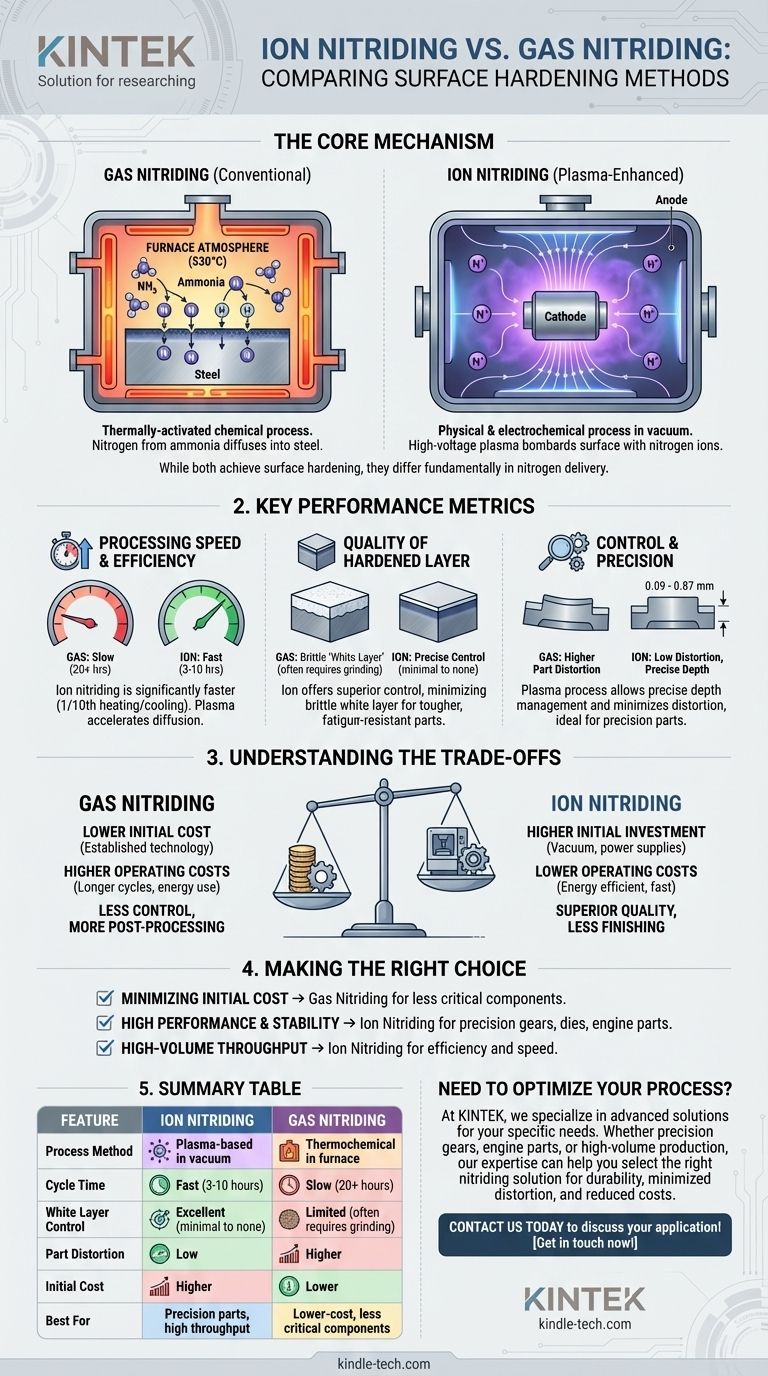
The fundamental difference between ion and gas nitriding lies in the method used to deliver nitrogen to a component's surface for hardening. Gas nitriding uses a thermally-activated chemical process in a nitrogen-rich furnace atmosphere. In contrast, ion nitriding (or plasma nitriding) uses a high-voltage electric field in a vacuum to create an ionized gas (plasma), which physically bombards the surface with nitrogen ions.
While both processes achieve surface hardening, the choice between them is a strategic decision. Ion nitriding offers superior speed, control, and material properties in exchange for a higher initial investment, whereas traditional gas nitriding represents a more conventional, lower-cost approach.

The Core Mechanism: Gas vs. Plasma
To understand the practical outcomes of each process, it's essential to first grasp how they work at a fundamental level.
Gas Nitriding: The Conventional Approach
Gas nitriding is a thermochemical process. The component is placed inside a sealed furnace heated to a specific temperature (e.g., 530°C). A nitrogen-bearing gas, typically ammonia (NH₃), is introduced into the furnace.
The heat causes the ammonia to dissociate at the steel's surface, releasing active nitrogen atoms. These atoms are then absorbed and diffuse into the material, forming hard nitride compounds and creating the hardened case.
Ion Nitriding: The Plasma-Enhanced Method
Ion nitriding is a physical and electrochemical process conducted in a vacuum. The workpiece itself is made the cathode, and the chamber wall is the anode.
A high-voltage electrical field is applied, causing the low-pressure nitrogen gas inside to form a plasma. This plasma envelops the component, and positively charged nitrogen ions are accelerated toward the negatively charged workpiece, bombarding its surface. This bombardment provides both the heat and the active nitrogen required for diffusion, making the process highly efficient.
Comparing Key Performance Metrics
The differences in mechanism lead to significant variations in speed, quality, and control.
Processing Speed and Efficiency
Ion nitriding is significantly faster. The direct surface heating from ion bombardment reduces heating and cooling times to as little as one-tenth of traditional methods.
The plasma process also accelerates the nitrogen diffusion rate. For example, achieving a 0.3 mm nitrided layer can take over 20 hours with traditional gas nitriding, whereas ion nitriding can often achieve this in a fraction of that time, with typical cycles running from 3-10 hours.
Quality of the Hardened Layer
A common byproduct of nitriding is a brittle "white layer" (iron nitride compounds like Fe₂N) on the surface, which often must be ground off.
Ion nitriding offers precise control over this white layer, minimizing or even eliminating it. This results in a tougher, more fatigue-resistant surface straight out of the furnace, reducing the need for costly secondary operations.
Control and Precision
The plasma process provides exceptional control. Ion nitriding allows for precise management of the hardened layer's depth (typically between 0.09 mm and 0.87 mm) and its composition.
Furthermore, because the heat is generated directly on the workpiece's surface rather than heating the entire part in a furnace, part distortion is significantly minimized. This is a critical advantage for finishing high-precision components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a nitriding process requires balancing investment against performance requirements.
Initial Investment vs. Operating Cost
The primary advantage of traditional gas nitriding is its lower initial capital cost for equipment. Furnaces are a well-established technology.
Ion nitriding systems require a higher upfront investment due to the need for vacuum chambers and sophisticated high-voltage power supplies. However, their higher speed and energy efficiency result in lower long-term operating costs.
Part Quality vs. Process Simplicity
Gas nitriding is a simpler, more straightforward thermal process. However, it offers less control over the final product, potentially requiring additional steps like grinding to remove the brittle white layer.
Ion nitriding is a more complex process to control, but it yields a superior, more consistent final part with better toughness and fatigue resistance, often with no post-processing required.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision should be driven by the specific demands of your component and production goals.
- If your primary focus is minimizing initial cost for less critical components: Traditional gas nitriding is an established and cost-effective solution.
- If your primary focus is high performance and dimensional stability: Ion nitriding's low distortion and superior control over the hardened layer make it the ideal choice for precision gears, dies, and engine parts.
- If your primary focus is high-volume throughput and efficiency: The significantly shorter cycle times and lower energy consumption of ion nitriding provide a clear advantage for production environments.
Ultimately, the choice hinges on whether you prioritize a lower barrier to entry or invest in a process that delivers superior speed, precision, and long-term performance.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Ion Nitriding | Gas Nitriding |
|---|---|---|
| Process Method | Plasma-based in vacuum | Thermochemical in furnace |
| Cycle Time | Fast (3-10 hours) | Slow (20+ hours) |
| White Layer Control | Excellent (minimal to none) | Limited (often requires grinding) |
| Part Distortion | Low | Higher |
| Initial Cost | Higher | Lower |
| Best For | Precision parts, high throughput | Lower-cost, less critical components |
Need to optimize your surface hardening process?
Choosing between ion and gas nitriding is critical for achieving the right balance of performance, cost, and efficiency for your components. At KINTEK, we specialize in providing advanced laboratory equipment and consumables tailored to your specific needs.
Whether you're working with precision gears, engine parts, or high-volume production components, our expertise can help you select the right nitriding solution to enhance durability, minimize distortion, and reduce operational costs.
Contact us today to discuss your application and discover how KINTEK's solutions can bring superior quality and efficiency to your lab. Get in touch now!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Molybdenum Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace with Ceramic Fiber Liner
- Vacuum Heat Treat Furnace and Levitation Induction Melting Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat Sintering Brazing Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
People Also Ask
- Why would you braze instead of solder? For Superior Joint Strength and High-Temperature Performance
- What happens to heat generated in a vacuum? Mastering Thermal Control for Superior Materials
- Can an arc happen in a vacuum? Yes, and here's how to prevent it in your high-voltage design.
- How long does it take to do a heat treatment? A Full Day for a 100% Bed Bug Kill Rate
- What temperature do you heat treat a furnace? It's All About Your Material and Goal



















