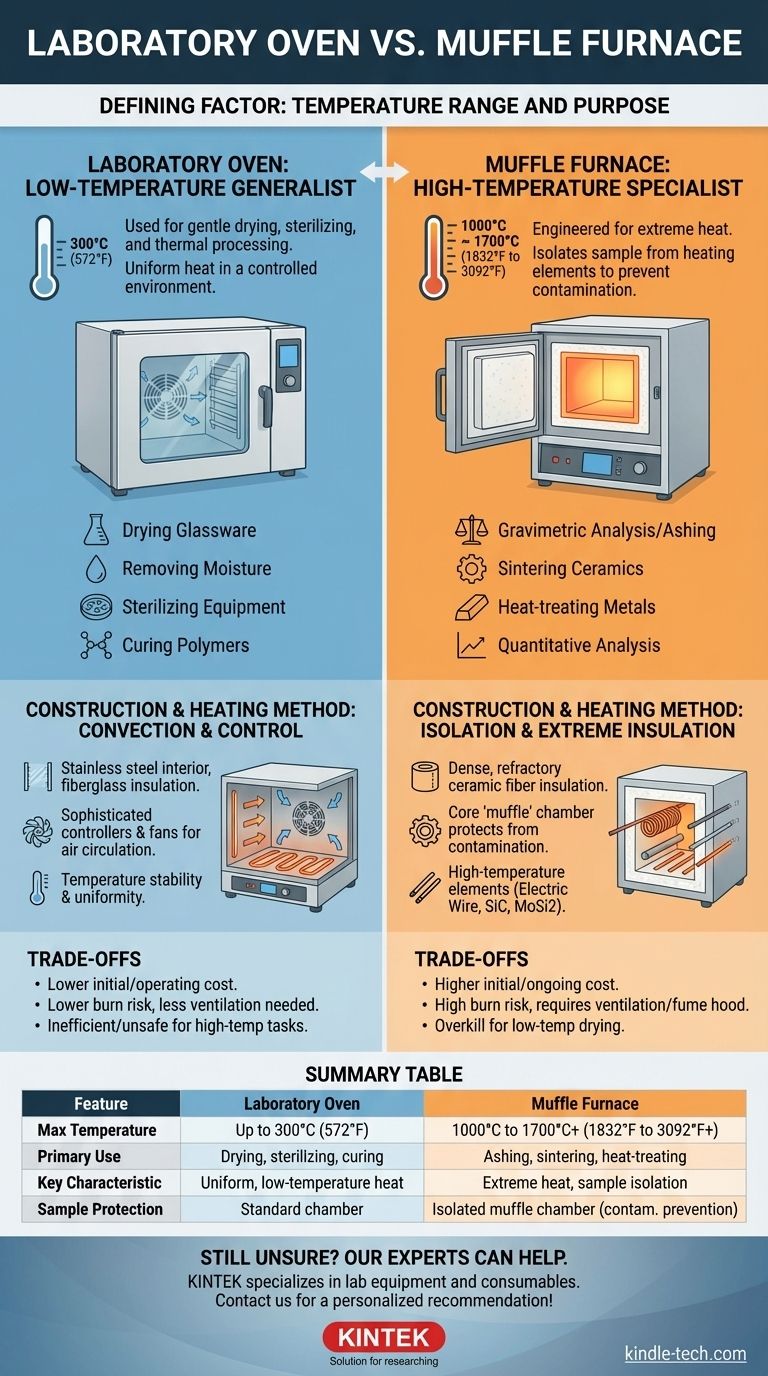
The fundamental difference between a laboratory oven and a muffle furnace lies in their operating temperature and intended application. A laboratory oven is used for gentle drying, sterilizing, and thermal processing at relatively low temperatures, typically up to 300°C (572°F). In contrast, a muffle furnace is a high-temperature specialist, designed to reach temperatures from 1000°C to over 1700°C (1832°F to 3092°F) for processes like ashing, sintering, and heat-treating metals.
The choice is not about which is "better," but which is designed for the task at hand. Ovens provide uniform, low-temperature heat for drying and sterilizing, while furnaces deliver the extreme temperatures needed to fundamentally alter or analyze a material's composition.

The Defining Factor: Temperature Range and Purpose
The most significant distinction between these two instruments is the thermal work they are built to perform. This dictates their design, materials, and cost.
Laboratory Ovens: Low-Temperature Generalists
A laboratory oven is a workhorse for a wide range of general-purpose applications. Its primary function is to provide uniform heat in a controlled environment, typically from just above ambient temperature to around 300°C.
Common applications include drying glassware, removing moisture from samples, sterilizing equipment, and curing polymers or epoxies. Many ovens use fans to create forced-air convection, ensuring temperature uniformity throughout the chamber, which is critical for sensitive processes.
Muffle Furnaces: High-Temperature Specialists
A muffle furnace is engineered for processes that require extreme heat. Its name comes from the "muffle," an insulating chamber that isolates the sample from direct contact with the heating elements, preventing contamination.
These furnaces are essential for applications like gravimetric analysis, where a sample is heated until only its inorganic components remain (ashing). Other key uses include sintering ceramics, heat-treating metals, and conducting quantitative analysis on materials at very high temperatures.
A Look Inside: Construction and Heating Method
The vast difference in operating temperature requires completely different approaches to insulation and heating element technology.
Oven Construction: Convection and Control
Laboratory ovens are typically built with a stainless steel interior and fiberglass insulation. Their design prioritizes temperature stability and uniformity across their lower operating range, often featuring sophisticated controllers and fans for air circulation.
Furnace Construction: Isolation and Extreme Insulation
A muffle furnace is constructed with dense, refractory ceramic fiber insulation. This material provides exceptional heat retention and allows for rapid heating ramps, as noted in high-performance models.
The core "muffle" chamber protects the sample from the byproducts of combustion or electrical element degradation, which is critical for achieving pure results in analytical chemistry.
High-Temperature Heating Elements
The heating elements in a muffle furnace are chosen based on the maximum required temperature.
- Electric heating wires are sufficient for temperatures up to 1200°C.
- Silicon-carbon rods are used for processes requiring 1300°C to 1400°C.
- Silicon molybdenum rods are necessary to achieve the highest temperatures, from 1400°C up to 1700°C.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the wrong instrument can lead to failed experiments, damaged equipment, or safety hazards.
The Cost of Power
Muffle furnaces are significantly more expensive to purchase and operate than laboratory ovens. Their specialized insulation, high-temperature elements, and robust power supplies contribute to higher initial and ongoing energy costs.
Safety and Ventilation
Operating a muffle furnace, especially for ashing organic materials, produces fumes and requires placement inside a fume hood or under dedicated ventilation. The extreme external temperatures also present a greater burn risk than a standard lab oven.
Function and Application Mismatch
Attempting to use a laboratory oven for a high-temperature application like ashing will fail and likely destroy the oven. Conversely, using a powerful muffle furnace for simple, low-temperature drying is inefficient and may not provide the temperature uniformity of a purpose-built convection oven.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct instrument is a straightforward decision once you define your thermal requirements.
- If your primary focus is drying, sterilizing, or curing below 300°C: A laboratory oven is the correct, efficient, and safe tool for the job.
- If your primary focus is ashing, sintering, or heat-treating materials above 1000°C: A muffle furnace is the only instrument capable of reaching the required temperatures.
- If you need to protect your sample from heating element contamination: The isolated chamber of a muffle furnace is a non-negotiable feature for high-purity analytical work.
Ultimately, choosing between an oven and a furnace is a matter of matching the tool's thermal capabilities to your specific scientific or industrial process.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Laboratory Oven | Muffle Furnace |
|---|---|---|
| Max Temperature | Up to 300°C (572°F) | 1000°C to 1700°C+ (1832°F to 3092°F+) |
| Primary Use | Drying, sterilizing, curing | Ashing, sintering, heat-treating |
| Key Characteristic | Uniform, low-temperature heat | Extreme heat for material alteration |
| Sample Protection | Standard chamber | Isolated muffle chamber to prevent contamination |
Still unsure which thermal processing equipment is right for your lab? KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you select the perfect oven or furnace for your specific application, ensuring optimal performance and safety. Contact us today to discuss your requirements and get a personalized recommendation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Muffle Oven Furnace Bottom Lifting Muffle Furnace
- 1400℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1700℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
People Also Ask
- Why do we need to use properly some of the laboratory apparatus in the laboratory? The Foundation of Safe and Accurate Science
- What is the working principle of laboratory muffle furnace? Achieve Contamination-Free High-Temperature Processing
- What precautions should you take while using a muffle furnace? Ensure Safe High-Temperature Processing in Your Lab
- What precautions you will take while handling the muffle furnace? Ensure Safe and Efficient Operation
- What is the role of muffle furnace in fluid mechanics? A Key Tool for Material Preparation



















