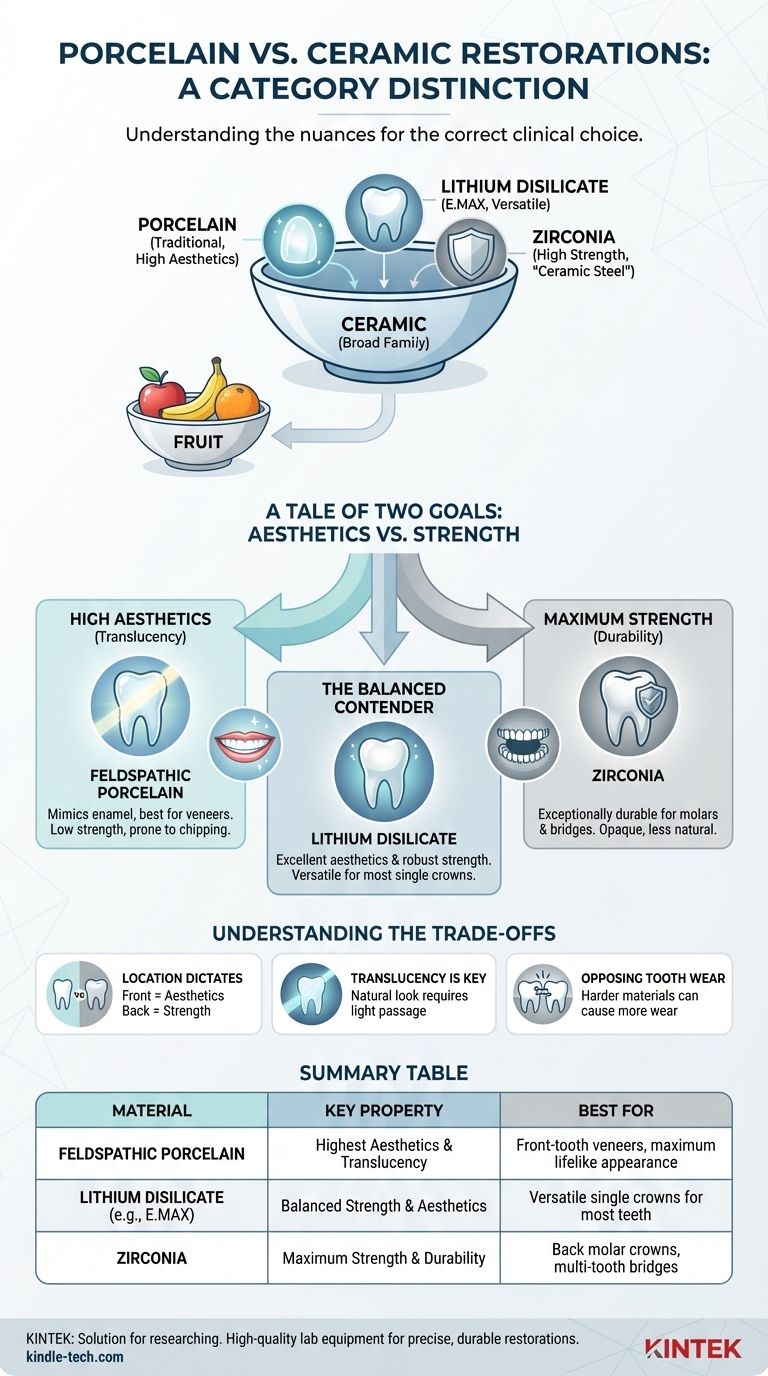
In practice, the distinction is a matter of categories. All porcelain is a type of ceramic, but not all modern dental ceramics are porcelain. Think of "ceramic" as the broad family of materials and "porcelain" as one of its oldest, most artistically refined members.
The core issue isn't choosing between porcelain and ceramic, but rather understanding which specific type of advanced dental ceramic—each with unique properties of strength and aesthetics—is the correct clinical choice for your specific tooth and functional needs.

The Foundation: What Is a Dental Ceramic?
A Broad Class of Materials
A dental ceramic is any inorganic, non-metallic material that is hardened by firing at a high temperature. This category is vast, encompassing a range of materials developed over decades.
Using an analogy, asking for a "ceramic" restoration is like asking for a "fruit." To get what you need, you must be more specific—do you need an apple, a banana, or an orange?
From Clay to High-Tech Compounds
Traditional ceramics, like porcelain, are primarily composed of kaolin, feldspar, and silica. However, the term "ceramic" in modern dentistry also includes highly engineered materials like Zirconia and Lithium Disilicate, which have vastly different compositions and properties.
A Tale of Two Goals: Aesthetics vs. Strength
The evolution of dental ceramics has been driven by the need to solve two different problems: creating a perfectly natural appearance and withstanding immense bite forces.
Traditional Porcelain: The Gold Standard for Aesthetics
Feldspathic porcelain is the original material used for cosmetic restorations like veneers. Its structure allows it to mimic the translucency and light-reflecting properties of natural tooth enamel better than almost any other material.
Its primary weakness is its relatively low strength. It is more brittle and prone to chipping under pressure, making it an ideal choice for the front teeth but a poor choice for high-stress molars.
High-Strength Ceramics (Zirconia): The Powerhouse
Zirconia is an exceptionally strong and durable ceramic, sometimes marketed as "ceramic steel." Its incredible resistance to fracture makes it the undisputed champion for restorations in high-pressure areas.
It is the ideal material for crowns on back molars and for multi-tooth bridges that must endure significant chewing forces. While early forms of zirconia were opaque and chalky, modern variations have greatly improved translucency.
The Balanced Contender (Lithium Disilicate): The All-Rounder
Lithium disilicate (most famously branded as E.MAX) represents a powerful compromise. It offers excellent aesthetics that are far superior to older zirconia, combined with robust strength that is much greater than traditional porcelain.
This balance makes it one of the most versatile and widely used materials in dentistry today, suitable for single crowns on nearly any tooth in the mouth.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing the right material involves a direct trade-off between its visual properties and its mechanical strength. Your dentist evaluates this based on the tooth's location and function.
Location Dictates the Material
The core principle is simple: the demands placed on a front tooth are different from those placed on a back tooth.
Front teeth require the highest level of cosmetic perfection, making porcelain or lithium disilicate top choices. Back teeth require maximum durability, making zirconia the safest and most reliable option.
Translucency Is Key to a Natural Look
Natural teeth are not fully opaque; they allow some light to pass through them. A restoration's ability to replicate this translucency is what makes it look lifelike and undetectable. Porcelain has the highest translucency, while zirconia is the most opaque.
Wear and Tear on Opposing Teeth
An important consideration is how the material affects the teeth it bites against. Extremely hard materials like zirconia can, over many years, cause more wear on the opposing natural tooth than softer materials like porcelain or lithium disilicate.
Making the Right Choice for Your Restoration
Your conversation with your dentist should not be about "porcelain vs. ceramic," but about which specific material is best suited for your clinical situation and personal priorities.
- If your primary focus is maximum, lifelike aesthetics for front-tooth veneers: Traditional feldspathic porcelain remains the gold standard for its unparalleled beauty.
- If your primary focus is an indestructible crown for a back molar: Zirconia is the most durable and fracture-resistant choice available.
- If your primary focus is a strong, beautiful, and versatile crown for most teeth: Lithium disilicate (E.MAX) offers an outstanding balance of cosmetic appeal and reliable strength.
Ultimately, partnering with your dentist to select the right material ensures your restoration will be a long-lasting fusion of science and art.
Summary Table:
| Material | Key Property | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Feldspathic Porcelain | Highest Aesthetics & Translucency | Front-tooth veneers, maximum lifelike appearance |
| Lithium Disilicate (e.g., E.MAX) | Balanced Strength & Aesthetics | Versatile single crowns for most teeth |
| Zirconia | Maximum Strength & Durability | Back molar crowns, multi-tooth bridges |
Ready to select the perfect dental ceramic for your laboratory's restorations? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for dental technicians, helping you achieve precise, durable, and aesthetically perfect results with materials like zirconia, lithium disilicate, and porcelain. Let our expertise support your craft—contact us today to discuss your specific laboratory needs!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Dental Porcelain Zirconia Sintering Ceramic Furnace Chairside with Transformer
- Vacuum Dental Porcelain Sintering Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1800℃ Muffle Oven Furnace for Laboratory
People Also Ask
- What are the white spots on zirconia after sintering? A Guide to Diagnosing and Preventing Defects
- What is a dental oven? The Precision Furnace for Creating Strong, Aesthetic Dental Restorations
- Can you change the color of zirconia crowns? Understanding the Permanent Nature of Zirconia
- What is the effect of zirconia sintering temperature? Master the Key to Strength and Stability
- What is the price of zirconia sintering furnace? Invest in Precision, Not Just a Price Tag



















