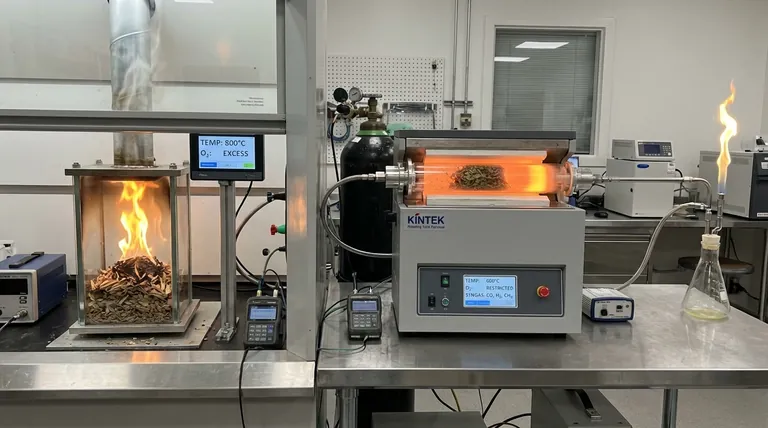
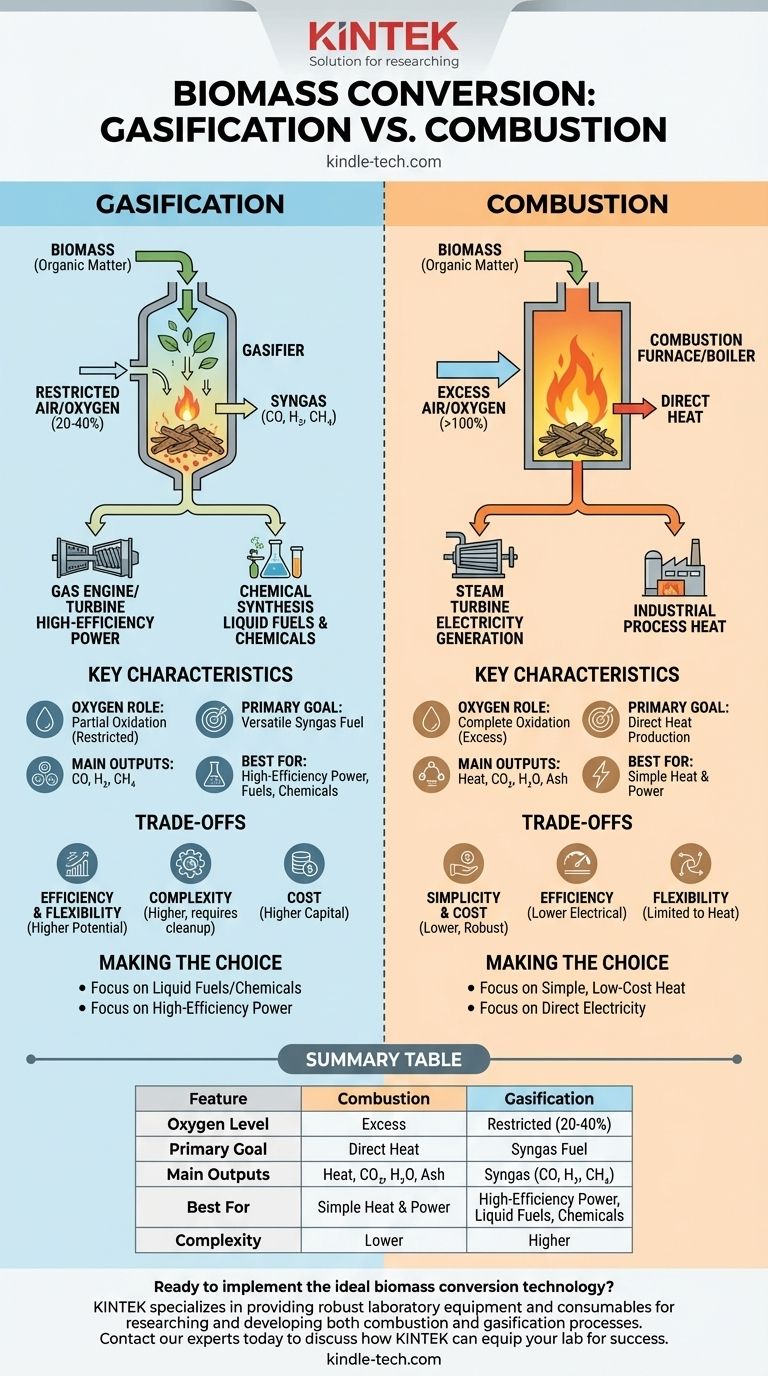
In simple terms, combustion completely burns biomass with excess oxygen to release heat, while gasification intentionally "starves" the biomass of oxygen to convert it into a combustible gas fuel. Combustion is a direct process for producing thermal energy, whereas gasification is a transformation process to create a more versatile energy carrier.
The fundamental choice between these two technologies is not about which is "better," but about your end goal. Combustion is a simple path to heat, while gasification is a more complex but flexible path to a fuel that can be used for power, chemicals, or liquids.

The Fundamental Difference: The Role of Oxygen
The core distinction between these two thermochemical processes comes down to the amount of oxygen supplied and the resulting chemical reaction.
Combustion: Complete Oxidation
In combustion, biomass is reacted with more oxygen than is stoichiometrically required to ensure it burns completely.
The primary goal is the full oxidation of the carbon and hydrogen in the biomass. This reaction is highly exothermic, releasing the maximum amount of energy directly as heat.
Gasification: Partial Oxidation
Gasification uses a restricted amount of an oxidizing agent (air, pure oxygen, steam, or a combination). This is typically only 20-40% of the oxygen needed for complete combustion.
This controlled environment prevents full burning. Instead, it provides just enough energy to break down the complex biomass molecules into a mixture of simpler, combustible gases known as synthesis gas or syngas.
Key Chemical Outputs
The difference in process chemistry leads to vastly different outputs.
Combustion primarily produces inert gases like carbon dioxide (CO2) and water (H2O), along with ash and heat.
Gasification produces a fuel, syngas, which is rich in carbon monoxide (CO), hydrogen (H2), and some methane (CH4). This gas retains a significant portion of the biomass's original chemical energy.
Comparing the End Products and Applications
Because their outputs are so different, combustion and gasification serve very different purposes.
Combustion's Goal: Direct Heat and Power
Combustion is a one-step process for thermal energy. This heat is typically used to boil water, creating high-pressure steam that drives a turbine to generate electricity or is used directly for industrial process heat.
This is a mature, straightforward technology widely used in biomass power plants around the world.
Gasification's Goal: A Versatile Fuel (Syngas)
Gasification creates an intermediate product—syngas—that opens up multiple application pathways.
The syngas can be burned in highly efficient gas engines or gas turbines for power generation. More importantly, it can serve as a chemical feedstock to produce liquid fuels (like synthetic diesel or ethanol) or valuable chemicals (like methanol or ammonia).
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing between these technologies involves a clear set of trade-offs in complexity, cost, and efficiency.
Simplicity and Cost (Advantage: Combustion)
Combustion systems are technologically simpler, more robust, and generally have a lower capital cost. The technology is well-established, making it a lower-risk and more direct option for heat and power.
Efficiency and Flexibility (Advantage: Gasification)
While more complex, gasification can lead to higher overall electrical efficiencies, especially when integrated with a combined-cycle gas turbine (IGCC).
Its true advantage is flexibility. Gasification allows biomass to be converted into high-value products beyond simple heat, acting as a bridge to the liquid fuels and chemical industries.
Operational Complexity and Purity
Gasification is a more sensitive process that requires careful control of temperature, pressure, and feedstock. A major challenge is syngas cleanup.
The raw syngas contains impurities like tars, particulates, and sulfur compounds that must be removed before use in engines or chemical synthesis, adding significant cost and complexity to the system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The optimal technology is defined entirely by your objective.
- If your primary focus is simple, low-cost heat or electricity: Combustion is the more direct, mature, and cost-effective pathway.
- If your primary focus is high-efficiency power generation from biomass: Gasification, coupled with a gas engine or combined-cycle system, offers a higher potential efficiency ceiling.
- If your primary focus is producing liquid fuels, hydrogen, or chemicals: Gasification is the only viable option of the two, as it creates the necessary chemical building blocks.
Ultimately, your choice depends on whether your biomass resource is better suited for a simple furnace or a sophisticated chemical refinery.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Combustion | Gasification |
|---|---|---|
| Oxygen Level | Excess | Restricted (20-40% of requirement) |
| Primary Goal | Direct Heat Production | Production of Syngas Fuel |
| Main Outputs | Heat, CO₂, H₂O, Ash | Syngas (CO, H₂, CH₄) |
| Best For | Simple Heat & Power | High-Efficiency Power, Liquid Fuels, Chemicals |
| Complexity | Lower | Higher |
Ready to implement the ideal biomass conversion technology for your project?
KINTEK specializes in providing robust laboratory equipment and consumables for researching and developing both combustion and gasification processes. Whether you are optimizing thermal efficiency or analyzing syngas composition, our solutions support your innovation in renewable energy.
Contact our experts today to discuss how KINTEK can equip your lab for success.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Vacuum Tilt Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- How are composites processed using sintering? Engineered Material Solutions Through Advanced Thermal Bonding
- How are tube furnaces classified based on the orientation of the tube? Choose the Right Design for Your Process
- What is the temperature of a rotary hearth furnace? Find the Right Heat for Your Process
- What are the process advantages of using a rotary tube furnace for WS2 powder? Achieve Superior Material Crystallinity
- What is the process of zirconium production? From Ore to High-Performance Metal & Ceramic



















