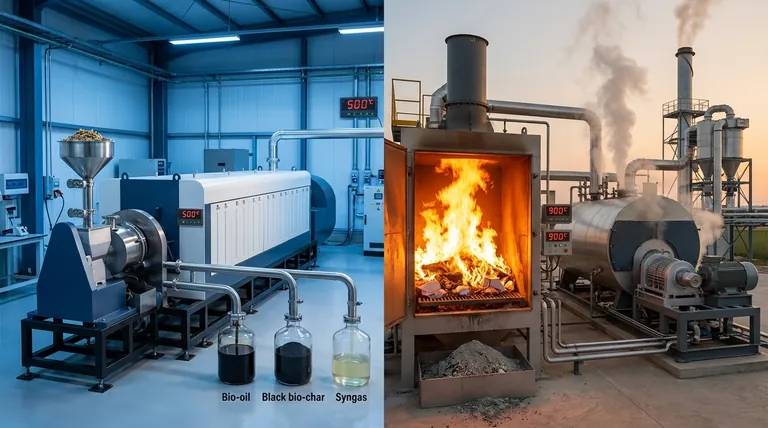
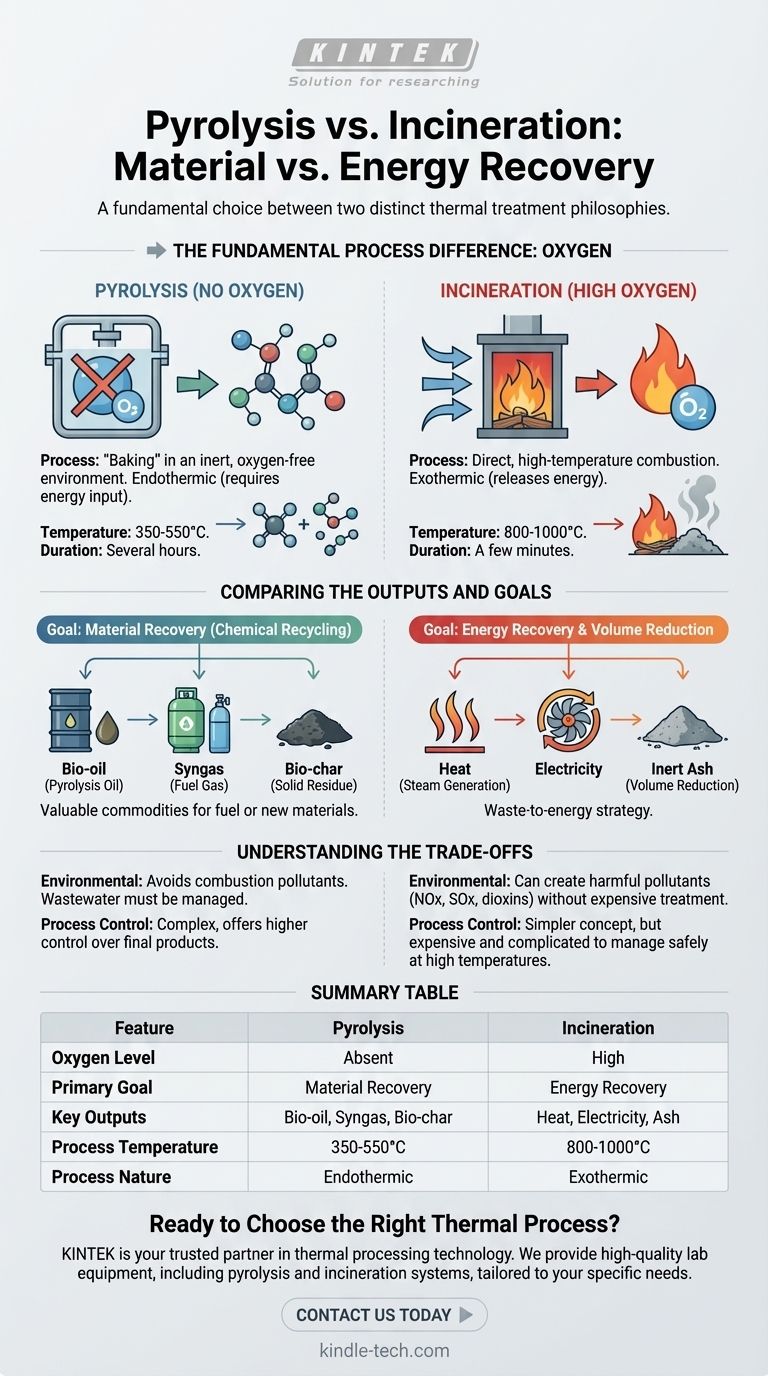
In simple terms, the core difference between pyrolysis and incineration lies in the presence of oxygen and the ultimate goal of the process. Pyrolysis is a thermal decomposition process that occurs in the complete absence of oxygen, breaking down materials into valuable chemical products and fuels. In contrast, incineration is a combustion process that uses high levels of oxygen to burn waste, primarily to generate heat and electricity.
The choice between pyrolysis and incineration is a choice between two distinct philosophies: material recovery vs. energy recovery. Pyrolysis deconstructs waste into reusable chemical components, while incineration destroys waste to release its stored energy as heat.

The Fundamental Process Difference: Oxygen
The role of oxygen is the single most important factor that distinguishes these two thermal treatment methods. It dictates the chemical reactions, the outputs, and the entire purpose of each technology.
How Pyrolysis Works (No Oxygen)
Pyrolysis is essentially "baking" material in an inert, oxygen-free environment. Because there is no oxygen to react with, the material does not burn.
Instead, the intense heat breaks the complex chemical bonds, "cracking" large molecules into smaller, more valuable ones. This process is primarily endothermic, meaning it requires a consistent energy input to sustain the reaction, preserving the high energy content within its products.
How Incineration Works (High Oxygen)
Incineration is direct, high-temperature combustion. By introducing large amounts of air (oxygen), the process facilitates the complete oxidation of the waste material.
This rapid, exothermic reaction releases a tremendous amount of energy as heat, effectively destroying the original material and converting it into ash, flue gas, and heat.
Comparing the Outputs and Goals
The difference in process leads to fundamentally different outcomes. Each method is optimized for a specific goal, making them suitable for very different applications.
Pyrolysis: Creating New Materials
The goal of pyrolysis is to capture and refine the chemical building blocks locked within waste. It is a form of chemical recycling.
The primary outputs are valuable commodities like bio-oil (also called pyrolysis oil), syngas, and a solid residue called bio-char. These products can be used as fuels or further processed into new chemicals, plastics, and other materials.
Incineration: Generating Heat and Power
The goal of incineration is energy recovery and maximum volume reduction. It is a waste-to-energy strategy.
Its main useful output is heat. This heat is used to boil water, creating high-pressure steam that drives turbines to generate electricity. The solid byproduct is an inert ash, which is significantly smaller in volume than the original waste.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Neither technology is a perfect solution. Choosing between them involves understanding their operational and environmental trade-offs.
Environmental Byproducts
Because incineration is a combustion process, it can create harmful pollutants like oxides (NOx, SOx) and dioxins if not carefully controlled. Modern incinerators require complex and expensive flue gas treatment systems to capture these toxins.
Pyrolysis, by occurring in an oxygen-free environment, inherently avoids the formation of these specific combustion-related pollutants. However, its own output streams (like wastewater) must still be managed properly.
Process Control and Conditions
Pyrolysis generally operates at lower temperatures (350-550°C) but over a longer duration of several hours. This process tends to be more complex but offers a higher degree of control over the final products.
Incineration occurs at much higher temperatures (800-1000°C) over just a few minutes. While conceptually simpler, managing the high temperatures and potential for harmful emissions makes the overall system expensive and complicated to control safely.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
The decision to use pyrolysis or incineration should be driven by the desired outcome for the waste stream.
- If your primary focus is creating valuable chemical feedstocks or fuels from waste: Pyrolysis is the superior choice as it preserves the chemical energy in new products, fitting into a circular economy model.
- If your primary focus is maximizing energy generation and reducing the sheer volume of waste: Incineration is the more direct and established pathway for converting the raw energy content of waste directly into electricity.
Ultimately, selecting the right technology depends entirely on whether you view waste as a resource to be repurposed or as a fuel to be burned.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Pyrolysis | Incineration |
|---|---|---|
| Oxygen Level | Absent | High |
| Primary Goal | Material Recovery (Chemical Recycling) | Energy Recovery (Waste-to-Energy) |
| Key Outputs | Bio-oil, Syngas, Bio-char | Heat, Electricity, Ash |
| Process Temperature | 350-550°C | 800-1000°C |
| Process Nature | Endothermic (Requires energy input) | Exothermic (Releases energy) |
Ready to Choose the Right Thermal Process for Your Lab?
Understanding the precise differences between pyrolysis and incineration is critical for selecting the right equipment for your research, waste management, or material recovery goals. The wrong choice can lead to inefficient processes or missed opportunities for resource recovery.
KINTEK is your trusted partner in thermal processing technology. We specialize in providing high-quality lab equipment, including pyrolysis and incineration systems, tailored to meet the specific needs of laboratories and research facilities. Our experts can help you navigate these complex decisions to ensure you achieve optimal results—whether your focus is on creating valuable new materials from waste or efficiently generating energy.
Let KINTEK empower your lab's innovation.
Contact us today to discuss your project requirements and discover how our solutions can enhance your efficiency and outcomes.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace Biomass Pyrolysis Plant
- Electric Rotary Kiln Pyrolysis Furnace Plant Machine Calciner Small Rotary Kiln Rotating Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Continuous Working Small Rotary Furnace Heating Pyrolysis Plant
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Electric Rotary Kiln Small Rotary Furnace for Activated Carbon Regeneration
People Also Ask
- What are the advantages of pyrolysis technology? Turn Waste into Profit and Reduce Emissions
- What is a disadvantage of biomass energy? The Hidden Environmental and Economic Costs
- What are the components of biomass pyrolysis? A Complete Guide to the System, Products, and Process
- How is energy converted into biomass? Harnessing Nature's Solar Power for Renewable Energy
- What are the conditions for biomass pyrolysis? Optimize Temperature, Heating Rate & Time



















