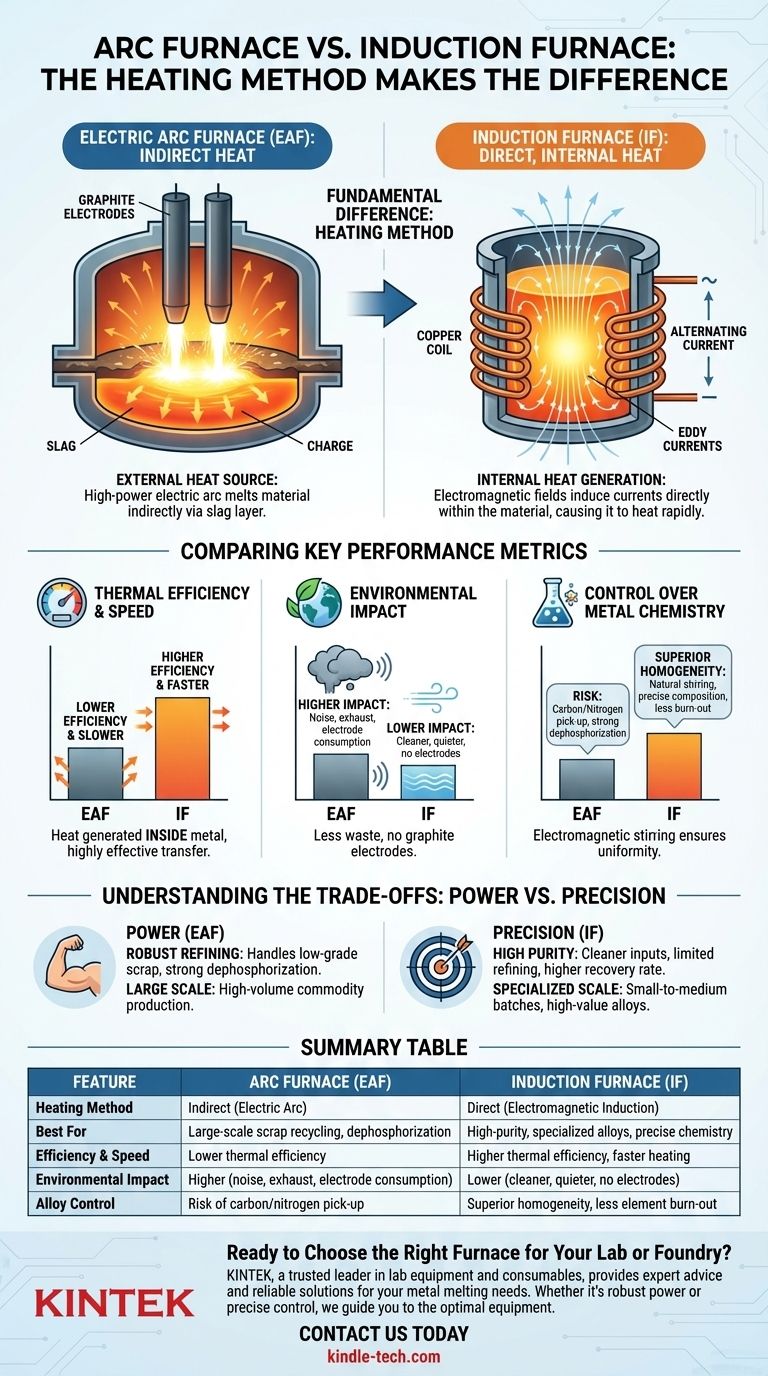
The fundamental difference between an electric arc furnace and an induction furnace lies in their heating method. An arc furnace uses a high-power electric arc to melt material indirectly, while an induction furnace uses electromagnetic fields to generate heat directly within the material itself. This core distinction drives significant differences in their efficiency, environmental impact, and the chemical purity of the final product.
The choice between an arc and induction furnace is a strategic decision between industrial scale and chemical precision. Arc furnaces are powerful workhorses for large-scale recycling, while induction furnaces offer superior efficiency, cleanliness, and control for producing high-quality, specialized alloys.
How They Work: A Tale of Two Heating Methods
To understand the practical differences, you must first grasp how each furnace generates heat. Their mechanisms are fundamentally opposed: one is external, the other is internal.
The Electric Arc Furnace (EAF): Indirect Heat
An electric arc furnace melts metal using an external heat source.
Large graphite electrodes are lowered into the furnace, and an immense electrical current passes through them, creating an arc that jumps to the metal charge. This arc can reach temperatures of thousands of degrees, melting the metal by transferring heat through a layer of slag. This process is a form of indirect heating.
The Induction Furnace (IF): Direct, Internal Heat
An induction furnace works much like a microwave, but for conductive metals. It uses internal heat generation.
An alternating current flows through a copper coil, creating a powerful, fluctuating magnetic field. When conductive material like steel is placed inside this field, the field induces electrical currents (eddy currents) directly within the metal. The metal's own electrical resistance causes it to heat up rapidly and melt from the inside out. This is direct heating.
Comparing Key Performance Metrics
The difference between indirect and direct heating creates cascading effects on every aspect of furnace performance, from energy use to the quality of the steel produced.
Thermal Efficiency and Speed
The induction furnace is the clear winner in efficiency. Because heat is generated inside the metal, energy transfer is extremely effective. This results in faster heating and higher overall thermal efficiency.
The arc furnace is less efficient. Heat must first be generated by the arc and then transferred through slag to the molten steel. Significant thermal energy is also lost through the furnace's large cover and walls, contributing to its poorer thermal efficiency.
Environmental Impact
Induction furnaces are significantly more environmentally friendly. They produce less waste residue and exhaust gas. Crucially, they do not use graphite electrodes, which eliminates noise pollution from the arc and prevents the steel from picking up excess carbon.
Arc furnace steelmaking is a harsher process. It generates considerable waste residue, exhaust gas, and powerful noise from the electric arc.
Control Over Metal Chemistry
The furnace type directly impacts the final chemistry of the alloy. The electromagnetic field in an induction furnace naturally stirs the molten metal, ensuring a highly uniform and homogeneous product quality. This makes it ideal for specialized alloys where precise composition is critical.
The arc furnace process is stronger at dephosphorization, a key step in refining raw steel. However, the high-energy arc can cause nitrogen from the air to ionize and dissolve into the steel, resulting in higher nitrogen content. The graphite electrodes also introduce the risk of unwanted carbon pick-up in the final product.
Understanding the Trade-offs: Power vs. Precision
Neither furnace is universally superior; they are different tools designed for different jobs. Choosing between them involves understanding their inherent trade-offs.
Input Material and Refining Capability
The robust nature of the arc furnace makes it well-suited for melting large quantities of scrap metal of varying quality. Its powerful refining capability, especially its strength in dephosphorization, allows it to turn lower-grade inputs into usable steel.
Induction furnaces are more sensitive to the quality of the input material. Because their refining capabilities are more limited, they are typically charged with cleaner scrap or pre-refined materials to avoid contaminating the final, high-purity melt.
Alloy Integrity and Burn-Out
The gentler, direct heating of an induction furnace results in a higher metal recovery rate and a lower burn-out ratio for expensive alloy elements. This is a significant economic advantage when producing high-value alloys.
The intense, localized heat of the electric arc can cause more of the valuable alloying elements to oxidize and be lost to the slag, reducing the overall yield.
Scale of Operation
Electric arc furnaces are the backbone of modern, large-scale steel recycling, often built to handle hundreds of tons of material at a time. They are designed for high-volume commodity production.
Induction furnaces are more versatile in scale but excel in small-to-medium batch operations. Their efficiency and precision make them perfect for foundries producing specialized castings and high-performance alloys.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision must be guided by your specific operational goals, from the type of metal you are producing to your environmental and efficiency targets.
- If your primary focus is large-scale steel production from scrap with a need for dephosphorization: The electric arc furnace is the established and powerful choice for high-volume refining.
- If your primary focus is producing high-purity, specialized alloys with precise chemical composition: The induction furnace offers superior control, cleanliness, and homogeneity.
- If your primary focus is maximizing energy efficiency and minimizing environmental impact: The induction furnace holds a clear advantage due to its direct heating method and lack of polluting electrodes.
Understanding these core differences empowers you to select the right tool not just for the metal, but for your specific operational and quality goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Arc Furnace (EAF) | Induction Furnace (IF) |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Indirect (Electric Arc) | Direct (Electromagnetic Induction) |
| Best For | Large-scale scrap recycling, dephosphorization | High-purity, specialized alloys, precise chemistry |
| Efficiency & Speed | Lower thermal efficiency | Higher thermal efficiency, faster heating |
| Environmental Impact | Higher (noise, exhaust, electrode consumption) | Lower (cleaner, quieter, no electrodes) |
| Alloy Control | Risk of carbon/nitrogen pick-up | Superior homogeneity, less element burn-out |
Ready to Choose the Right Furnace for Your Lab or Foundry?
Selecting between an arc furnace and an induction furnace is a critical decision that impacts your product quality, efficiency, and operational costs. KINTEK, a trusted leader in lab equipment and consumables, is here to help you navigate this choice.
We specialize in providing solutions that meet the specific needs of laboratories and foundries. Whether you require the robust power of an arc furnace for large-scale applications or the precise control of an induction furnace for high-purity alloys, our experts can guide you to the optimal equipment for your goals.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss your metal melting requirements. Let KINTEK provide the expert advice and reliable equipment you need to enhance your laboratory's capabilities and achieve superior results.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Induction Melting Spinning System Arc Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How does a sputtering machine work? Achieve Atomic-Level Precision for Your Coatings
- What is RF magnetron sputtering? A Guide to Depositing Insulating Thin Films
- What is magnetron sputtering machine? Precision Thin-Film Deposition for Advanced Materials
- What is the difference between VAR and VIM? Legacy Vimscript Variables vs. Modern Neovim API
- What are sputtering systems used for? A Guide to Advanced Thin-Film Deposition



















