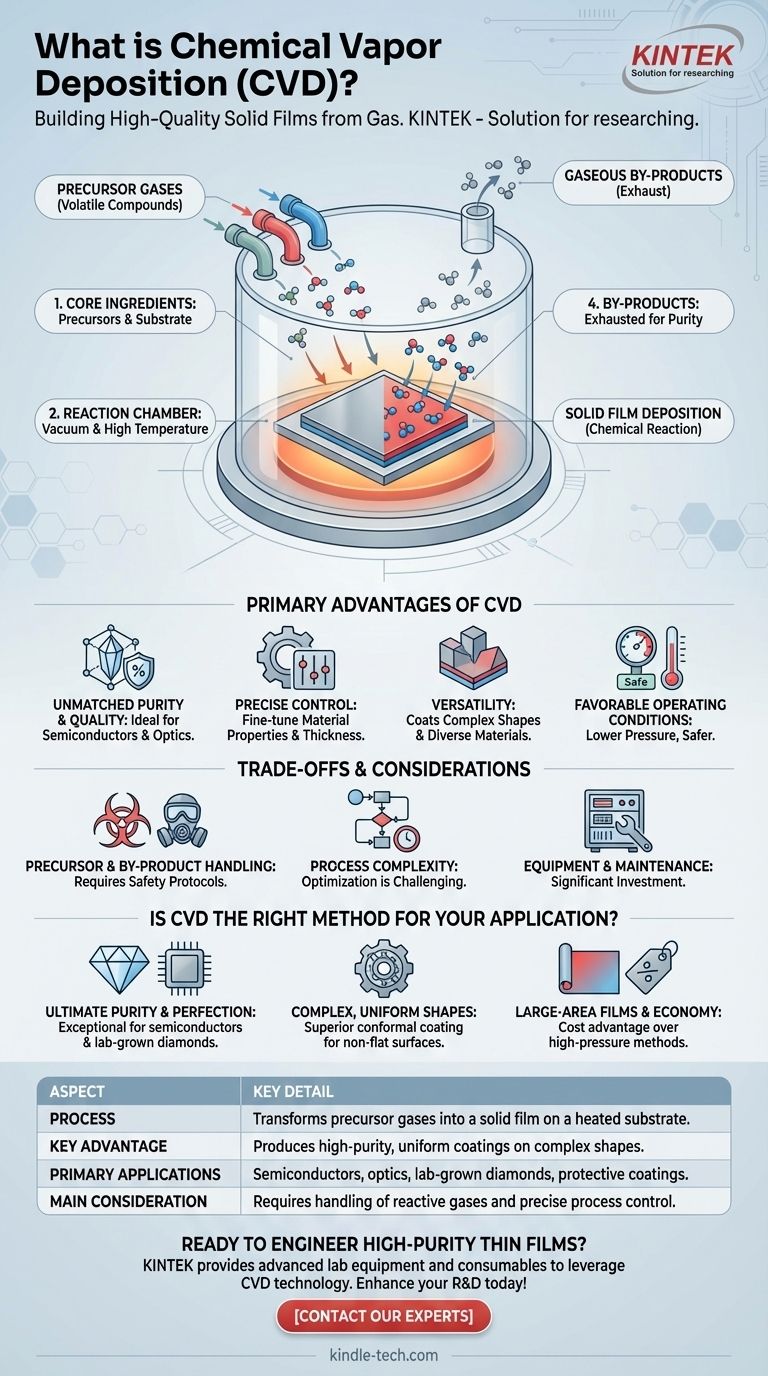
In essence, Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) is a method for building a high-quality solid film on a surface from a gas. It works by introducing specific precursor gases into a controlled chamber containing a substrate. When heated, these gases undergo a chemical reaction or decomposition, causing a solid material to deposit and bond directly onto the substrate's surface, forming a thin, uniform coating layer by layer.
CVD is not just about coating a surface; it's about growing a new material directly onto it through controlled chemical reactions. This method's power lies in its unparalleled precision, allowing for the creation of exceptionally pure and functional thin films with tailored properties.

How CVD Fundamentally Works
To understand the value of CVD, it’s crucial to visualize its core mechanics. The process can be broken down into a few fundamental stages that transform gas into a high-performance solid.
The Core Ingredients: Precursors and a Substrate
The process begins with one or more volatile precursor gases, which are chemical compounds that contain the elements you wish to deposit. These gases are introduced into a chamber where the substrate—the material or part to be coated—is placed.
The Environment: The Reaction Chamber
The entire process takes place within a reaction chamber, which is typically under a vacuum or controlled low pressure. The substrate is heated to a specific reaction temperature, which is a critical parameter for the entire process.
The Chemical Reaction: From Gas to Solid
The high temperature provides the energy needed to trigger a chemical reaction in the precursor gases on or near the substrate's surface. This reaction breaks the gases down, freeing the desired elements to deposit onto the substrate.
This deposition builds up over time, growing a dense and solid film. This film can be amorphous (lacking an ordered structure), polycrystalline (made of many small crystals), or even a perfect single crystal.
The By-products: Exhausting What's Left
The chemical reaction almost always produces unwanted gaseous by-products. These are removed from the chamber by a continuous gas flow, ensuring the deposited film remains pure.
The Primary Advantages of Using CVD
Engineers and scientists choose CVD when the quality and properties of the final film are paramount. Its benefits are directly tied to the precise control it offers.
Unmatched Purity and Quality
Because the process starts with high-purity gases in a controlled vacuum environment, CVD can produce films with extremely high purity. This is critical for applications like semiconductors and high-performance optics.
Precise Control Over Material Properties
The final characteristics of the film—such as thickness, crystal structure, and chemical properties—can be finely tuned. By adjusting parameters like temperature, pressure, and gas concentration, operators can engineer the exact material they need.
Versatility Across Materials and Shapes
CVD is not limited to one type of material. It can be used to deposit pure elements, complex alloys, and compounds. Furthermore, because the precursors are gases, they can reach and uniformly coat large areas and complex, non-flat surfaces.
Favorable Operating Conditions
Compared to competing technologies like High-Pressure/High-Temperature (HPHT) synthesis for diamonds, CVD often operates at much lower pressures (e.g., below 27 kPa). This can lead to lower equipment setup costs and safer operating conditions.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Considerations
No process is perfect for every application. To be objective, it is important to understand the practical challenges associated with CVD.
Precursor and By-product Handling
The precursor gases used in CVD can be toxic, flammable, or corrosive. This necessitates robust safety protocols and handling systems. Similarly, the waste by-products must be managed and treated appropriately.
Process Complexity and Optimization
Achieving a perfect, defect-free film is not trivial. It requires meticulous control over all process variables. Optimizing a new CVD process for a specific material and substrate can be a time-consuming and complex engineering challenge.
Equipment and Maintenance
While sometimes less expensive than high-pressure alternatives, CVD systems are sophisticated pieces of equipment. They require a significant capital investment and ongoing maintenance to ensure the vacuum chambers, gas delivery systems, and heating elements operate reliably.
Is CVD the Right Method for Your Application?
Your choice depends entirely on the material properties you need to achieve and the constraints of your project.
- If your primary focus is ultimate purity and crystalline perfection: CVD is an exceptional choice, offering control over impurities that is difficult to match for applications like semiconductor manufacturing.
- If your primary focus is coating complex, three-dimensional shapes uniformly: CVD's gas-phase nature allows it to deposit conformal layers on non-flat surfaces more effectively than line-of-sight methods.
- If your primary focus is producing large-area films or lab-grown diamonds economically: CVD often provides a cost and scalability advantage over high-pressure methods like HPHT for specific high-value materials.
Ultimately, CVD empowers engineers and scientists to build materials from the atom up, offering a powerful and precise tool for creating next-generation technology.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Key Detail |
|---|---|
| Process | Transforms precursor gases into a solid film on a heated substrate. |
| Key Advantage | Produces high-purity, uniform coatings on complex shapes. |
| Primary Applications | Semiconductors, optics, lab-grown diamonds, protective coatings. |
| Main Consideration | Requires handling of reactive gases and precise process control. |
Ready to engineer high-purity thin films for your laboratory? The precise control of Chemical Vapor Deposition is key to advancing semiconductor, optical, and materials research. KINTEK specializes in providing the advanced lab equipment and consumables needed to leverage CVD technology effectively. Our expertise ensures you have the right tools for depositing uniform, high-quality films on even the most complex substrates. Contact us today to discuss how our solutions can enhance your R&D and production capabilities.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Laboratory CVD Boron Doped Diamond Materials
People Also Ask
- Can plasma enhanced CVD deposit metals? Why PECVD is rarely used for metal deposition
- How are thin films deposited? A Guide to PVD vs. CVD Methods for Your Application
- Why does a PECVD vacuum system require both a rotary vane and turbo pump? Ensure High-Purity Coatings
- What are different types of thin films? A Guide to Function, Material, and Deposition Methods
- What is the difference between plasma CVD and thermal CVD? Choose the Right Method for Your Substrate



















