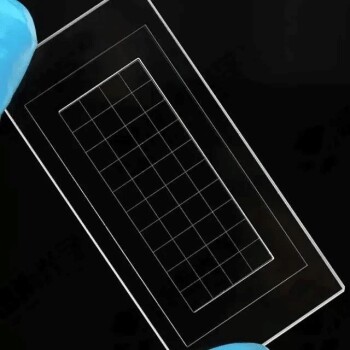
At its core, an electrolyte is the medium that allows ions to move, while an electrode is the physical conductor where the chemical reaction and electron transfer actually occur. The electrolyte is the "highway" for charged ions inside the cell, and the electrodes are the "on-ramps and off-ramps" connecting that highway to the external electrical circuit.
In any electrochemical cell, electrodes are the solid conductors where chemical reactions happen, either releasing or consuming electrons. The electrolyte is the necessary liquid or gel medium that transports ions between these electrodes, completing the electrical circuit.
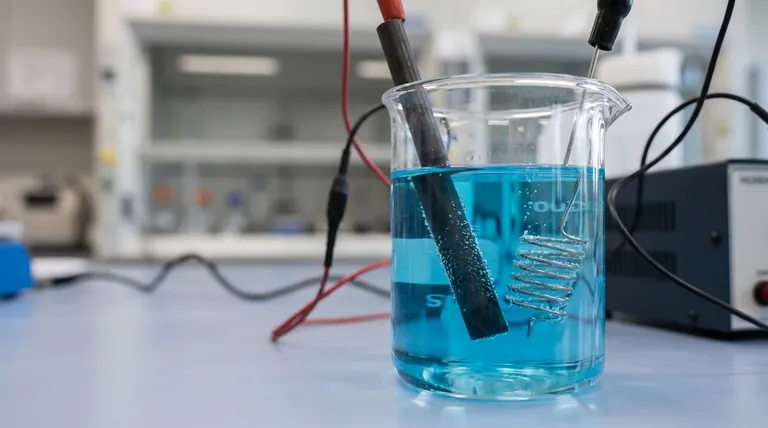

The Role of the Electrode: The Reaction Site
An electrode acts as the physical interface between the chemical components inside a cell and the external electronic circuit.
What an Electrode Is
An electrode is a solid electrical conductor, typically a metal or carbon, placed into the electrolyte. Its job is to transfer electrons to or from the species in the solution.
Directing Electron Flow
Electrons cannot travel through the electrolyte. Instead, they flow into or out of the cell through the electrodes and the connected external wire.
Anode vs. Cathode
All cells have two types of electrodes defined by the reaction that occurs on their surface:
- The anode is where oxidation happens (a substance loses electrons).
- The cathode is where reduction happens (a substance gains electrons).
The Role of the Electrolyte: The Ion Highway
The electrolyte is just as crucial as the electrodes. Without it, the circuit is incomplete, and no current can flow.
What an Electrolyte Is
An electrolyte is a substance, typically a solution containing salts, acids, or bases, that produces an electrically conducting solution when dissolved. It contains mobile, charged ions.
Maintaining Charge Neutrality
As electrons are released at the anode and consumed at the cathode, a charge imbalance would quickly build up and stop the reaction. The electrolyte prevents this by allowing its ions to migrate between the electrodes, neutralizing the charge and allowing the process to continue.
How They Interact in Different Cells
The specific charge of the anode and cathode depends on whether the cell is generating or consuming electricity.
In Galvanic (Voltaic) Cells
These cells, like common batteries, convert chemical energy into electrical energy through a spontaneous reaction.
- The anode is negative, as it is the source of electrons for the external circuit.
- The cathode is positive, as it is where electrons return to the cell.
In Electrolytic Cells
These cells use external electrical energy to drive a non-spontaneous reaction, such as in electroplating or water splitting.
- The anode is positive, as it is connected to the positive terminal of the external power source to pull electrons away.
- The cathode is negative, as it is connected to the negative terminal to force electrons onto it.
Common Pitfalls and Nuances
Understanding the basic definitions is the first step. Recognizing the nuances is what leads to true comprehension.
Electrode Material Is Critical
The electrode is not always just an inert conductor. In many batteries, the electrode material itself is an active participant in the chemical reaction, such as the zinc casing of an alkaline battery acting as the anode.
Functional Electrode Types
In analytical chemistry and sensor applications, electrodes are given more specific names based on their function.
- A working electrode is where the chemical reaction of interest occurs.
- A reference electrode provides a stable, constant potential to measure against.
- A counter electrode completes the circuit, passing current to the working electrode.
Making the Right Distinction for Your Goal
To apply this knowledge, focus on the fundamental role each component plays within your specific context.
- If your primary focus is basic battery science: See the electrode as the site of electron gain/loss (anode/cathode) and the electrolyte as the essential ion mover that keeps the battery running.
- If your primary focus is performing electrolysis: Remember that the polarity (+/-) of the electrodes is reversed from a battery, but their fundamental chemical roles (anode=oxidation, cathode=reduction) remain exactly the same.
- If your primary focus is building electrochemical sensors: You must distinguish between the working electrode (where the event happens), the reference electrode (for a stable measurement), and the counter electrode (to complete the circuit).
Ultimately, the electrode and electrolyte are two distinct but inseparable components that form the foundation of all electrochemical technology.
Summary Table:
| Component | Role in an Electrochemical Cell | Analogy |
|---|---|---|
| Electrode | Solid conductor where electron transfer (oxidation/reduction) occurs. | On/off ramps for electrons to the external circuit. |
| Electrolyte | Medium (liquid/gel) that allows ion movement to maintain charge balance. | Highway for charged ions inside the cell. |
| Anode | Electrode where oxidation (loss of electrons) occurs. | Electron source (Galvanic) or electron sink (Electrolytic). |
| Cathode | Electrode where reduction (gain of electrons) occurs. | Electron destination (Galvanic) or electron source (Electrolytic). |
Ready to Power Your Research with Precision Electrochemical Equipment?
Understanding the fundamentals is the first step. Applying them with the right tools is what drives discovery. Whether you are developing new battery materials, performing precise electrolysis, or building sensitive sensors, KINTEK provides the high-quality lab equipment and consumables you need.
We specialize in serving the precise needs of laboratories. Let us help you select the perfect electrochemical cells, electrodes, and electrolytes to ensure accurate and reliable results for your specific application.
Contact KINTEL today to discuss your project requirements and discover how our solutions can enhance your lab's capabilities!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Coating Evaluation
- H-Type Double-Layer Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Water Bath
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Five-Port
- Quartz Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell for Electrochemical Experiments
- Customizable Swagelok Type Test Cells for Advanced Battery Research Electrochemical Analysis
People Also Ask
- What is the volume range of the coating evaluation electrolytic cell? A Guide to Choosing the Right Size
- What role does a water-jacketed electrolytic cell play in variable-temperature electrochemical corrosion measurements?
- How is a high-precision electrolytic cell used to evaluate metal corrosion resistance? Validate DCT Results Accurately
- What are the advantages of a flat electrochemical cell for corrosion? Achieve Precise Pitting & Crevice Analysis
- What is the difference between electrolytic corrosion cell and electrochemical corrosion cell? Understand the Driving Force Behind Corrosion