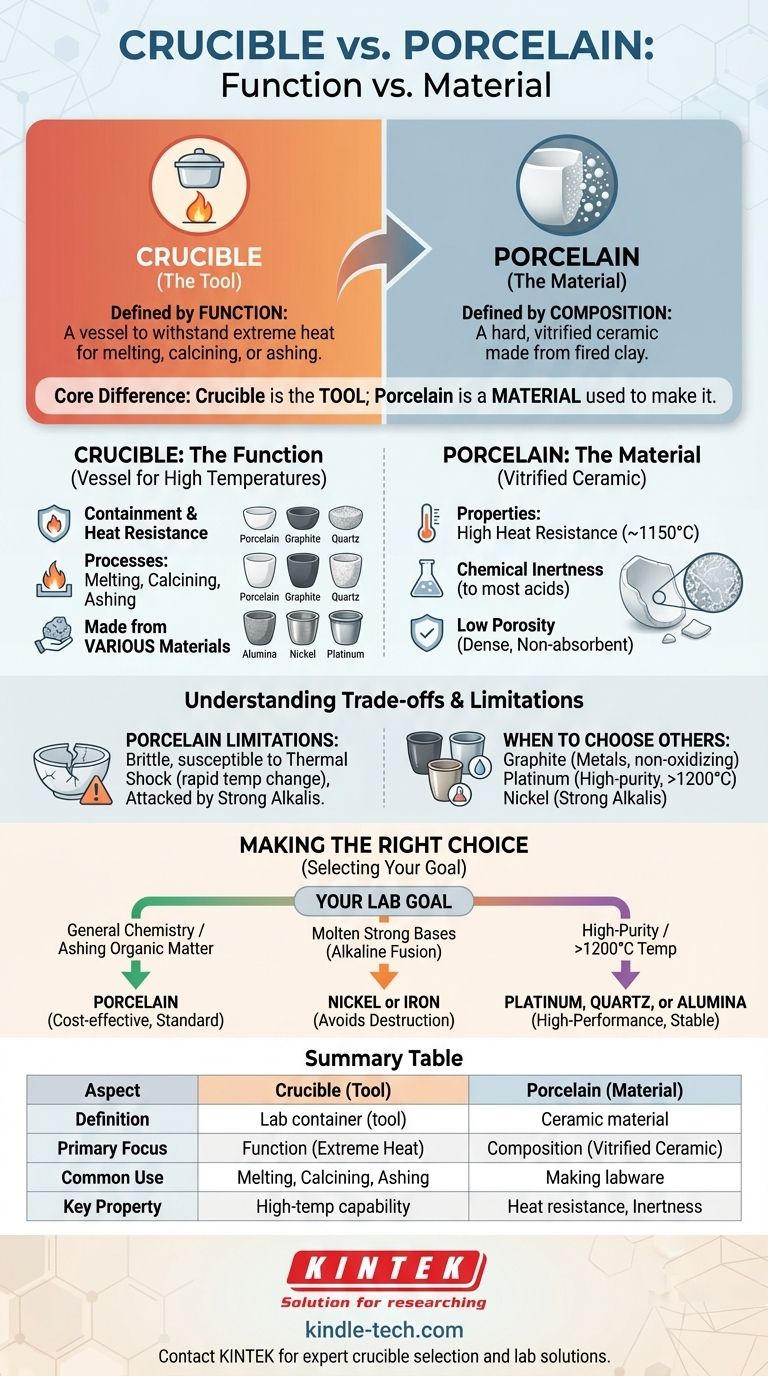
The fundamental difference is that "crucible" and "porcelain" describe different things. A crucible is a type of laboratory container defined by its function—to hold substances for heating to extremely high temperatures. In contrast, porcelain is a type of ceramic material defined by its composition, and it is one of the most common materials used to make a crucible.
The core misunderstanding is comparing a tool to a material. A crucible is the tool; porcelain is a material the tool is often made from. You can have a porcelain crucible, just as you can have a steel hammer.

What is a Crucible? The Function
A crucible is a specific piece of laboratory equipment designed for one primary purpose: withstanding extreme heat.
A Vessel for High Temperatures
A crucible’s job is to contain chemical compounds when they are heated to high temperatures for processes like melting, calcining, or ashing. Its shape, typically a small cup, is designed for stability and easy handling with tongs.
Made from Many Materials
Because different chemical processes require different conditions, crucibles are made from a variety of materials. The choice of material depends entirely on the temperature required and the chemical reactivity of the substance being heated.
Common crucible materials include porcelain, graphite, quartz, alumina, nickel, and even expensive metals like platinum.
What is Porcelain? The Material
Porcelain is not a tool itself, but a material with a specific set of properties that make it highly useful in a laboratory setting.
A Type of Vitrified Ceramic
Porcelain is a hard, dense, and non-porous ceramic. It is made by firing a refined clay mixture (primarily kaolin) at a very high temperature until it becomes vitrified, or glass-like.
Key Properties for Lab Use
Porcelain is an excellent and cost-effective choice for general-purpose crucibles because of its properties:
- High Heat Resistance: It can typically withstand temperatures up to 1150°C (2100°F).
- Chemical Inertness: It is unreactive to most acids and other chemicals, preventing contamination of the sample.
- Low Porosity: Its vitrified surface does not absorb the material being heated.
Understanding the Trade-offs
While porcelain crucibles are common, they are not always the right choice. Understanding their limitations is key to proper lab procedure.
Limitations of Porcelain
Porcelain can be brittle and may crack if subjected to thermal shock—a very rapid change in temperature. It can also be attacked and damaged by strong alkaline substances, such as molten sodium hydroxide.
When to Choose Other Materials
The limitations of porcelain are why other crucible materials exist.
- A graphite crucible is used for melting metals, as it is not "wetted" by molten metals and can handle very high temperatures in non-oxidizing atmospheres.
- A platinum crucible is chosen for tasks requiring extreme chemical inertness and higher temperatures, such as trace metal analysis where sample purity is paramount.
- A nickel crucible is specifically used for fusions with strong alkalis that would destroy a porcelain one.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Selecting the correct crucible requires matching the material's properties to the demands of your specific experiment.
- If your primary focus is general chemistry or ashing organic matter: A standard porcelain crucible is the most common and cost-effective tool for the job.
- If your primary focus is working with molten strong bases (alkaline fusion): You must use a crucible made of nickel or iron to avoid destroying the container.
- If your primary focus is high-purity analysis or work above 1200°C: A crucible made of platinum, quartz, or alumina is necessary to prevent sample contamination and ensure stability.
Ultimately, knowing the difference between a tool's function and its material composition is fundamental to selecting the correct equipment for your work.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Crucible | Porcelain |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A type of lab container (tool) | A type of ceramic material |
| Primary Focus | Function (withstands extreme heat) | Composition (vitrified ceramic) |
| Common Use | Melting, calcining, ashing samples | Material for making crucibles and other labware |
| Key Property | High-temperature capability | Heat resistance, chemical inertness |
Selecting the right crucible is critical for your lab's success. The choice of material—whether porcelain, platinum, graphite, or nickel—directly impacts the accuracy and safety of your high-temperature processes like melting, ashing, or fusion.
At KINTEK, we specialize in providing the precise lab equipment and consumables your laboratory needs. Our experts can help you choose the perfect crucible material for your specific application, ensuring optimal performance and results.
Contact us today to discuss your requirements and let KINTEK equip your lab for success. ➡️ Get in touch now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Crucibles (Al2O3) for Thermal Analysis TGA DTA
- Arc-Shaped Alumina Ceramic Crucible High Temperature Resistant for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible Semicircle Boat with Lid for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics Alumina Al2O3 Crucible With Lid Cylindrical Laboratory Crucible
- Engineering Advanced Fine Alumina Al2O3 Ceramic Crucible for Laboratory Muffle Furnace
People Also Ask
- What temperature can alumina crucible withstand? A Guide to High-Temperature Stability and Safety
- What temperature is an Al2O3 crucible? Key Factors for High-Temperature Success Up to 1700°C
- What is the purpose of using alumina crucibles as liners in autoclaves? Ensure Purity in High-Pressure Static Tests
- What are the advantages of selecting an alumina crucible for TGA? Ensure High-Precision Thermal Analysis Data
- Why are High-purity Alumina Crucibles selected for corrosion testing? Ensure Data Fidelity in Molten Salt Experiments



















