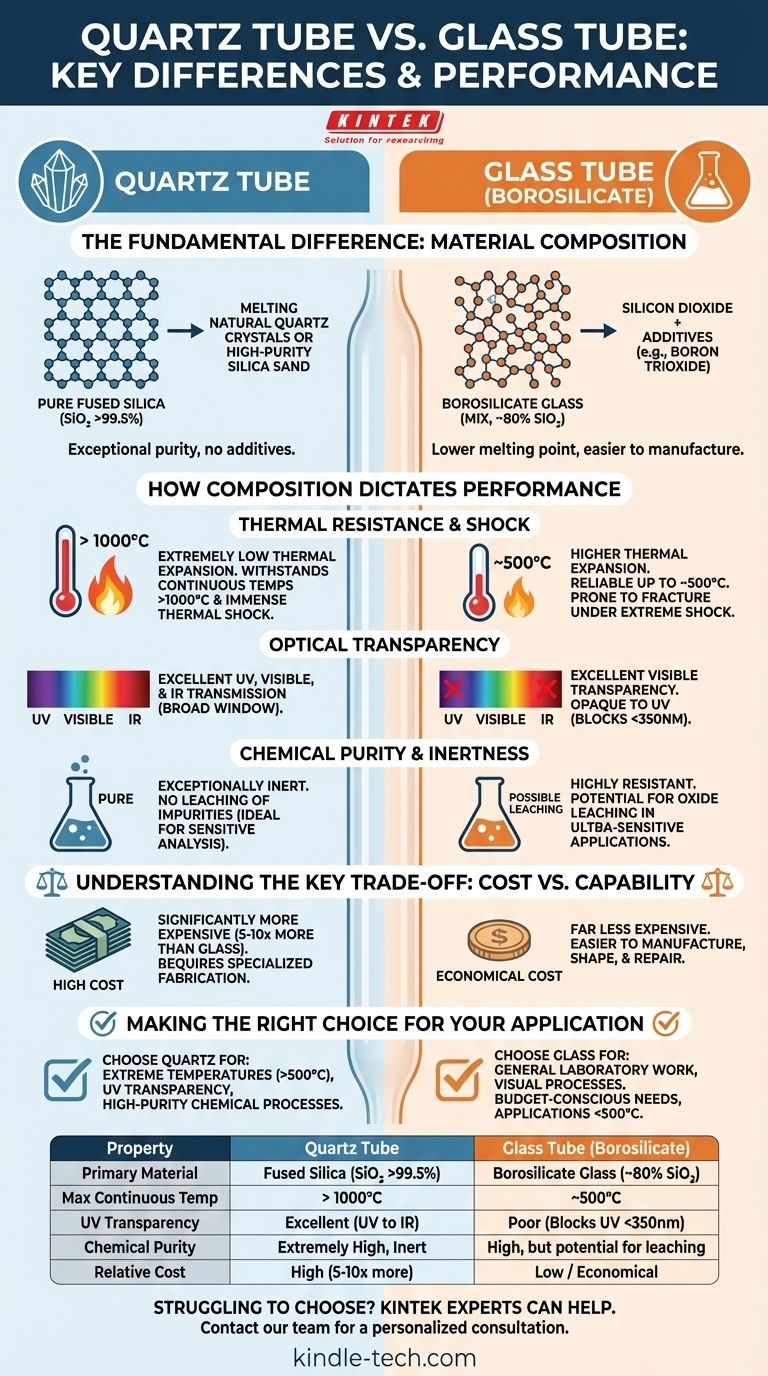
In short, a quartz tube is made of high-purity silicon dioxide, while a glass tube is made from silicon dioxide mixed with other oxides. This fundamental difference in chemical composition is the source of their vastly different properties, particularly in thermal resistance and optical transparency. Quartz is a specialized, high-performance material, while glass is a versatile and economical one.
The choice between a glass tube and a quartz tube is not about which is universally "better," but which is appropriate for the task. Your decision hinges on three key factors: the operating temperature, the need for ultraviolet (UV) light transmission, and your budget.

The Fundamental Difference: Material Composition
The distinct behaviors of glass and quartz originate from what they are made of at a molecular level. One is a pure element compound, the other is a calculated mixture.
Quartz: The Purity Benchmark
A quartz tube is not made from crystalline quartz but from fused quartz or fused silica. This material is produced by melting natural quartz crystals or high-purity silica sand at extremely high temperatures.
The result is a material that is almost entirely pure silicon dioxide (SiO₂), often exceeding 99.5% purity. This lack of additives gives quartz its exceptional and extreme performance characteristics.
Glass: A Practical & Modified Formula
Technical glass tubes are typically made from borosilicate glass (familiar from brands like PYREX® or Duran®). While its primary component is still silicon dioxide (around 80%), it is intentionally mixed with other chemicals.
Additives like boron trioxide are introduced to lower the melting temperature and soften the material. This makes glass far easier and less expensive to manufacture, shape, and repair compared to pure quartz.
How Composition Dictates Performance
The purity of quartz and the blended nature of glass create clear performance divides. Understanding these is key to selecting the right material for your application.
Thermal Resistance and Shock
This is the most significant differentiator. Due to its pure SiO₂ structure, a quartz tube has an extremely low coefficient of thermal expansion.
It can withstand continuous operating temperatures above 1000°C and endure immense thermal shock, such as being heated red-hot and plunged into cold water without cracking.
Borosilicate glass is far superior to standard window glass but has a much lower service ceiling. It is reliable for applications up to about 500°C and will fracture under the extreme thermal shock that quartz can easily tolerate.
Optical Transparency
If your work involves light, this distinction is critical. A quartz tube offers a very broad transmission window, allowing light from the ultraviolet (UV), through the visible spectrum, and into the infrared (IR) range to pass through.
In contrast, borosilicate glass is excellent for transparency in the visible spectrum but is largely opaque to UV radiation. It effectively blocks most light below 350 nanometers.
Chemical Purity and Inertness
Because it is almost pure SiO₂, quartz is exceptionally inert and will not leach impurities into high-purity chemicals. This makes it essential for semiconductor manufacturing and sensitive trace-element analysis.
Borosilicate glass is highly resistant to most chemicals and is perfect for the vast majority of laboratory work. However, in ultra-sensitive applications, the oxides within the glass (like boron, sodium, or aluminum) could potentially leach and become contaminants.
Understanding the Key Trade-off: Cost vs. Capability
Your choice will almost always involve a compromise between the ultimate performance of quartz and the practical economy of glass.
The Cost Factor
There is no contest here: quartz is significantly more expensive than borosilicate glass. The extreme temperatures required to melt and process pure silica demand specialized equipment and more energy, driving up the price. A quartz tube can easily cost 5 to 10 times more than a borosilicate glass tube of the same dimensions.
Fabrication and Workability
The additives in borosilicate glass make it softer and easier to work with. It can be cut, joined, and shaped with standard glassblowing torches. Working with quartz requires much hotter and more specialized torches, making custom fabrication more difficult and expensive.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your decision should be guided by your primary operational requirement. Do not pay for performance you do not need.
- If your primary focus is extreme temperature (>500°C) or UV transparency: Quartz is the only viable option for applications like high-temperature furnaces, UV water purification systems, or photochemical reactors.
- If your primary focus is general laboratory work or visual processes: Borosilicate glass offers excellent clarity and sufficient thermal resistance for most heating, boiling, and chemical reaction applications at a fraction of the cost.
- If your primary focus is budget and general-purpose use: Borosilicate glass provides the best balance of performance and cost for the vast majority of non-specialized technical needs.
By understanding these core differences, you can select the material that provides the necessary performance without over-engineering your solution.
Summary Table:
| Property | Quartz Tube | Glass Tube (Borosilicate) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Material | Fused Silica (SiO₂ >99.5%) | Borosilicate Glass (~80% SiO₂) |
| Max Continuous Temp | > 1000°C | ~500°C |
| UV Transparency | Excellent (UV to IR) | Poor (Blocks UV <350nm) |
| Chemical Purity | Extremely High, Inert | High, but potential for leaching |
| Relative Cost | High (5-10x more) | Low / Economical |
Struggling to choose the right tube for your specific lab process? The experts at KINTEK can help! We specialize in providing the ideal lab equipment and consumables for your unique needs. Whether your application demands the extreme temperature resistance and UV transparency of quartz or the cost-effective versatility of borosilicate glass, we have the solution. Contact our team today for a personalized consultation to ensure optimal performance and value for your laboratory.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- High Temperature Aluminum Oxide (Al2O3) Protective Tube for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
- High Temperature Alumina (Al2O3) Furnace Tube for Engineering Advanced Fine Ceramics
People Also Ask
- How do vertical split tube furnaces and preheaters facilitate SCWO? Achieve Optimal Supercritical Water Oxidation
- What are the advantages of using multi-stage split tube furnaces for heating methane pyrolysis reactors? Boost Efficiency
- Why is high-temperature hydrogen reduction in a tube furnace necessary before carbon nanofiber growth? Catalyst Activation Explained
- How do high-temperature tube furnaces or rotary furnaces facilitate the regeneration of spent activated carbon?
- What function does a high-temperature tube furnace serve in alkali fusion hydroxide recovery? Precision Thermal Control



















