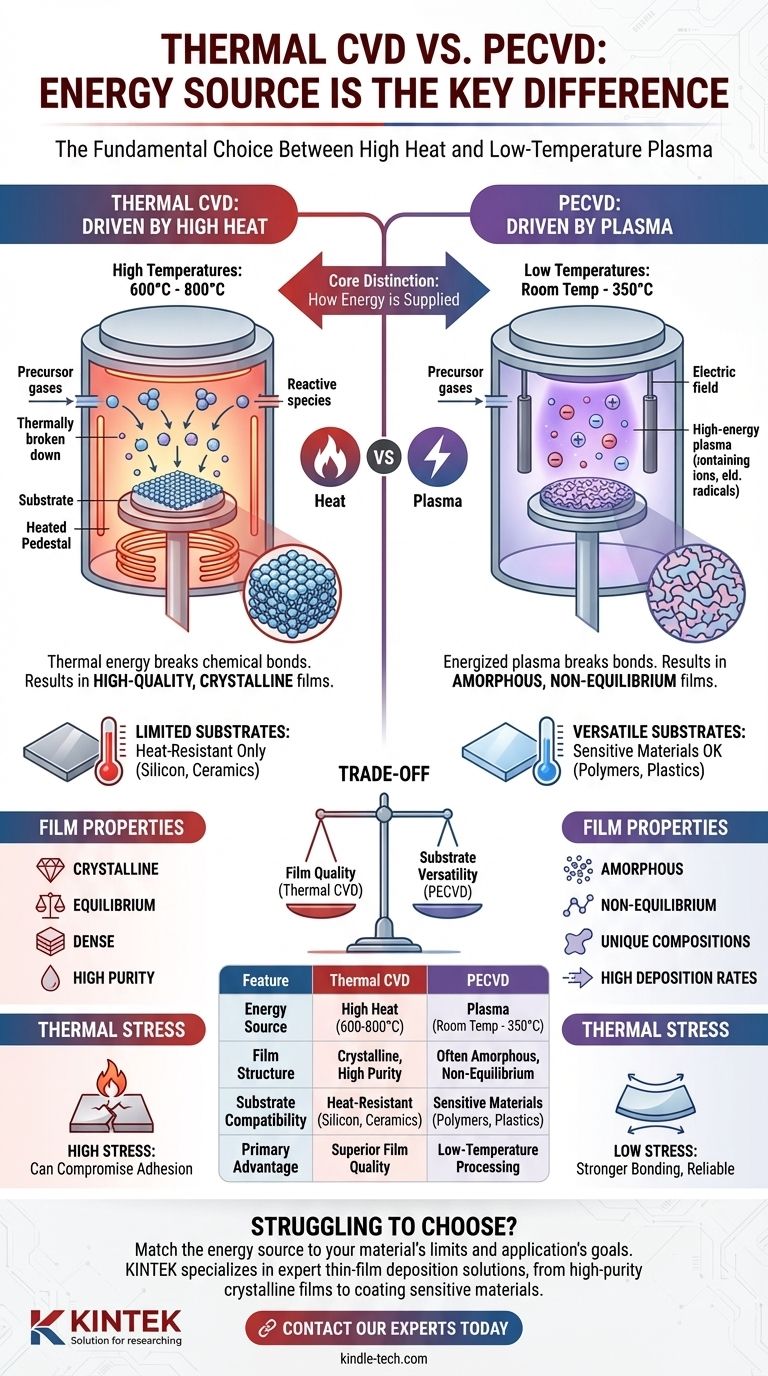
The fundamental difference between Thermal Chemical Vapor Deposition (CVD) and Plasma-Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition (PECVD) is the energy source used to drive the chemical reaction. Thermal CVD uses high heat to break down precursor gases, while PECVD uses an energized plasma to achieve the same result at much lower temperatures.
The choice between these two methods boils down to a critical trade-off: Thermal CVD's high heat produces high-quality, crystalline films but limits you to heat-resistant substrates. PECVD's low-temperature plasma process unlocks deposition on sensitive materials but often results in amorphous, non-equilibrium films.

The Core Distinction: How Energy is Supplied
The goal of any CVD process is to provide enough energy to break chemical bonds in a precursor gas, allowing a new solid material to form as a thin film on a substrate. The method of supplying this energy is what separates Thermal CVD from PECVD.
Thermal CVD: Driven by Heat
Thermal CVD is the traditional method, relying solely on high temperatures to initiate the deposition reaction. The substrate is heated, typically between 600°C and 800°C, providing the thermal energy required to overcome the reaction's activation barrier.
This process is governed by equilibrium thermodynamics, often resulting in highly pure, dense, and crystalline films.
PECVD: Driven by Plasma
PECVD utilizes an electric field to ionize the precursor gas, creating a plasma. This plasma contains high-energy electrons and ions that collide with gas molecules, breaking chemical bonds without the need for extreme heat.
This allows the reaction to proceed at significantly lower temperatures, often between room temperature and 350°C.
How This Difference Impacts the Process and Outcome
Using heat versus plasma has profound implications for the deposition process, the types of materials you can use, and the properties of the final film.
Operating Temperature
The most significant consequence is the vast difference in operating temperature. PECVD's low-temperature capability is its primary advantage, making it suitable for depositing films on substrates that would melt or degrade under Thermal CVD conditions.
Film Properties and Structure
Because Thermal CVD is a heat-driven, equilibrium process, it tends to produce films with a stable, highly ordered crystalline structure.
In contrast, PECVD is a non-equilibrium process. The high-energy plasma can create unique chemical species not found in thermal processes, often resulting in films that are amorphous (lacking a crystalline structure) and possess unique properties.
Substrate Compatibility
The high heat of Thermal CVD restricts its use to substrates that can withstand extreme temperatures, such as silicon wafers, ceramics, or certain metals.
PECVD’s gentle, low-temperature nature makes it compatible with a much wider range of materials, including polymers, plastics, and other heat-sensitive substrates.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a deposition method requires balancing the need for specific film properties against the limitations of your substrate material.
Film Quality vs. Substrate Sensitivity
The primary trade-off is between the high-quality, crystalline films of Thermal CVD and the substrate versatility of PECVD. If your substrate cannot tolerate high temperatures, PECVD is often the only viable option.
Thermal Stress and Adhesion
The extreme heat of Thermal CVD can introduce significant thermal stress in both the substrate and the deposited film, potentially compromising adhesion and device integrity.
PECVD's lower operating temperature drastically reduces thermal stress, which can lead to stronger bonding and more reliable films, especially when depositing on materials with different thermal expansion coefficients.
Control and Complexity
While PECVD offers incredible flexibility, managing a plasma process adds complexity. Controlling plasma chemistry, power, and pressure is critical to achieving the desired film properties, which can be more intricate than managing the temperature and gas flow in a Thermal CVD system.
Making the Right Choice for Your Application
Your final decision must be guided by the specific requirements of your substrate and the desired characteristics of the thin film.
- If your primary focus is the highest possible film purity and crystallinity on a heat-resistant substrate: Thermal CVD is the established and reliable choice.
- If your primary focus is coating a temperature-sensitive material like a polymer or plastic: PECVD is the necessary and effective solution.
- If your primary focus is achieving unique, non-equilibrium film compositions or high deposition rates at low temperatures: PECVD provides the flexibility to create materials not possible with thermal methods.
Ultimately, selecting the right process means matching the energy source to your material's limits and your application's goals.
Summary Table:
| Feature | Thermal CVD | PECVD |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Source | High Heat (600-800°C) | Plasma (Room Temp - 350°C) |
| Film Structure | Crystalline, High Purity | Often Amorphous, Non-Equilibrium |
| Substrate Compatibility | Heat-Resistant (Silicon, Ceramics) | Sensitive Materials (Polymers, Plastics) |
| Primary Advantage | Superior Film Quality | Low-Temperature Processing |
Struggling to choose the right deposition method for your substrates? The choice between Thermal CVD and PECVD is critical for your project's success. KINTEK specializes in lab equipment and consumables, providing expert solutions for all your thin-film deposition needs. Whether you require high-purity crystalline films or need to coat temperature-sensitive materials, our team can help you select and optimize the perfect system.
Let's discuss your application: Contact our experts today!
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Chemical Vapor Deposition CVD Equipment System Chamber Slide PECVD Tube Furnace with Liquid Gasifier PECVD Machine
- Customer Made Versatile CVD Tube Furnace Chemical Vapor Deposition Chamber System Equipment
- Split Chamber CVD Tube Furnace with Vacuum Station Chemical Vapor Deposition System Equipment Machine
- 915MHz MPCVD Diamond Machine Microwave Plasma Chemical Vapor Deposition System Reactor
- HFCVD Machine System Equipment for Drawing Die Nano-Diamond Coating
People Also Ask
- What is low pressure plasma enhanced chemical vapor deposition? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin Film Coating
- What is the PECVD method? Enable Low-Temperature, High-Quality Thin Film Deposition
- What is the function of a Microwave PECVD system for Diamond Nanospikes? Precision 1-Step Nanostructure Synthesis
- What are the components of PECVD? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition Systems
- What is the process of PECVD? A Guide to Low-Temperature Thin Film Deposition
- What temperature is DLC coating application? Achieve Superior Hardness Without Compromising Your Substrate
- What is the role of the plasma power supply in PECVD? Enable High-Quality Thin Films at Low Temperatures
- How does radio frequency (RF) power affect the PECVD process? Master Ionization for Superior Thin Film Quality



















