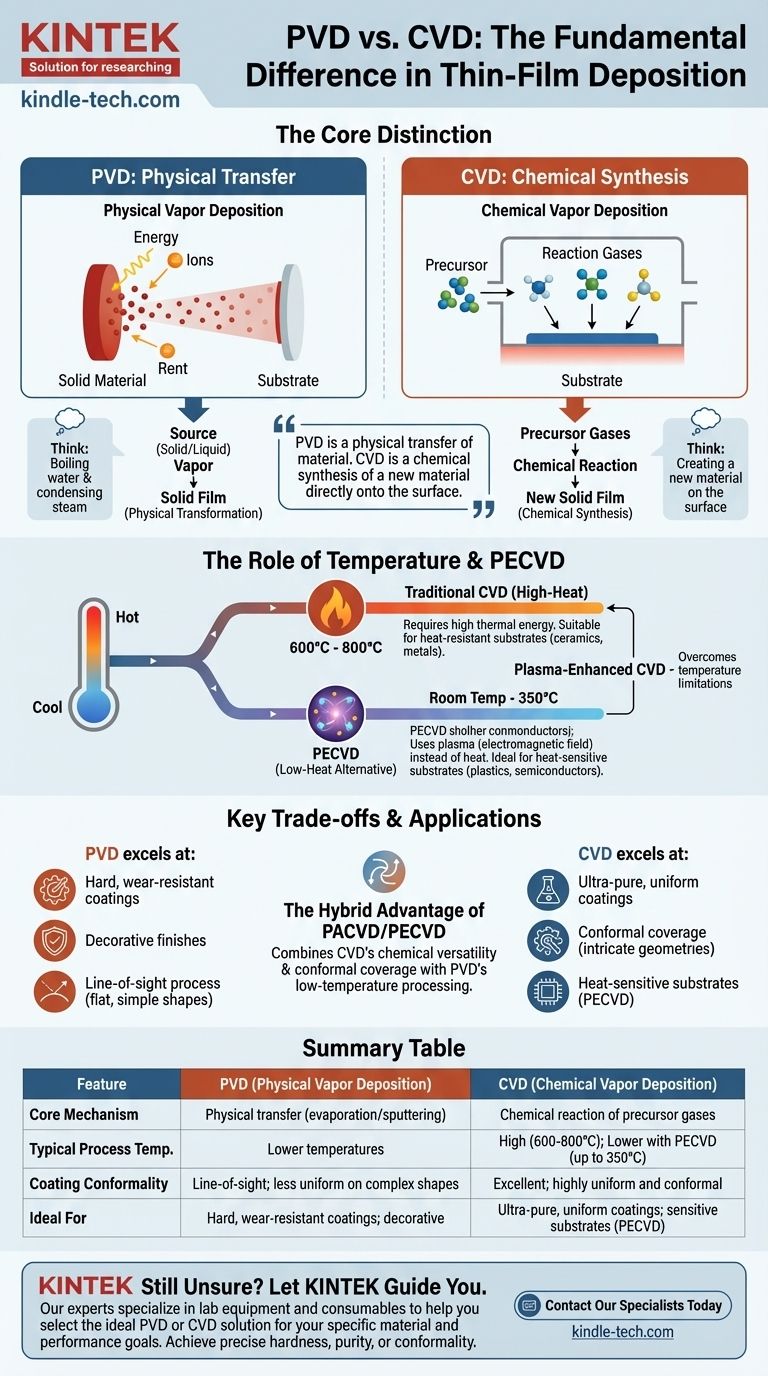
The fundamental difference between Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) and Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) lies in how the coating material arrives at the substrate. In PVD, the material is physically transformed from a solid or liquid source into a vapor and then deposited. In CVD, precursor gases undergo a chemical reaction at the substrate's surface to create a new, solid film.
The choice between PVD and CVD is not just about the final coating, but about the process itself. The core distinction is one of mechanism: PVD is a physical transfer of material, while CVD is a chemical synthesis of a new material directly onto the surface.
The Fundamental Mechanism: Physical vs. Chemical
To understand these techniques, you must first grasp how they create a vapor and form a film. They are fundamentally different processes at a molecular level.
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD): A Change of State
In PVD, a solid target material is bombarded with energy to physically "knock off" or evaporate atoms, turning it into a vapor. This vapor then travels through a vacuum and condenses onto the cooler substrate, forming a thin film.
Think of it like boiling water. You heat the liquid (the source), it turns into a gas (vapor), and then it condenses on a cold surface (the substrate).
A common PVD method is arc vapor deposition, which uses a high-current arc to vaporize the source material. This creates a high proportion of ionized atoms, making it excellent for forming thick, hard, and durable coatings.
Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD): A Chemical Reaction
CVD does not start with the final coating material in solid form. Instead, it introduces one or more volatile precursor gases into a reaction chamber.
These gases decompose and react with each other and the substrate surface, creating an entirely new solid material that deposits as a film. It is a process of synthesis, not simple transfer.
The Critical Role of Temperature
The energy required to drive these processes is a major differentiator and a critical factor in selecting the right method for a given substrate.
Traditional CVD: The High-Heat Approach
Standard thermal CVD requires significant heat to provide the activation energy for the chemical reactions. Temperatures typically range from 600°C to 800°C.
This high heat is necessary to break the chemical bonds in the precursor gases, allowing them to recombine and form the desired film. Consequently, this method is only suitable for substrates that can withstand extreme temperatures, such as ceramics or certain metals.
Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD): The Low-Heat Alternative
Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD), also known as Plasma-Assisted CVD (PACVD), was developed to overcome the temperature limitations of traditional CVD. It operates at much lower temperatures, from room temperature to 350°C.
Instead of relying on thermal energy, PECVD uses an electromagnetic field to generate a plasma. This plasma contains highly energetic electrons and ions that can break chemical bonds and drive the reaction at low temperatures, making it ideal for heat-sensitive substrates like plastics and advanced semiconductor components.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Each process offers a unique combination of advantages and limitations that make it better suited for different applications.
When to Choose PVD
PVD excels at producing extremely hard, wear-resistant, and decorative coatings. It is a direct "line-of-sight" process, which is highly effective for coating flat or simply-curved surfaces but can be challenging for complex, three-dimensional shapes.
When to Choose CVD
CVD is the superior choice for creating exceptionally pure, uniform, and conformal coatings. Because the precursor is a gas, it can flow around and into intricate geometries, ensuring complete and even coverage over complex parts.
The Hybrid Advantage of PACVD/PECVD
Plasma-assisted CVD combines the chemical versatility and conformal coverage of CVD with the low-temperature processing capabilities often associated with PVD. This makes it a powerful tool for depositing high-quality, chemically synthesized films onto delicate materials.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Selecting the correct method requires a clear understanding of your primary goal and substrate limitations.
- If your primary focus is extreme hardness or wear resistance on a metal part: PVD techniques like arc deposition are often the most direct and effective solution.
- If your primary focus is an ultra-pure, conformal coating on a heat-resistant substrate: Traditional high-temperature CVD is the superior choice for its purity and uniformity.
- If your primary focus is applying a chemically-derived coating onto a temperature-sensitive substrate: Plasma-Enhanced CVD (PECVD) is the necessary technology to enable the reaction without damaging the part.
Understanding this fundamental distinction between physical transfer and chemical reaction is the key to selecting the right deposition technology for your specific material and performance goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) | CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) |
|---|---|---|
| Core Mechanism | Physical transfer of material (evaporation/sputtering) | Chemical reaction of precursor gases on the substrate |
| Typical Process Temp. | Lower temperatures | High (600-800°C); Lower with PECVD (up to 350°C) |
| Coating Conformality | Line-of-sight; less uniform on complex shapes | Excellent; highly uniform and conformal on complex geometries |
| Ideal For | Hard, wear-resistant coatings on metals; decorative finishes | Ultra-pure, uniform coatings; temperature-sensitive substrates (with PECVD) |
Still unsure which deposition method is right for your project?
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, serving laboratory needs. Our experts can help you select the ideal PVD or CVD solution to achieve the precise coating properties—whether for hardness, purity, or conformality—that your materials demand.
Contact our specialists today for a personalized consultation and unlock the full potential of your thin-film applications.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is chemical vapor phase deposition? A Guide to High-Performance Thin Film Growth
- What is the apparatus of chemical vapor deposition? The Essential Components for Thin Film Deposition
- What is the principle of chemical vapor deposition? Build High-Performance Coatings Through Controlled Chemistry
- What techniques can be used to improve the quality of CVD graphene growth? Expert Methods for High-Quality Graphene
- What advantages do CVD furnaces offer for Wf/W composites? Preserving Fiber Ductility and Interface Integrity
- What is the full form of CVD coated? Unlock the Secrets of Advanced Material Engineering
- What are the modern applications of CVD-grown graphene? Exploring Advanced Electronics and Energy Solutions
- What is the vapor deposition growth process? Grow High-Performance Thin Films Atom by Atom



















