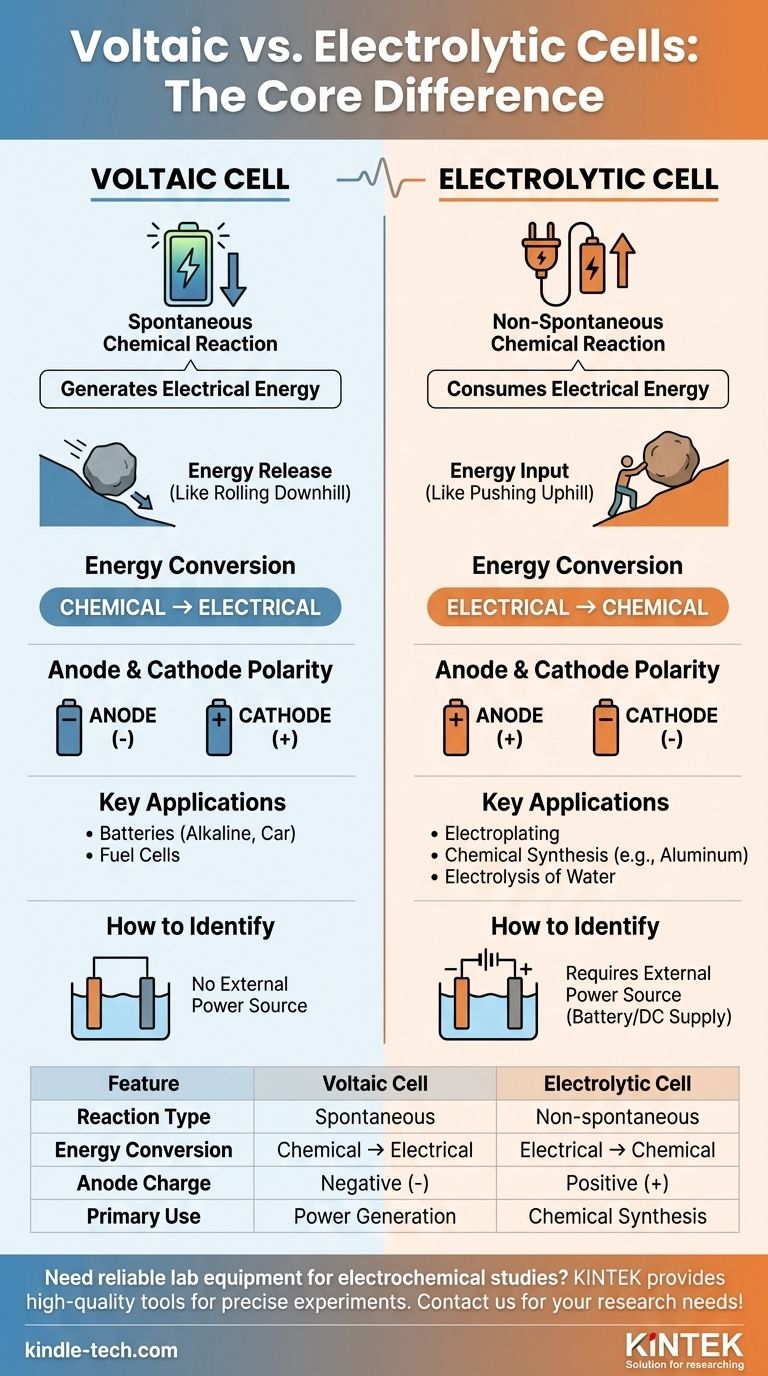
The primary difference between a voltaic cell and an electrolytic cell lies in their fundamental purpose and the nature of the chemical reactions involved. A voltaic cell, such as a common battery, uses a spontaneous chemical reaction to generate electrical energy. In contrast, an electrolytic cell uses external electrical energy to drive a chemical reaction that would not happen on its own.
At its core, the distinction is about energy flow. A voltaic cell is a power source that releases energy from a willing chemical reaction. An electrolytic cell is an energy consumer that forces an unwilling chemical reaction to occur.

The Core Principle: Spontaneity
The most important concept separating these two cells is whether the chemical reaction is spontaneous or non-spontaneous. This dictates the entire function and structure of the cell.
Voltaic Cells: Spontaneous Energy Release
In a voltaic cell (also called a galvanic cell), the redox reaction is spontaneous. The reactants have higher chemical potential energy than the products.
This natural tendency to react releases energy, which is harnessed as an electrical current. Think of it like a boulder rolling downhill—it happens without any external push.
The standard cell potential (E°cell) for a voltaic cell is always positive, indicating a spontaneous reaction.
Electrolytic Cells: Forced Chemical Change
In an electrolytic cell, the redox reaction is non-spontaneous. The products are at a higher energy state than the reactants.
To make this reaction happen, an external power source (like a battery or DC supply) must be applied. This is like pushing the boulder uphill—it requires a constant input of energy.
The standard cell potential (E°cell) for the reaction in an electrolytic cell is negative, confirming it will not proceed without external help.
Key Functional and Structural Differences
The difference in spontaneity leads to several crucial distinctions in how these cells are built and how they operate.
Energy Conversion
A voltaic cell performs the conversion of chemical energy to electrical energy. It's a chemical power generator.
An electrolytic cell does the exact opposite. It converts electrical energy to chemical energy, using power to create new substances.
Anode and Cathode Polarity
This is a frequent point of confusion, but it's simple if you remember the core definitions. In both cell types, oxidation always occurs at the anode and reduction always occurs at the cathode.
However, the charge of these electrodes is reversed:
- In a voltaic cell, the anode is the source of electrons from the spontaneous reaction, making it the negative (-) terminal. The cathode is where electrons are consumed, making it the positive (+) terminal.
- In an electrolytic cell, the external power source dictates the charge. It pushes electrons to the cathode, making it the negative (-) terminal. It pulls electrons away from the anode, making it the positive (+) terminal.
Practical Applications
The applications for each cell type directly reflect their function.
Voltaic cells are used to power devices. Examples include everyday alkaline batteries, car batteries (while discharging), and fuel cells.
Electrolytic cells are used for synthesis and purification. Common applications include electroplating metals, producing pure aluminum, and the electrolysis of water to generate hydrogen and oxygen gas.
Common Pitfalls and Key Distinctions
To avoid common mistakes, focus on the cell's purpose and the presence of an external power source.
Purpose: Power vs. Production
The most straightforward way to distinguish them is by their goal. Is the cell making electricity, or is it using electricity to make a chemical? The first is voltaic; the second is electrolytic.
The Role of the Salt Bridge
Voltaic cells often consist of two separate half-cells connected by a salt bridge. This component is crucial for maintaining charge neutrality as ions flow during the spontaneous reaction.
Electrolytic cells are typically simpler in construction, often taking place in a single container where the electrolyte itself allows for ion movement.
The External Power Supply
The clearest visual indicator in a diagram is the presence of a battery or power supply. If you see one connected to the electrodes, you are looking at an electrolytic cell. Its absence implies a voltaic cell.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To identify the cell type or understand its function, consider the primary objective of the system.
- If your primary focus is to power a device: You are working with a voltaic cell, which harnesses a spontaneous chemical reaction to produce a current.
- If your primary focus is to produce a pure substance (like chlorine gas or copper metal): You are using an electrolytic cell, which drives a non-spontaneous reaction with an external power source.
- If you are analyzing a diagram with an external battery: This signifies an electrolytic cell, as it provides the necessary energy to force the chemical change.
Understanding this fundamental divide between spontaneous generation and forced reaction is the key to mastering electrochemistry.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Voltaic Cell | Electrolytic Cell |
|---|---|---|
| Reaction Type | Spontaneous | Non-spontaneous (requires external power) |
| Energy Conversion | Chemical → Electrical | Electrical → Chemical |
| Anode Charge | Negative (-) | Positive (+) |
| Primary Use | Power generation (e.g., batteries) | Chemical synthesis (e.g., electroplating) |
Need reliable lab equipment for your electrochemical studies? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, providing the precise tools you need for experiments involving voltaic and electrolytic cells. From electrodes to power supplies, our solutions help ensure accurate and reproducible results in your laboratory. Contact us today to find the perfect equipment for your research needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Five-Port
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell Gas Diffusion Liquid Flow Reaction Cell
- Multifunctional Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell Water Bath Single Layer Double Layer
- Battery Lab Equipment Battery Capacity and Comprehensive Tester
People Also Ask
- How can the reaction within an electrolysis cell be controlled? Master Voltage, Current, and Electrolyte
- What is the function of a three-chamber H-type electrolytic cell? Unlock Complex Multi-Step Electrochemical Reactions
- Are there any chemical substances that should be avoided with an all-PTFE electrolytic cell? Know the Critical Limits for Your Lab
- What are the limitations of electrochemical deposition? Overcome ECD's Constraints for Your Application
- What specific mechanical and physical properties are required for PPS woven separators in zero-gap electrolytic cells?
- What checks should be performed on the H-type electrolytic cell before use? Ensure Accurate Electrochemical Data
- Why are electrolytic cells configured with ion-exchange membranes required? Enhancing Safety and Efficiency
- What is the correct shutdown procedure after an experiment? A Step-by-Step Guide to Safe Deactivation














