon Paper Carbon Felt for Electrodes and Batteries
- Electrode Polishing Material for Electrochemical Experiments
- Laboratory Hydraulic Press Lab Pellet Press for Button Battery
- Custom PTFE Teflon Parts Manufacturer Corrosion Resistant Cleaning Rack Flower Basket
- Conductive Boron Nitride BN Ceramics Composite for Advanced Applications
People Also Ask
- What should heating element be made of? A Guide to High-Temp, Durable Materials
- What is the best electric heating element? Match the Right Material to Your Application's Needs
- How effective is electrical resistance heating? It's 100% efficient at the point of use.
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of tungsten? Master Extreme Heat & Wear Resistance
- What is the temperature range of molybdenum disilicide heating elements? Choose the Right Grade for Your High-Temp Needs
- How efficient is a quartz heating element? Unlock Up to 96% Radiant Efficiency for Targeted Heating
- Which is better nichrome or tungsten? Choose the Right Heating Element for Your Application
- Are quartz heating elements better? Discover the Key to Fast, Targeted Infrared Heat



















