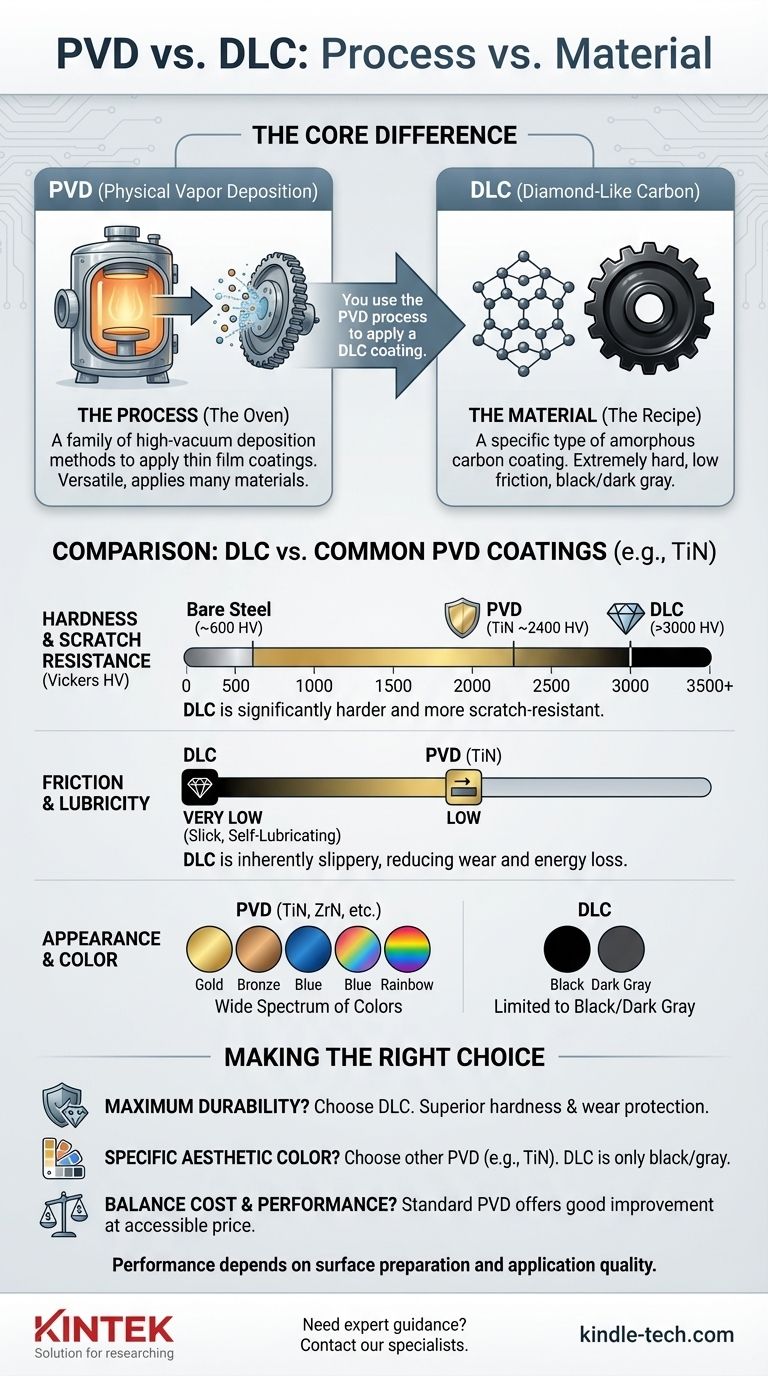
The primary difference is a matter of category. PVD is a manufacturing process, while DLC is a specific material that is often applied using that process. Think of PVD as the oven and DLC as one specific, high-performance recipe you can bake in it.
The core misunderstanding arises because the terms are used interchangeably, but they are not the same. PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) is the method used to apply a thin film coating, while DLC (Diamond-Like Carbon) is the substance being applied. You use the PVD process to apply a DLC coating.

What is PVD? The Process Explained
A High-Vacuum Application Method
Physical Vapor Deposition (PVD) is not a single coating but a family of vacuum deposition processes.
In a PVD process, a solid source material is vaporized into a plasma of atoms or molecules within a high-vacuum chamber. This vapor is then deposited onto the target object, creating a very thin, dense, and highly-adherent coating.
PVD Creates Many Different Coatings
The PVD process is incredibly versatile. By changing the source material that is vaporized, you can create a wide range of coatings with different properties and colors.
Common coatings applied via PVD include Titanium Nitride (TiN), Zirconium Nitride (ZrN), and Chromium Nitride (CrN), as well as Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC).
What is DLC? The Material Explained
A Unique Form of Carbon
Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC) is a specific class of amorphous carbon material that displays some of the unique properties of natural diamond.
The Key Properties of DLC
DLC coatings are renowned for their exceptional characteristics. Their primary benefits are extremely high hardness (excellent scratch resistance) and a very low coefficient of friction (it's incredibly slick).
This combination makes DLC a premium choice for applications demanding superior wear resistance and durability, from high-end watch cases to critical engine components and cutting tools.
The Real Comparison: DLC vs. Other PVD Coatings
When people ask for the difference between PVD and DLC, they are usually trying to compare a DLC finish to other common hard coatings that are also applied using the PVD process.
Hardness and Scratch Resistance
This is where DLC truly excels. On the Vickers hardness scale, a high-quality DLC coating can exceed 3000 HV (and some forms are much higher), making it one of the hardest and most scratch-resistant coatings available.
Other common PVD coatings like Titanium Nitride (TiN) are also very hard, typically around 2400 HV. While significantly harder than bare steel (which is often below 600 HV), they are generally less scratch-resistant than DLC.
Friction and Lubricity
DLC is famous for its low-friction properties, making it naturally "slippery." This reduces the energy needed for moving parts to slide against each other, minimizing wear and heat. This is a major advantage for knife blades, engine pistons, and firearm bolts.
Appearance and Color
This is a critical distinction. DLC coatings are almost exclusively black or dark gray.
Other PVD coatings offer a wide spectrum of colors. TiN produces a signature gold finish, while ZrN can be pale gold or champagne. Other formulations can create bronze, blue, rainbow, and graphite finishes.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Coating is Only as Good as its Application
The performance of any PVD coating, including DLC, is critically dependent on the surface preparation of the underlying material (the substrate). A poorly prepared surface will result in poor adhesion, causing even the hardest coating to chip or flake off.
Not All DLC is Created Equal
"DLC" is a family of coatings, not a single monolithic substance. Different formulations and application parameters result in DLC coatings with varying degrees of hardness, slickness, and durability. A cheap, poorly-applied DLC may perform worse than a high-quality TiN coating.
Cost and Complexity
Applying a high-quality DLC coating is generally a more complex and expensive process than applying standard coatings like TiN. This increased cost is directly reflected in the price of the final product.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
- If your primary focus is maximum durability and scratch resistance: A well-applied DLC coating is the superior technical choice, offering the highest level of surface hardness and wear protection.
- If your primary focus is a specific aesthetic color (gold, bronze, etc.): You will need to choose a different PVD coating like TiN or ZrN, as DLC is limited to black and gray.
- If your primary focus is balancing cost and performance: Standard PVD coatings like TiN offer a substantial improvement in hardness over bare metal at a more accessible price point than premium DLC.
Ultimately, your choice depends on a clear understanding of your priorities and the performance you demand from the product.
Summary Table:
| Feature | PVD (Process) | DLC (Material) |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | A family of vacuum deposition methods | A specific type of amorphous carbon coating |
| Primary Role | The application technique | The coating substance being applied |
| Key Characteristic | Versatile; can apply many coatings | Extremely hard and low-friction |
| Hardness (Vickers HV) | Varies by coating (e.g., TiN ~2400 HV) | Typically >3000 HV |
| Common Colors | Gold, bronze, blue, etc. | Black or dark gray only |
Need expert guidance on the ideal coating for your application?
At KINTEK, we specialize in advanced lab equipment and consumables for surface engineering. Whether you're developing products that require the extreme hardness of DLC or the versatile aesthetics of other PVD coatings, our expertise ensures you select the right solution for maximum performance and durability.
Let's discuss your project's specific requirements. Contact our specialists today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- RF PECVD System Radio Frequency Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition RF PECVD
- Hemispherical Bottom Tungsten Molybdenum Evaporation Boat
- Aluminized Ceramic Evaporation Boat for Thin Film Deposition
- Vacuum Hot Press Furnace Machine for Lamination and Heating
- Ceramic Evaporation Boat Set Alumina Crucible for Laboratory Use
People Also Ask
- How does RF power create plasma? Achieve Stable, High-Density Plasma for Your Applications
- What are the applications of PECVD? Essential for Semiconductors, MEMS, and Solar Cells
- What are the advantages of PECVD? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin-Film Deposition
- Why does PECVD commonly use RF power input? For Precise Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What are the benefits of PECVD? Achieve Superior Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition



















