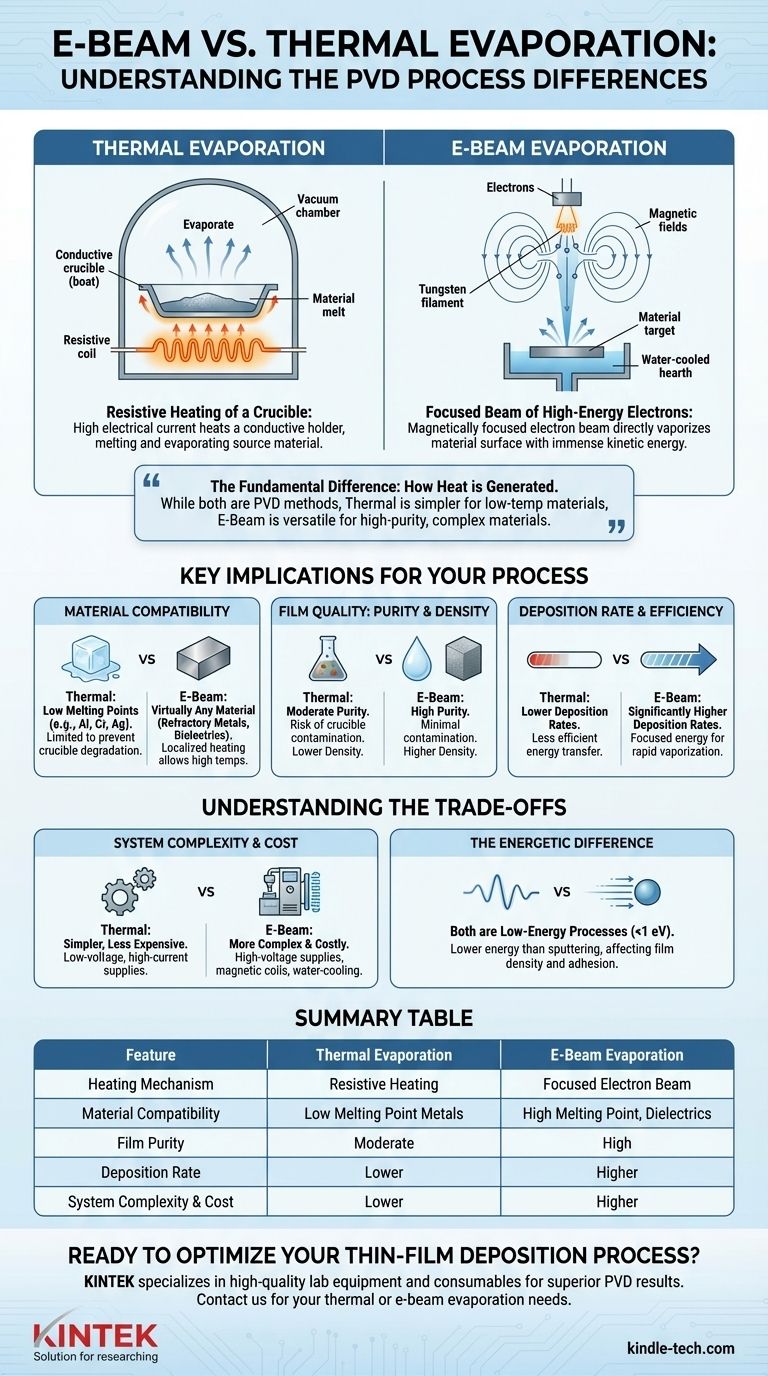
At its core, the difference between e-beam and thermal evaporation is how the source material is heated to a vapor. Thermal evaporation uses resistive heating to warm a crucible containing the material, much like a stovetop element. In contrast, e-beam evaporation uses a magnetically focused beam of high-energy electrons to directly vaporize the surface of the material itself.
While both are methods of physical vapor deposition (PVD), the choice is not arbitrary. Thermal evaporation is a simpler method for low-temperature materials, whereas e-beam evaporation is a more complex but versatile technique that delivers higher purity films and can handle nearly any material.
The Fundamental Difference: How Heat is Generated
To understand the practical implications, you must first grasp the two distinct heating mechanisms.
Thermal Evaporation: Resistive Heating of a Crucible
In thermal evaporation, a high electrical current is passed through a conductive holder, often called a "boat" or crucible, which is typically made of tungsten or molybdenum.
This boat heats up due to its own electrical resistance. The source material placed inside the boat absorbs this heat, eventually melting and then evaporating into the vacuum chamber.
E-Beam Evaporation: A Focused Beam of High-Energy Electrons
E-beam evaporation starts with a hot tungsten filament that emits a stream of electrons.
These electrons are accelerated by a high voltage and then precisely guided by magnetic fields to strike the source material. The immense kinetic energy of the electrons is instantly converted into thermal energy upon impact, causing a small spot on the material's surface to vaporize or sublimate directly.
Key Implications for Your Process
The difference in heating method directly impacts material choice, film quality, and process efficiency.
Material Compatibility: The Deciding Factor
Thermal evaporation is limited to materials with relatively low melting points, such as aluminum, chromium, or silver. Attempting to evaporate high-temperature materials would require so much heat that the crucible itself would melt or degrade.
E-beam evaporation excels here. It can evaporate virtually any material, including refractory metals (platinum, tungsten) and dielectrics (silicon dioxide, titanium oxide). This is possible because the heat is highly localized, and the crucible (or hearth) is actively water-cooled to prevent it from melting.
Film Quality: Purity and Density
E-beam evaporation generally produces purer films. Since only the source material is directly heated, there is minimal risk of the crucible material co-evaporating and contaminating the growing film.
In thermal evaporation, the entire boat becomes extremely hot, increasing the chance of impurities from the boat entering the vapor stream. Films deposited by e-beam are also typically denser than those from thermal evaporation.
Deposition Rate and Efficiency
E-beam evaporation offers significantly higher deposition rates. The focused energy transfer is an extremely efficient method for creating vapor.
This allows for thicker films to be deposited in a shorter amount of time, improving throughput for many industrial and research applications.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a method involves weighing complexity, performance, and the inherent physics of the process.
System Complexity and Cost
Thermal evaporation systems are mechanically simpler and generally less expensive. They consist primarily of a low-voltage, high-current power supply and resistive sources.
E-beam systems are more complex and costly. They require high-voltage power supplies, magnetic coils for beam steering, and a robust water-cooling infrastructure to manage the intense, localized heat.
The Energetic Difference
It is crucial to understand that both thermal and e-beam are low-energy deposition processes. The evaporated atoms travel to the substrate with thermal energies typically below 1 electron volt (eV).
This distinguishes them from a process like sputtering, where atoms are ejected with much higher kinetic energy (tens of eV). This higher energy results in even denser and more adherent films but can also introduce more internal stress.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Choosing the correct method depends entirely on your material requirements and desired film properties.
- If your primary focus is simplicity and depositing low-melting-point metals: Thermal evaporation is the most straightforward and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is high purity, refractory materials, or dielectrics: E-beam evaporation is the superior and often necessary choice for performance and versatility.
- If your primary focus is maximum film density and adhesion: You should investigate sputtering, as the higher particle energy offers distinct advantages over either evaporation method.
Ultimately, understanding these fundamental differences empowers you to select the precise tool needed to achieve your specific thin-film deposition goal.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Thermal Evaporation | E-Beam Evaporation |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Mechanism | Resistive heating of a crucible | Focused beam of high-energy electrons |
| Material Compatibility | Low melting point metals (Al, Ag, Cr) | High melting point materials (refractory metals, dielectrics) |
| Film Purity | Moderate (risk of crucible contamination) | High (minimal contamination) |
| Deposition Rate | Lower | Higher |
| System Complexity & Cost | Lower | Higher |
Ready to Optimize Your Thin-Film Deposition Process?
Choosing between e-beam and thermal evaporation is critical for achieving your desired film properties. KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables, providing the precise tools you need for superior PVD results.
Whether you require the simplicity of thermal evaporation for low-temperature metals or the high-purity capabilities of e-beam evaporation for refractory materials, we have the expertise and solutions to support your laboratory's unique requirements.
Contact KINTEK today to discuss your specific application and discover how our reliable equipment can enhance your research or production outcomes!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electron Beam Evaporation Coating Conductive Boron Nitride Crucible BN Crucible
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
- E Beam Crucibles Electron Gun Beam Crucible for Evaporation
People Also Ask
- What is thermal evaporation deposition techniques? A Simple Guide to Thin Film Coating
- What is the purpose of vacuum evaporation? Purify Water or Create High-Purity Coatings
- What materials are used in thermal evaporation? From Metals to Dielectrics for Thin-Film Coating
- What is the process of thermal evaporation thin film deposition? A Guide to Simple, Cost-Effective PVD
- Why is sputtering deposition much slower than evaporation deposition? The Trade-Off Between Speed and Quality
- What are the advantages of evaporation deposition? Achieve High-Purity Thin Films for Your Lab
- How is the thickness of a deposited film measured? Master Optical Interference Techniques
- What are the advantages of thermal evaporation method? Achieve Simple, Fast, and Cost-Effective Thin Films



















