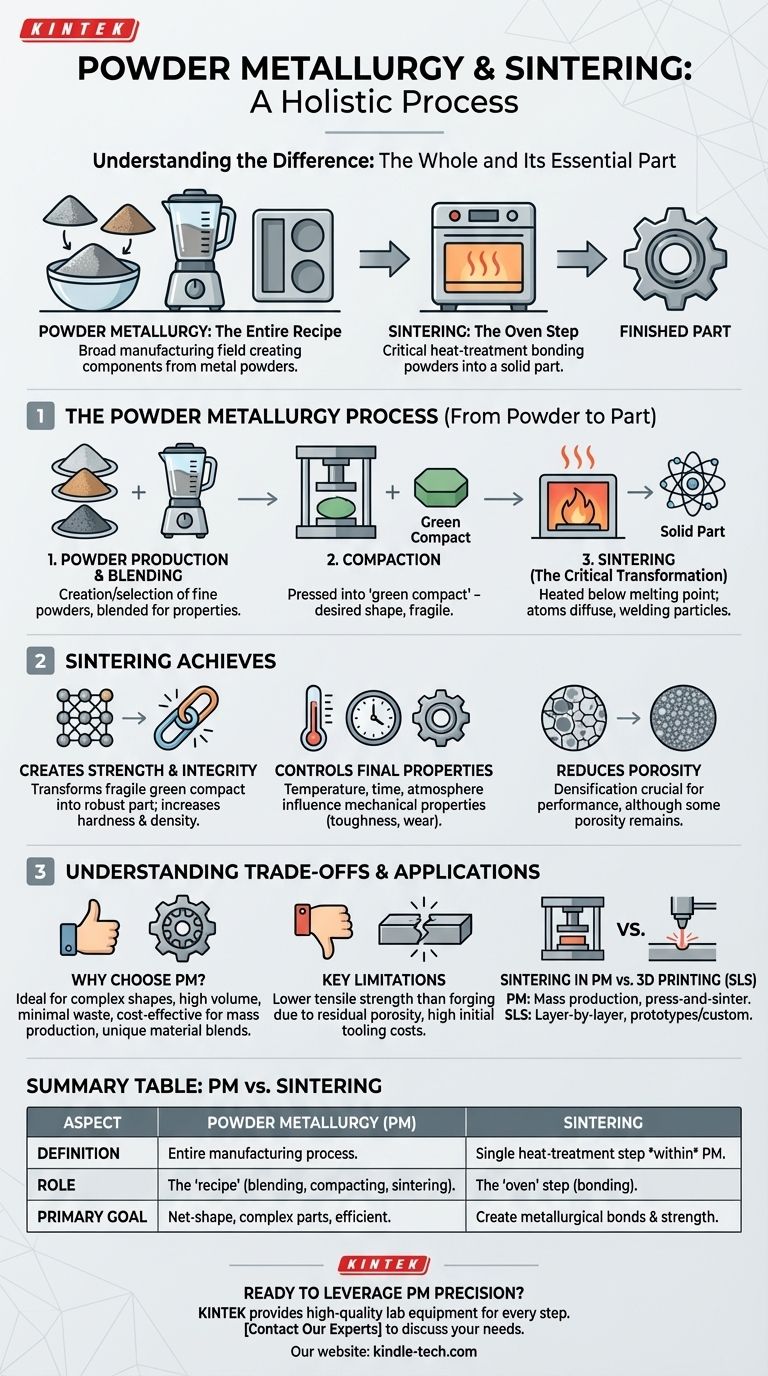
In short, the two are not separate concepts but are instead a whole and its essential part. Powder metallurgy is the broad manufacturing field focused on creating components from metal powders. Sintering is a single, critical heat-treatment step within the larger powder metallurgy process, responsible for bonding those powders into a solid, functional part.
To use a simple analogy, if powder metallurgy is the entire recipe for baking a cake, sintering is the crucial step of putting it in the oven. It's the transformative process that turns a loose mixture into a solid, finished product.

The Powder Metallurgy Process: From Powder to Part
To truly understand the relationship, it's best to view sintering in its proper context as a stage within the overall powder metallurgy workflow.
Step 1: Powder Production and Blending
The process begins with the creation or selection of fine metal powders. These powders can be blended with other elements, alloys, or lubricants to achieve the desired final properties for the component.
Step 2: Compaction
The blended powder is poured into a precision die and compacted under high pressure. This action forms the powder into a specific shape, known as a "green compact." This component has the desired geometry but is fragile, with low mechanical strength.
Step 3: Sintering (The Critical Transformation)
The green compact is then moved to a controlled-atmosphere furnace for sintering. Here, it is heated to a high temperature that is critically below the melting point of the primary metal.
This heat energizes the atoms, causing them to diffuse across the boundaries of the individual particles, effectively welding them together on a microscopic level. This solid-state diffusion is what creates strong metallurgical bonds.
What Sintering Actually Achieves
Sintering is not simply heating; it's a precise thermal process that fundamentally changes the material's character.
Creates Strength and Integrity
The primary goal of sintering is to transform the fragile green compact into a robust part with significant structural integrity. The bonding of particles dramatically increases the component's hardness, strength, and density.
Controls Final Properties
The exact temperature, time, and furnace atmosphere used during sintering are carefully controlled variables. These factors directly influence the final mechanical properties of the part, such as its toughness and wear resistance.
Reduces Porosity
While some porosity often remains, the sintering process significantly reduces the empty space between the powder particles. This densification is crucial for the performance of the finished component.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Powder metallurgy is a powerful technique, but its suitability depends entirely on the application.
Why Choose Powder Metallurgy?
This method is ideal for producing complex shapes in high volumes with minimal material waste, making it highly cost-effective for parts like automotive gears, valve seats, and bushings. It also allows for the creation of unique material blends that are impossible to produce through traditional melting and casting.
Key Limitations
The main trade-off is often strength. Due to inherent residual porosity, a part made via powder metallurgy may have lower tensile strength or fatigue resistance compared to a fully dense part made by forging. Initial tooling costs for the compaction dies can also be high, making it less economical for low-volume production.
Sintering in PM vs. 3D Printing
It's important not to confuse traditional sintering with processes like Selective Laser Sintering (SLS), a form of 3D printing. While both use powders, SLS builds parts layer-by-layer without a mold and is best for prototypes or custom parts. In contrast, powder metallurgy's press-and-sinter method is engineered for the accuracy and cost-efficiency of mass production.
How to Apply This to Your Project
Understanding the distinction helps you evaluate if the powder metallurgy process is the right choice for your manufacturing needs.
- If your primary focus is mass production of small, complex parts: Powder metallurgy is an extremely cost-effective and precise method for achieving net-shape components with little waste.
- If your goal is to create unique material alloys: PM excels at combining metals with vastly different melting points or blending metals with non-metallic materials.
- If maximum strength is your absolute priority: A process like forging or machining from solid bar stock may be a more appropriate choice over standard powder metallurgy.
Recognizing sintering as the crucial bonding stage within the broader powder metallurgy framework is key to mastering this powerful manufacturing technology.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Powder Metallurgy (PM) | Sintering |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The entire manufacturing process for creating parts from metal powders. | A single heat-treatment step within the PM process. |
| Role | The "recipe" for making a part (blending, compacting, sintering). | The "oven" step that bonds powder particles into a solid part. |
| Primary Goal | To produce net-shape, complex parts efficiently and with minimal waste. | To create metallurgical bonds and strength in the "green" compact. |
Ready to leverage the precision of powder metallurgy for your components? KINTEK specializes in providing the high-quality lab equipment and consumables essential for every step of the PM process, from powder blending to controlled sintering. Our expertise ensures you achieve the material properties and part integrity your projects demand. Contact our experts today to discuss how we can support your laboratory and manufacturing needs.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Rapid Thermal Processing (RTP) Quartz Tube Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace with 9MPa Air Pressure
- Spark Plasma Sintering Furnace SPS Furnace
- Vacuum Heat Treat and Molybdenum Wire Sintering Furnace for Vacuum Sintering
- 2200 ℃ Tungsten Vacuum Heat Treat and Sintering Furnace
People Also Ask
- What is the primary function of quartz tubes in halide electrolyte synthesis? Ensure Purity & Precise Stoichiometry
- Why are quartz tubes preferred for chromium powder combustion? Superior Heat Resistance & Optical Clarity
- What role does a quartz tube furnace play in hBN synthesis? Optimize Your Chemical Vapor Deposition Results
- Why use quartz tubes and vacuum sealing for sulfide solid-state electrolytes? Ensure Purity & Stoichiometry
- What happens when quartz is heated? A Guide to Its Critical Phase Transitions and Uses



















