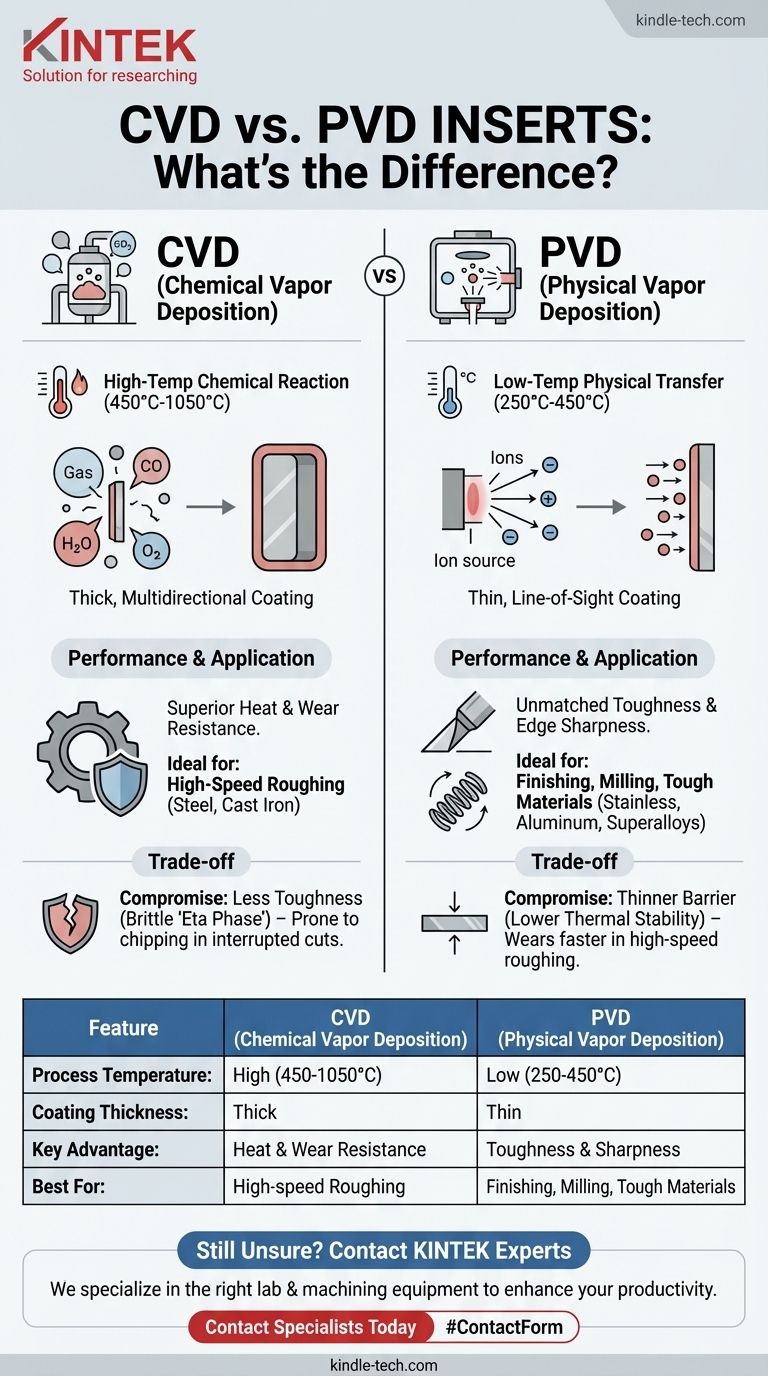
The fundamental difference between CVD and PVD inserts is how the protective coating is applied. Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) uses a high-temperature chemical reaction between gases to grow a thick, heat-resistant coating on the insert. Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD), in contrast, uses a lower-temperature physical process in a vacuum to deposit a thin, smooth, and tough coating.
The choice is not about which process is better, but which is right for the job. The high-temperature CVD process creates coatings ideal for high-speed, high-wear applications, while the low-temperature PVD process excels at creating sharp, tough edges for finishing and machining difficult materials.

The Fundamental Process Distinction
To understand why these inserts perform differently, you must first understand the core mechanics of each coating process. The temperature and method of deposition directly dictate the final properties of the cutting edge.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): A High-Temperature Reaction
CVD involves placing carbide inserts into a reactor heated to very high temperatures, often between 450°C and 1050°C.
Precursor gases are introduced into the chamber, which then react with each other and the surface of the insert. This chemical reaction forms a new, solid coating layer that is chemically bonded to the substrate.
Because the deposition happens through a gas that surrounds the entire insert, the coating is multidirectional and very uniform.
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD): A Low-Temperature Transfer
PVD is a physical process, not a chemical one. It takes place in a vacuum chamber at much lower temperatures, typically between 250°C and 450°C.
A solid source material (like titanium) is vaporized by physical means, such as being struck by ions. This vaporized material then travels in a direct line-of-sight and condenses onto the inserts, forming the coating.
This method is more like spray-painting on an atomic level, where atoms are physically transferred from a source to the target.
How Process Dictates Performance
The significant differences in temperature and deposition method result in coatings with distinct advantages and disadvantages for machining.
CVD Coatings: Superior Heat and Wear Resistance
The high temperatures of the CVD process create coatings that are exceptionally thick and chemically stable.
This thickness provides an excellent thermal barrier, protecting the carbide substrate from the extreme heat generated during high-speed cutting. This makes CVD inserts highly resistant to crater wear, a common failure mode in steel turning.
PVD Coatings: Unmatched Toughness and Edge Sharpness
The low-temperature PVD process is critical because it does not alter the underlying structure of the carbide substrate. This preserves the substrate's inherent toughness.
PVD coatings are also much thinner and smoother than CVD coatings. This allows for the creation of a much sharper cutting edge, which is crucial for reducing friction and preventing built-up edge (BUE) when machining "gummy" materials like aluminum or stainless steel.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither coating is universally superior; each comes with a compromise that makes it suitable for different tasks.
The CVD Compromise: Toughness for Heat Resistance
The extreme heat of the CVD process can cause a slight reduction in the substrate's toughness. It can form a brittle layer known as the "eta phase" at the interface between the coating and the carbide.
This makes traditional CVD-coated inserts slightly more prone to chipping or cracking in applications with intermittent cuts, such as milling.
The PVD Compromise: Sharpness for Wear Resistance
While PVD coatings are exceptionally tough, they are also thinner. They provide less of an insulating barrier and have lower overall thermal stability compared to thick CVD coatings.
In high-speed, continuous roughing operations, a PVD coating will typically wear out faster than a CVD coating designed for that purpose.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct insert coating is a matter of aligning its properties with the demands of your specific machining operation.
- If your primary focus is high-speed roughing of steel or cast iron: Choose a CVD-coated insert for its superior heat and crater wear resistance in continuous cuts.
- If your primary focus is finishing or threading: Choose a PVD-coated insert for its sharp edge, which produces a better surface finish and lower cutting forces.
- If your primary focus is milling or interrupted cutting: Choose a PVD-coated insert for its superior toughness and resistance to chipping on impact.
- If your primary focus is machining stainless steel, superalloys, or aluminum: Choose a PVD-coated insert for its lubricity and sharp edge, which minimizes material build-up.
Understanding the underlying process is the key to matching the right insert coating to your specific machining challenge.
Summary Table:
| Feature | CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) | PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) |
|---|---|---|
| Process Temperature | High (450°C - 1050°C) | Low (250°C - 450°C) |
| Coating Thickness | Thick | Thin |
| Key Advantage | Superior heat & wear resistance | Superior toughness & edge sharpness |
| Best For | High-speed roughing of steel/cast iron | Finishing, milling, tough materials (e.g., stainless steel) |
Still unsure which insert coating is right for your specific application? The experts at KINTEK are here to help. We specialize in providing the right lab and machining equipment, including cutting tools, to enhance your productivity and results.
Contact our specialists today for a personalized consultation and let us help you select the perfect tooling solution for your needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- CVD Diamond Domes for Industrial and Scientific Applications
- CVD Diamond Dressing Tools for Precision Applications
- Precision Wire Saw Laboratory Cutting Machine with 800mm x 800mm Workbench for Diamond Single Wire Circular Small Cutting
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
- Vacuum Cold Mounting Machine for Sample Preparation
People Also Ask
- What is the application of diamond coating? Solve Complex Wear, Heat, and Corrosion Problems
- What is the use of CVD diamond? Unlock Superior Performance in Extreme Applications
- How much does CVD diamond equipment cost? A Breakdown of Investment from Lab to Production
- What is the hardness of CVD diamond? The Ultimate Guide to Engineered Super-Materials
- How thick is diamond coating? Achieve Unprecedented Precision with Ultra-Thin Films



















