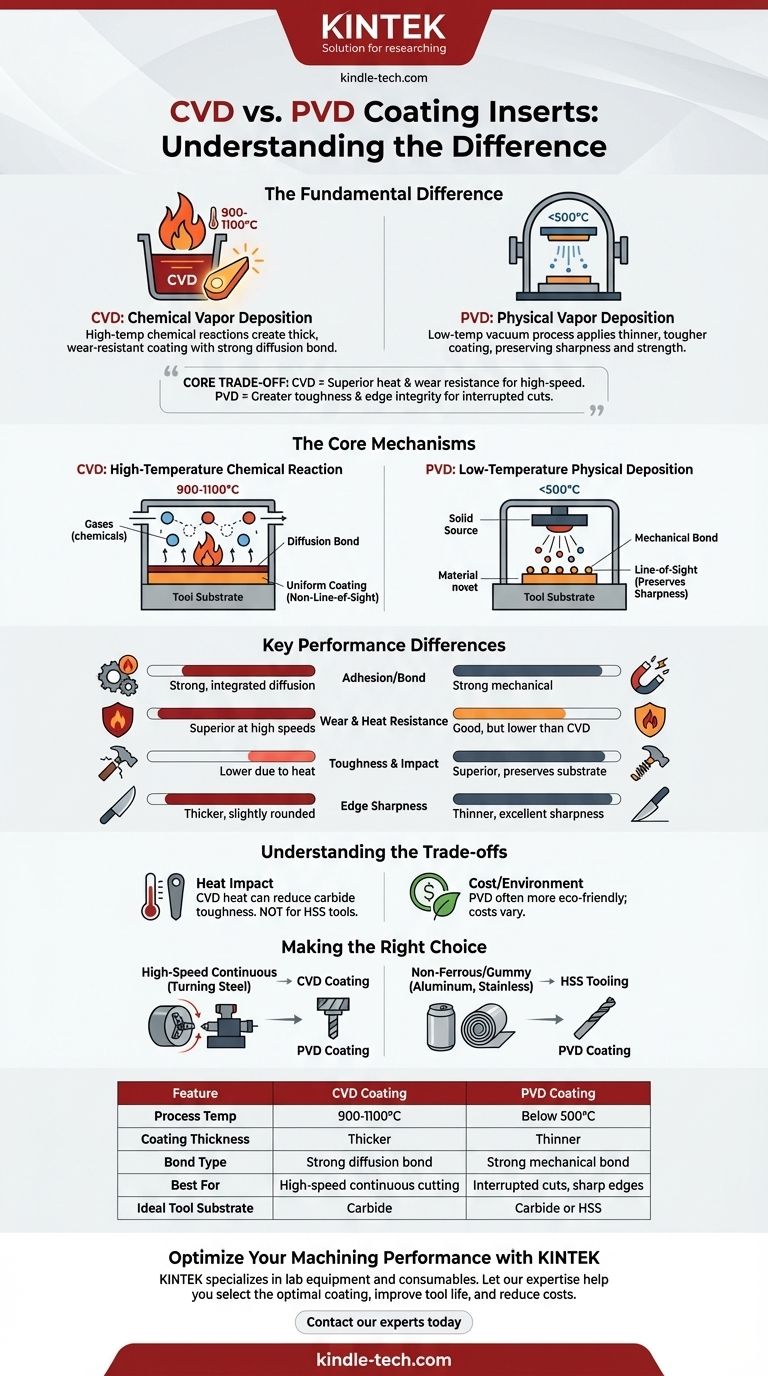
The fundamental difference between CVD and PVD coatings lies in their application process and resulting properties. Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) uses high temperatures and chemical reactions to create a thick, wear-resistant coating with a very strong chemical bond to the tool. Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) uses lower temperatures in a vacuum to apply a thinner, tougher coating that better preserves the tool's original sharpness and strength.
The core trade-off is simple: CVD provides superior heat and wear resistance for high-speed, continuous cutting, while PVD offers greater toughness and edge integrity for interrupted cuts and applications where tool sharpness is critical.
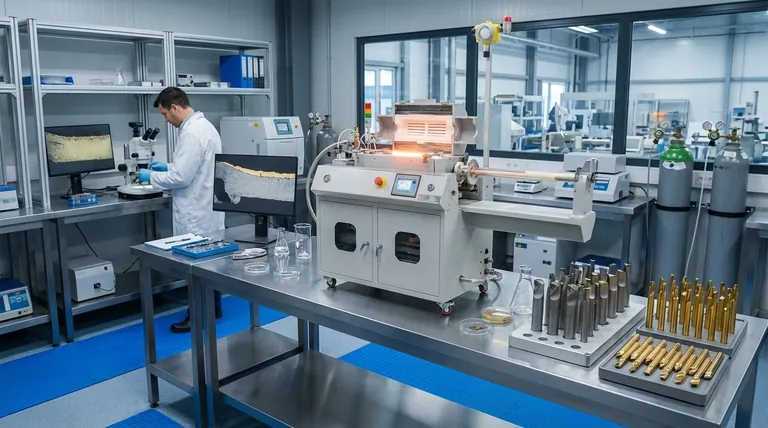

The Core Mechanisms: How They Work
To understand which coating to choose, you must first understand how each is applied. The process directly dictates the final performance of the cutting insert.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD)
CVD is a high-temperature process, typically running between 900-1100°C. Gaseous chemicals react within a chamber, causing a new material layer to form and diffuse into the surface of the tool substrate.
This creates an exceptionally strong, intermingled diffusion bond between the coating and the insert. Because it's a chemical reaction involving gases, CVD is not a "line-of-sight" process, resulting in a very uniform coating, even on complex shapes.
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD)
PVD is a lower-temperature process, generally operating below 500°C within a high-vacuum environment. A solid source material (like titanium) is vaporized, and the resulting atoms or molecules are physically deposited onto the tool's surface.
This process creates a strong mechanical bond but lacks the deep diffusion of CVD. PVD is a line-of-sight process, which results in thinner coatings that are excellent at preserving the fine details of a sharp cutting edge.
Key Performance Differences Explained
The differences in the application process lead to distinct advantages and disadvantages in a real-world machining environment.
Adhesion and Bond Strength
CVD's high-temperature diffusion process creates a fundamentally stronger bond with the substrate. This makes it highly resistant to delamination under extreme thermal loads.
Wear and Heat Resistance
CVD coatings, particularly those using Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3), offer exceptional chemical stability and hardness at high temperatures. This makes them ideal for high-speed cutting applications that generate significant heat, such as turning steel.
Toughness and Impact Resistance
PVD is the clear winner here. The lower process temperature does not degrade the inherent toughness of the carbide substrate. The thinner PVD layers also have lower internal stresses, making them less prone to micro-cracking during interrupted cuts like milling.
Edge Sharpness and Finish
PVD's thinner application preserves the original sharpness of the ground cutting edge. This is critical for machining gummy materials like aluminum or for finishing operations where a clean cut is paramount. CVD's thicker coating can slightly round the edge.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between CVD and PVD is a matter of balancing competing priorities. There is no single "best" coating for all situations.
The Impact of Heat on the Substrate
This is the most critical trade-off. The extreme heat of the CVD process can reduce the toughness of the underlying carbide. For tools made of High-Speed Steel (HSS), CVD is not an option as the heat would ruin the tool's temper and cause it to distort.
Coating Material Options
Historically, CVD has been superior for applying highly stable Al2O3 coatings. However, modern PVD technology has expanded its range of materials (such as TiN and TiAlN) and is continuously improving its performance, closing the gap in many areas.
Cost and Environmental Impact
While costs vary, PVD processes are often considered more environmentally friendly as they do not produce the same hazardous chemical byproducts as some CVD processes.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should always be based on the specific demands of your machining operation.
- If your primary focus is high-speed, continuous cutting (e.g., turning steel): Choose a CVD-coated insert for its superior heat and flank wear resistance.
- If your primary focus is interrupted cutting (e.g., milling, drilling): Choose a PVD-coated insert for its superior toughness and resistance to chipping.
- If your primary focus is machining non-ferrous or sticky materials (e.g., aluminum, stainless steel): Choose a PVD-coated insert to maintain a sharper cutting edge and reduce built-up edge.
- If you are using HSS tooling: You must use PVD, as its low process temperature will not damage the tool.
Ultimately, selecting the correct coating technology is about matching the tool's properties to the specific challenges of the material and the cut.
Summary Table:
| Feature | CVD Coating | PVD Coating |
|---|---|---|
| Process Temperature | 900-1100°C | Below 500°C |
| Coating Thickness | Thicker | Thinner |
| Bond Type | Strong diffusion bond | Strong mechanical bond |
| Best For | High-speed continuous cutting (e.g., turning steel) | Interrupted cuts, sharp edges (e.g., milling, aluminum) |
| Ideal Tool Substrate | Carbide | Carbide or High-Speed Steel (HSS) |
Optimize Your Machining Performance with the Right Coating Solution
Choosing between CVD and PVD coatings is critical for maximizing tool life, productivity, and part quality. The wrong choice can lead to premature tool failure, poor surface finishes, and increased downtime.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our expertise in material science and cutting tool technology can help you:
- Select the optimal coating for your specific material and machining operation
- Improve tool life and efficiency with the right coating technology
- Reduce machining costs by minimizing tool changes and downtime
Don't leave your machining performance to chance. Contact our experts today for a personalized consultation on the best coating solution for your application. Let us help you achieve superior results and maximize your return on investment.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Cylindrical Resonator MPCVD Machine System Reactor for Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition and Lab Diamond Growth
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Precision Wire Saw Laboratory Cutting Machine with 800mm x 800mm Workbench for Diamond Single Wire Circular Small Cutting
People Also Ask
- How does chirality affect carbon nanotubes? It Determines If They Are Metal or Semiconductor
- How do nanotubes affect the environment? Balancing Low Carbon Footprint with Ecological Risks
- What are the challenges of carbon nanotubes? Overcoming Production and Integration Hurdles
- What is a CVD tube furnace? A Complete Guide to Thin-Film Deposition
- How high of temperature do carbon nanotubes in air have the ability to sustain? Understanding the Oxidation Limit



















