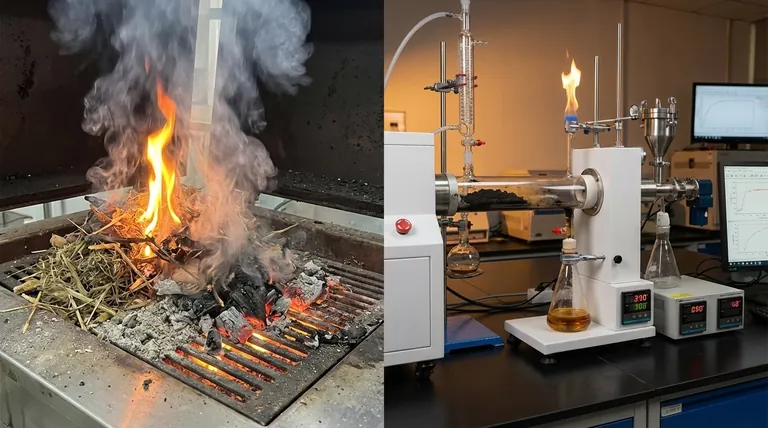
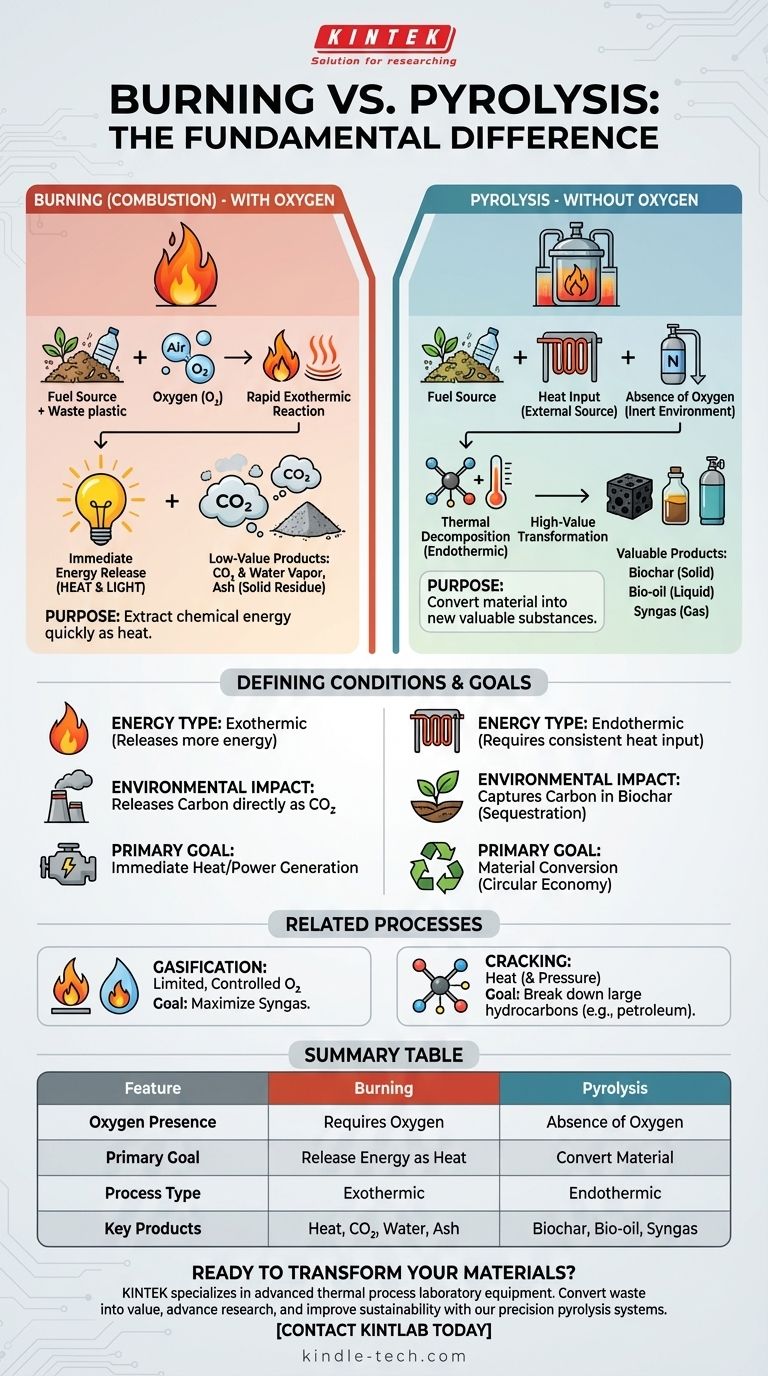
At its core, the difference is oxygen. Burning, or combustion, is a chemical reaction that uses oxygen to rapidly release energy from a material as heat and light. Pyrolysis is a thermal decomposition process that uses heat to break down a material in the complete absence of oxygen, transforming it into new valuable substances instead of simply burning it away.
The fundamental distinction is one of purpose. Burning is an oxidation process designed to release energy, producing low-value ash and gases. Pyrolysis is a decomposition process designed to convert material, producing high-value solids (biochar), liquids (bio-oil), and gases (syngas).

Defining the Core Processes
To understand the practical implications, we must first clearly define the conditions and outputs of each process.
What is Burning (Combustion)?
Combustion is a high-temperature reaction between a fuel source and an oxidant, almost always atmospheric oxygen.
It is an exothermic process, meaning it releases more energy than it consumes, which we experience as a flame.
The primary outputs are typically carbon dioxide (CO2), water vapor, and a solid residue known as ash.
What is Pyrolysis?
Pyrolysis is the thermal breakdown of a material at high temperatures in an inert or oxygen-free environment.
Because there is no oxygen to react with, the material does not burn. Instead, its complex molecules break apart into smaller, often more valuable ones.
This process is primarily endothermic, requiring a consistent external heat source. Its products—biochar (a solid), bio-oil (a liquid), and syngas (a gas)—retain a high energy content.
How Pyrolysis Differs from Related Processes
The term "pyrolysis" is specific and often confused with other thermal treatments. Clarifying these distinctions is key to understanding its unique role.
Pyrolysis vs. Gasification
Gasification involves heating a material with a very limited and controlled amount of oxygen—not enough for full combustion.
It typically operates at higher temperatures than pyrolysis (>700°C) with the primary goal of maximizing the production of synthesis gas (syngas), a mixture of hydrogen and carbon monoxide.
Pyrolysis vs. Cracking
Cracking is a broader term, common in the petroleum industry, for breaking down large hydrocarbon molecules into smaller, more useful ones using heat and often pressure.
Pyrolysis can be considered a specific type of thermal cracking, but it is most often applied to biomass, plastics, or other waste materials, whereas "cracking" is more associated with refining crude oil.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Purpose
The choice between burning and pyrolysis is dictated entirely by the desired outcome. One process destroys material for its energy, while the other transforms it into new feedstocks.
The Goal of Burning: Immediate Energy Release
The sole purpose of combustion is to extract the chemical energy stored in a material as heat as quickly and completely as possible.
This heat can be used directly for industrial processes or to generate electricity. The resulting ash and flue gases are generally considered waste products.
The Goal of Pyrolysis: Material Transformation
The purpose of pyrolysis is to create valuable new products from a low-value feedstock, such as biomass or waste plastic.
Instead of being released as heat, the energy and chemical structure of the original material are preserved in the biochar, bio-oil, and syngas. Each of these can be further refined, used as fuel, or serve as a chemical building block.
The Environmental Equation
Combustion releases carbon directly into the atmosphere as CO2.
Pyrolysis offers a different path. It can capture carbon in the stable, solid form of biochar, which can be used for soil amendment or other applications, effectively sequestering it. This makes it a key technology in circular economy and carbon-capture strategies.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct thermal process depends entirely on what you intend to accomplish with the feedstock.
- If your primary focus is immediate, on-site heat or power generation: Burning is the most direct and established method for releasing energy.
- If your primary focus is creating value-added products from waste or biomass: Pyrolysis is the superior choice for converting feedstock into storable, transportable, and valuable new materials.
- If your primary focus is producing a gaseous fuel for specialized engines or chemical synthesis: Gasification is the optimized process for maximizing syngas yield.
Ultimately, choosing the right thermal process is about deciding whether you want to unlock a material's energy now or convert its structure into new forms of value for the future.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Burning (Combustion) | Pyrolysis |
|---|---|---|
| Oxygen Presence | Requires oxygen | Absence of oxygen |
| Primary Goal | Release energy as heat | Convert material into new products |
| Process Type | Exothermic (releases heat) | Endothermic (requires heat input) |
| Key Products | Heat, CO₂, water vapor, ash | Biochar (solid), bio-oil (liquid), syngas |
Ready to transform your waste materials into valuable resources?
KINTEK specializes in advanced laboratory equipment for thermal processes like pyrolysis. Whether you are researching biomass conversion, developing new materials from waste plastics, or optimizing your lab's capabilities, our solutions are designed for precision, efficiency, and reliability.
We help our customers:
- Convert waste into value: Produce high-value biochar, bio-oil, and syngas.
- Advance research: With precise, controlled pyrolysis systems.
- Improve sustainability: Implement circular economy and carbon-capture strategies in your lab.
Let's discuss how our pyrolysis equipment can meet your specific laboratory needs. Contact KINTLAB today for a consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
- High Temperature Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory Debinding and Pre Sintering
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- What are the process advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for WS2 powder? Achieve Superior Material Crystallinity
- How is a high-temperature calcination furnace utilized in BZY20 Sol-gel? Achieve Pure Cubic Perovskite Phases
- Why are high temperatures required when sintering stainless steels? Unlock Pure, High-Density Results
- What are the equipment requirements for loading platinum (Pt) onto composite supports? Precise Stirring for High Dispersion
- What are the factors affecting the yield of bio-oil from the pyrolysis of coconut shell? Control 4 Key Parameters



















