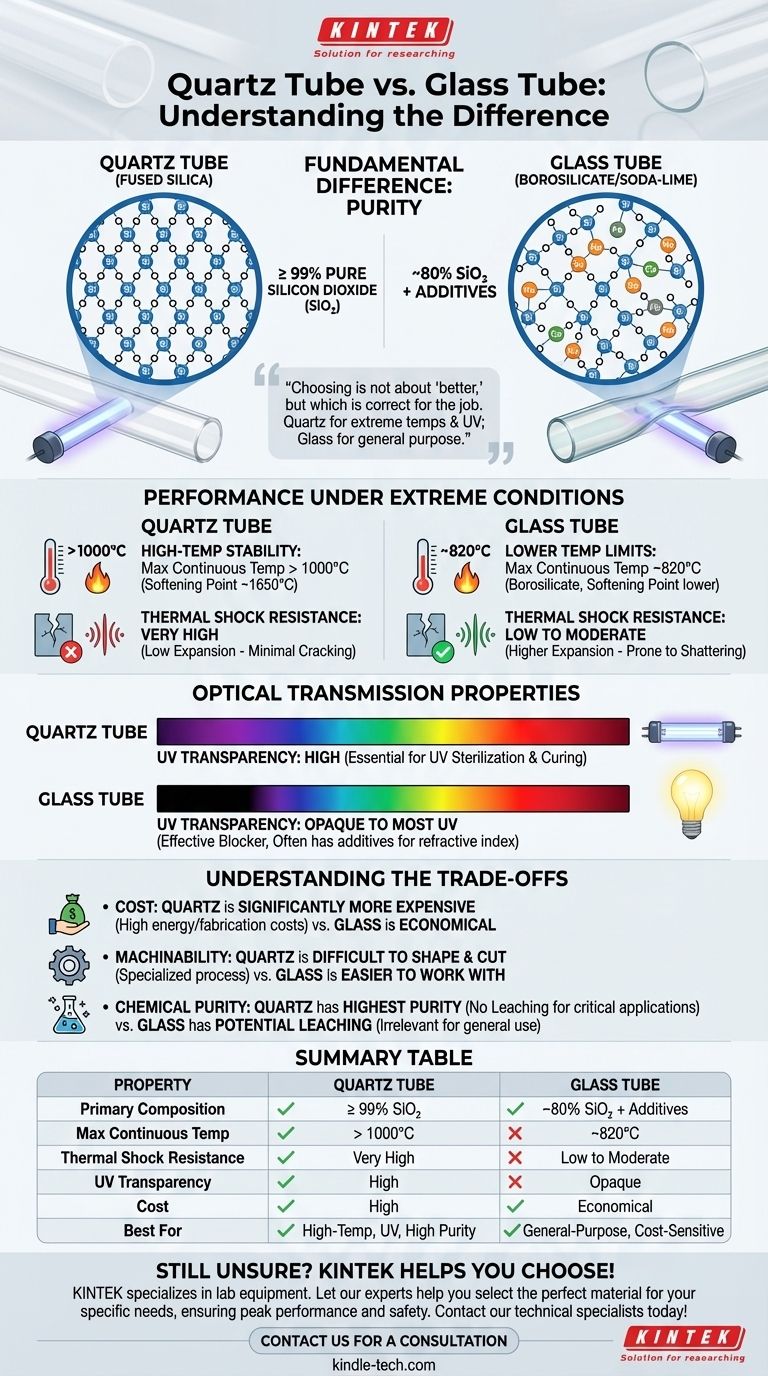
At a fundamental level, the difference between a quartz tube and a glass tube comes down to purity. A quartz tube is composed of at least 99% pure silicon dioxide (SiO₂), giving it superior thermal and optical properties. In contrast, a glass tube is a mixture of silicon dioxide (often 80% or less) with other ingredients like sodium oxide and lead, which makes it easier to manufacture but less resilient to extreme conditions.
Choosing between quartz and glass is not a question of which is "better," but which is correct for the job. Quartz is the specialized material for extreme temperatures and UV transparency, while glass is the economical, general-purpose solution.

The Defining Difference: Composition and Purity
The performance characteristics of both materials originate from their chemical makeup. Understanding this is key to choosing the right one.
Silicon Dioxide (SiO₂) Content
Quartz, in its fused form used for tubing, is essentially pure silicon dioxide. This high purity (99%+) is directly responsible for its high melting point and stable molecular structure.
Glass, however, contains a significantly lower percentage of SiO₂. Fluxing agents and stabilizers are added to the silica sand to lower its melting temperature, making it far easier and less energy-intensive to produce.
Additives in Glass
The other materials in glass are not impurities but deliberate additions. For example, lead oxide can be added to increase the refractive index of the glass, making it appear more brilliant and clear. Other additives, like soda and lime, are used primarily to make the glass workable at lower temperatures.
Performance Under Extreme Conditions
The most critical differences emerge when the materials are subjected to thermal stress. Here, the purity of quartz gives it a significant advantage.
Thermal Shock Resistance
Quartz has an extremely low coefficient of thermal expansion. This means it expands and contracts very little when its temperature changes, making it exceptionally resistant to cracking from sudden heating or cooling.
Standard glass has a much higher coefficient of thermal expansion. A rapid temperature change—like pouring cold water into a hot glass tube—will cause it to shatter. Borosilicate glass (e.g., Pyrex) is an improvement but is still far less resistant than quartz.
High-Temperature Stability
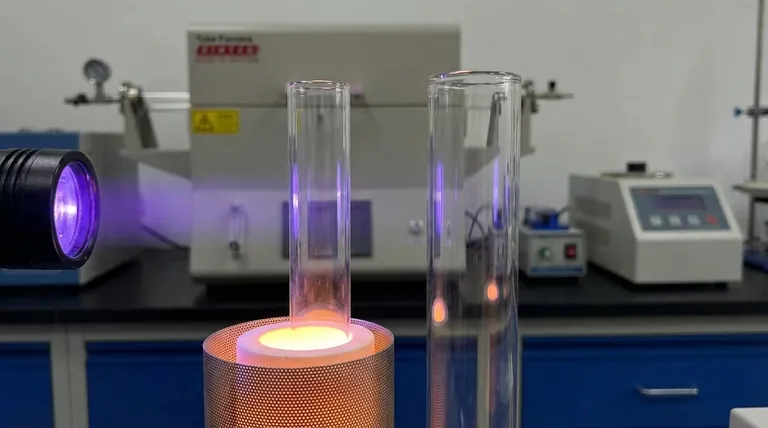
Quartz can be used continuously at temperatures over 1000°C and has a softening point of around 1650°C. This makes it essential for high-temperature industrial processes, such as in semiconductor manufacturing or furnace tubes.
Most common glass tubes have a much lower softening point. Even durable borosilicate glass begins to soften around 820°C, limiting its use in truly high-temperature environments.
Optical Transmission Properties
The material's purity also dictates what parts of the light spectrum can pass through it.
UV Transparency
This is a critical distinction. Fused quartz is highly transparent to a broad spectrum of light, including ultraviolet (UV) wavelengths. This makes it the only viable choice for applications like UV water sterilization lamps, UV curing, and specific scientific instruments.
Standard glass, due to its additives, is opaque to most UV light. It effectively blocks these wavelengths, rendering it useless for any application that relies on UV transmission.
Clarity and Refraction
While additives like lead can enhance the "sparkle" of decorative glass by increasing its refractive index, pure fused quartz offers superior optical clarity across a wider spectrum (from UV to infrared). Its purity ensures that light passes through with minimal distortion or absorption.
Understanding the Trade-offs
The superior performance of quartz comes with clear disadvantages that make glass the better choice for many common applications.
The Cost Factor
Quartz is significantly more expensive than glass. The process of melting and purifying silicon dioxide requires immense energy and specialized equipment, driving up the material and fabrication costs. Glass, with its lower melting point, is far more economical to produce.
Machinability and Fabrication
The same high melting point that gives quartz its thermal stability also makes it much more difficult to shape, cut, and form. Fabricating custom quartz components is a specialized and costly process compared to working with glass.
Chemical Purity
For applications like semiconductor processing or trace-element analysis, the purity of quartz is non-negotiable. It does not leach ions or contaminants into samples, ensuring the integrity of the process. For a simple school laboratory beaker, the minimal potential for leaching from glass is irrelevant and not worth the extra cost of quartz.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision must be guided by the specific demands of your project.
- If your primary focus is high-temperature applications or thermal shock resistance: Quartz is the only reliable choice due to its extremely low coefficient of thermal expansion.
- If your application requires UV light transmission: You must use a UV-grade fused quartz, as standard glass is opaque to most UV wavelengths.
- If your primary focus is cost-effectiveness for general-purpose use: Glass provides excellent value and performance for non-extreme environments.
- If you require the highest chemical purity: Fused quartz is essential to prevent the leaching of contaminants found in standard glass.
By understanding these core material properties, you can select the right material with confidence, ensuring both performance and cost-efficiency for your project.
Summary Table:
| Property | Quartz Tube | Glass Tube |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Composition | ≥ 99% Silicon Dioxide (SiO₂) | ~80% SiO₂ + Additives (Soda, Lime, Lead) |
| Max Continuous Temp | > 1000°C | ~820°C (Borosilicate) |
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Very High (Low Expansion) | Low to Moderate |
| UV Transparency | High | Opaque to most UV |
| Cost | High | Economical |
| Best For | High-temp processes, UV applications, high purity | General-purpose, cost-sensitive applications |
Still Unsure Which Tube Material is Right for Your Lab?
Choosing between quartz and glass is critical for the success and safety of your experiments. The wrong material can lead to equipment failure, contaminated samples, or inaccurate results.
KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables. Our experts can help you select the perfect tubing material—whether you need the extreme temperature resistance and UV transparency of quartz or the cost-effectiveness of high-quality glass—ensuring your lab operates at peak performance and efficiency.
Let us provide the right solution for your specific needs. Contact our technical specialists today for a personalized consultation!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Laboratory High Pressure Vacuum Tube Furnace
- 1200℃ Split Tube Furnace with Quartz Tube Laboratory Tubular Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- Why is a high-precision tube furnace required for CVD metal oxide films? Ensure Purity and Uniformity
- What are the uses of ceramic tube? The Ultimate Guide for Extreme Environments
- What functions does a laboratory high-temperature tube furnace perform? Master Catalyst Synthesis & Carbonization
- What is the function of a high-vacuum tube furnace in graphene CVD? Optimize Synthesis for High-Quality Nanomaterials
- What are the advantages of using multi-stage split tube furnaces for heating methane pyrolysis reactors? Boost Efficiency
- What is the purpose of treating metal precursors in a high-temperature tube furnace under a hydrogen atmosphere?
- What is the pyrolysis method of waste? A Guide to Converting Trash into Fuel and Chemicals
- How does a Tube Atmosphere Furnace ensure stability for steam oxidation? Master Precise Alloy Testing



















