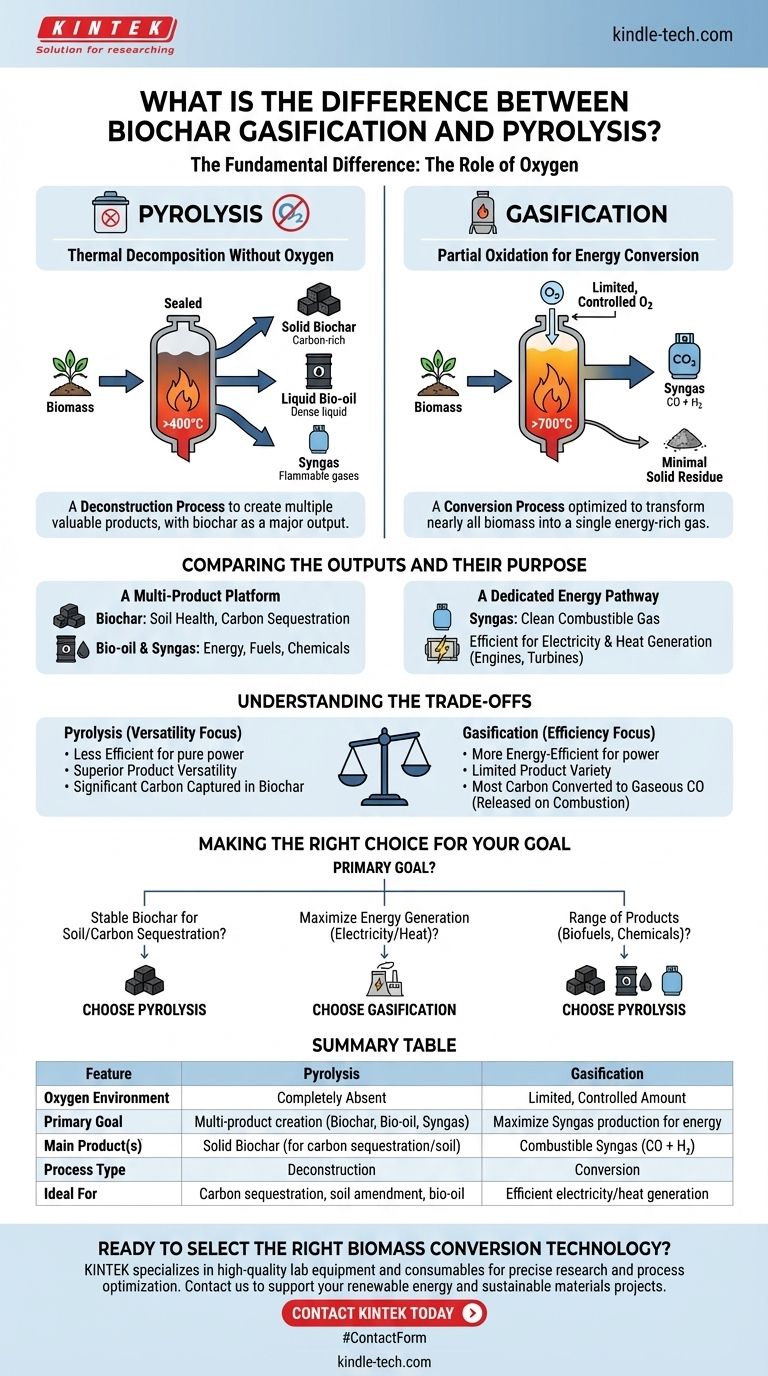
At a fundamental level, the difference between biochar gasification and pyrolysis is the presence of a small, controlled amount of oxygen. Pyrolysis is the thermal decomposition of biomass in a completely oxygen-free environment, which breaks it down into solid biochar, liquid bio-oil, and syngas. Gasification, in contrast, uses a higher temperature and introduces a limited amount of oxygen to primarily convert biomass into a combustible synthesis gas (syngas), leaving behind minimal solid residue.
The choice between these two processes is determined by your primary goal. Pyrolysis is a deconstruction process designed to create multiple valuable products (solid, liquid, gas), with biochar being a major output. Gasification is a conversion process optimized to transform nearly all of the biomass into a single energy-rich gas.

The Defining Difference: The Role of Oxygen
The presence or absence of oxygen fundamentally changes the chemical reactions that occur and, consequently, the final products you create.
Pyrolysis: Thermal Decomposition Without Oxygen
Think of pyrolysis as cooking biomass in a sealed, oxygen-starved container. Without oxygen to burn, the high heat breaks the complex organic material down into simpler components.
This process yields three distinct products in varying proportions:
- Biochar (Solid): A stable, carbon-rich solid similar to charcoal.
- Bio-oil (Liquid): A dense, acidic liquid that can be refined into fuels or chemicals.
- Syngas (Gas): A mixture of flammable gases like hydrogen, carbon monoxide, and methane.
Gasification: Partial Oxidation for Energy Conversion
Gasification operates at higher temperatures (>700°C) and intentionally introduces a limited amount of an oxidizing agent, like air or pure oxygen.
This is not enough oxygen for full combustion (burning), but just enough to drive chemical reactions that convert nearly all the biomass carbon into a gaseous fuel. The main output is syngas, a mixture of primarily carbon monoxide and hydrogen, with very little solid char left over.
Comparing the Outputs and Their Purpose
The different outputs from each process are suited for very different applications. Understanding your desired outcome is critical to selecting the right method.
Pyrolysis: A Multi-Product Platform
Pyrolysis is inherently versatile because it creates a slate of products. The solid biochar is its most unique output, valued for its ability to improve soil health and sequester carbon.
The bio-oil and syngas are co-products that can be used to generate the heat needed to sustain the pyrolysis reaction itself or be used for other energy applications.
Gasification: A Dedicated Energy Pathway
Gasification is engineered for one primary purpose: creating a large volume of clean, combustible syngas. This syngas can be used far more efficiently than burning solid biomass directly.
It is an ideal feedstock for gas engines or turbines to generate electricity and heat. The process is optimized for maximum energy conversion from the solid biomass into a usable gas.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither process is universally "better"; they are simply optimized for different goals, and each comes with trade-offs.
Efficiency vs. Versatility
Gasification is generally considered more energy-efficient if your sole objective is to produce electricity or heat from biomass. It excels at converting the feedstock's energy into syngas.
Pyrolysis is less efficient for pure power generation but offers superior product versatility. It allows you to create a high-value solid (biochar) and a liquid fuel precursor (bio-oil) in addition to a fuel gas.
The Fate of the Carbon
This is a critical distinction. In pyrolysis, a significant portion of the carbon from the original biomass is captured and stabilized in the solid biochar. This makes it an excellent method for carbon sequestration.
In gasification, most of the carbon is converted into gaseous carbon monoxide (CO) within the syngas. The goal is to then combust this gas, releasing the carbon back into the atmosphere as CO2 while harnessing its energy.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
To select the correct process, you must first define your primary objective.
- If your primary focus is producing stable biochar for soil amendment or carbon sequestration: Pyrolysis is the only viable choice, as it is specifically designed to create a solid char product.
- If your primary focus is maximizing energy generation (electricity or heat) from biomass: Gasification is generally more efficient and purpose-built for converting solid feedstock into a combustible syngas for power.
- If your primary focus is creating a range of products, including liquid biofuels and specialty chemicals: Pyrolysis offers the unique ability to produce bio-oil alongside char and gas, providing more pathways for valorization.
Ultimately, understanding your end goal is the key to selecting the right thermal process for your needs.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Pyrolysis | Gasification |
|---|---|---|
| Oxygen Environment | Completely absent | Limited, controlled amount |
| Primary Goal | Multi-product creation (Biochar, Bio-oil, Syngas) | Maximize Syngas production for energy |
| Main Product(s) | Solid Biochar (for carbon sequestration/soil) | Combustible Syngas (CO + H₂) |
| Process Type | Deconstruction | Conversion |
| Ideal For | Carbon sequestration, soil amendment, bio-oil | Efficient electricity/heat generation |
Ready to Select the Right Biomass Conversion Technology?
Choosing between pyrolysis and gasification is critical for achieving your specific energy, carbon sequestration, or product goals. The right lab equipment is essential for research, development, and process optimization.
KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, serving the precise needs of laboratories and research facilities. We can provide the reliable tools you need to analyze feedstock, test processes, and scale your biomass conversion projects effectively.
Contact us today using the form below to discuss how our solutions can support your work in renewable energy and sustainable materials. Let's find the right equipment for your lab's challenges.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Graphite Vacuum Continuous Graphitization Furnace
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical High Temperature Graphite Vacuum Graphitization Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why can graphite withstand heat? Unlocking Its Extreme Thermal Stability for Your Lab
- How much temperature can graphite withstand? Unlock its true potential up to 3000°C
- How does graphite react to heat? Unlocking Its Unique High-Temperature Strengths
- At what temperature does graphite thermal decompose? The Critical Role of Atmosphere
- How well does graphite transfer heat? Unlock Superior Thermal Management for Your Electronics



















