In short, biochar dramatically increases the abundance and activity of soil microbial populations. It achieves this by fundamentally improving the soil's physical and chemical structure, creating a highly favorable habitat that offers microbes shelter, water, and a consistent supply of nutrients.
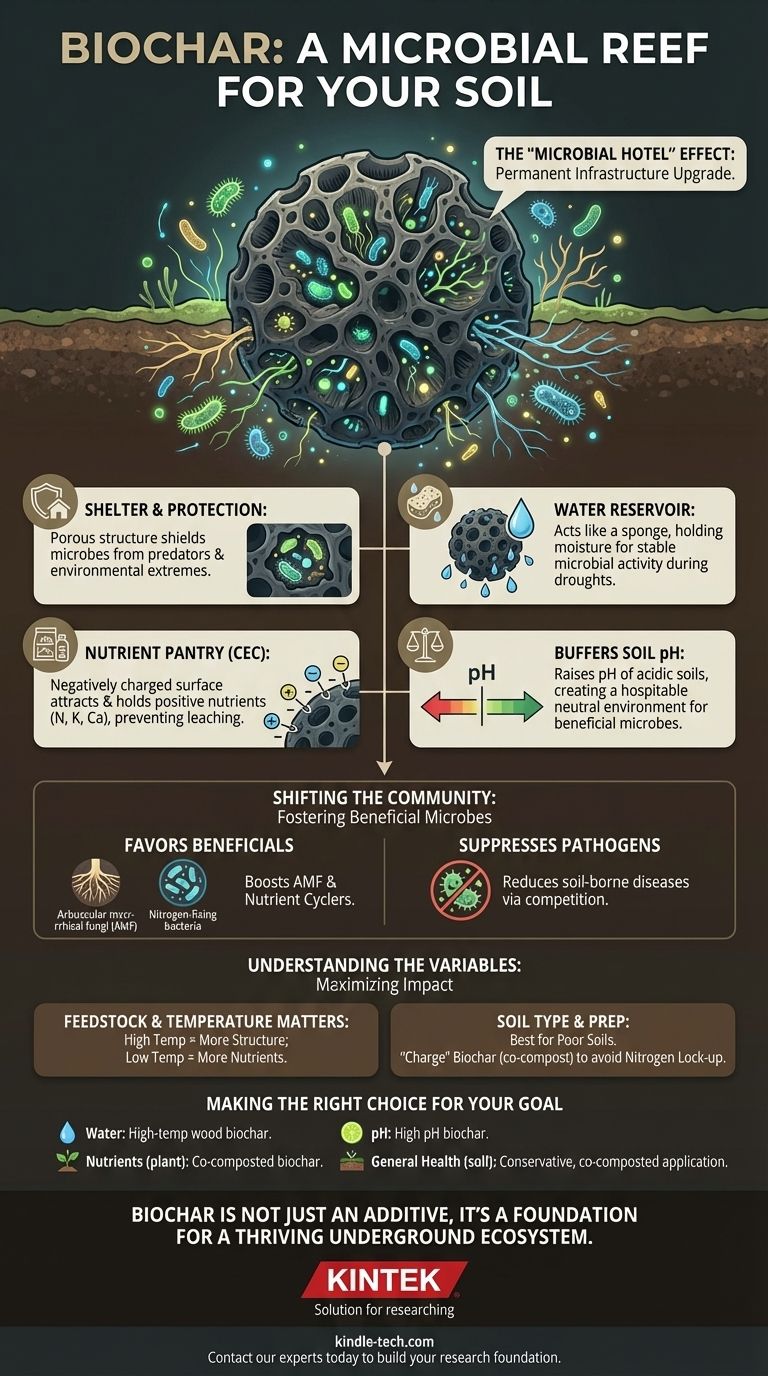
The most critical insight is to stop thinking of biochar as a simple soil additive and start seeing it as a permanent infrastructure upgrade for your soil. It functions as a "microbial reef," providing the physical housing and services that allow beneficial microbial communities to establish, thrive, and perform their essential functions more effectively.

How Biochar Creates a Microbial Haven
Biochar’s influence isn’t magic; it is a direct result of its unique physical and chemical properties. These properties create a stable and resource-rich environment, solving many of the core challenges microbes face in poor or degraded soils.
The "Microbial Hotel" Effect
Biochar possesses an incredibly vast surface area and a highly porous structure, full of microscopic nooks and crannies.
This structure provides physical protection for bacteria and fungi. It shields them from predators like protozoa and nematodes and buffers them from extreme environmental shifts like soil drying or compaction.
A Reliable Source of Water
The same porous structure that provides shelter also acts like a sponge, dramatically increasing the soil's water-holding capacity.
For microbes, this is critical. It ensures a more stable supply of moisture, allowing them to remain active for longer periods during dry spells and reducing population crashes caused by drought.
A Pantry for Nutrients
Biochar’s surface has a negative charge, which allows it to attract and hold onto positively charged nutrients (cations) like ammonium (a form of nitrogen), potassium, and calcium.
This property, known as cation exchange capacity (CEC), prevents these vital nutrients from being leached away by rain. It effectively creates a nutrient pantry on the biochar surface, providing a sustained food source for microbes and, by extension, plants.
Buffering Soil pH
Many biochars are alkaline and have a liming effect, meaning they can raise the pH of acidic soils.
Most beneficial soil bacteria and fungi function best in a near-neutral pH range. By correcting acidity, biochar creates a more hospitable chemical environment, unlocking the potential of these crucial microbial groups.
The Impact on Microbial Community Structure
Biochar doesn't just increase the number of microbes; it actively changes the types of microbes that dominate the soil community. This shift is often toward a more beneficial and resilient ecosystem.
Favoring Beneficial Fungi
Studies consistently show that biochar application can increase the abundance of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi (AMF).
These fungi form a symbiotic relationship with plant roots, extending their reach into the soil to retrieve water and nutrients like phosphorus. In return, the plant provides the fungi with carbon. A thriving AMF network is a cornerstone of healthy soil.
Promoting Nutrient-Cycling Bacteria
Biochar encourages the growth of bacteria involved in key nutrient cycles, such as nitrogen-fixing bacteria and phosphorus-solubilizing bacteria.
These microbes convert nutrients that are locked in the soil into forms that plants can actually absorb, effectively increasing the soil's natural fertility.
Suppressing Soil-Borne Pathogens
By creating ideal conditions for a diverse community of beneficial microbes, biochar fosters a competitive environment.
This "microbial buffer" can help suppress the growth and spread of harmful soil-borne pathogens, reducing the incidence of plant diseases through natural competition.
Understanding the Trade-offs and Variables
While overwhelmingly positive, the effect of biochar is not uniform. The outcome depends entirely on the type of biochar used and the soil it's applied to.
Not All Biochar is Created Equal
The feedstock (what the biochar is made from, e.g., wood, manure, straw) and the pyrolysis temperature are the two most important factors.
High-temperature (>500°C) biochars are more porous and stable, excelling at providing structure and water retention. Lower-temperature biochars are less stable but may contain more readily available nutrients.
The Influence of Soil Type
The benefits of biochar are most pronounced in poor-quality soils—those that are sandy, acidic, compacted, or low in organic matter.
In an already healthy, fertile loam, the positive effects will be far less dramatic because the soil's existing structure already provides many of these benefits.
The Risk of Nutrient Immobilization
Fresh, "raw" biochar has a very high carbon-to-nitrogen ratio. When first added to soil, microbes will rapidly colonize it, consuming available soil nitrogen in the process.
This can cause a temporary nitrogen deficiency for plants, known as nitrogen immobilization. To prevent this, it is crucial to "charge" or "inoculate" biochar before application by co-composting it or mixing it with a nitrogen-rich source like compost or manure.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Applying biochar effectively requires matching its properties to your specific soil improvement goal.
- If your primary focus is water retention in sandy soil: Select a high-temperature wood-based biochar for its high porosity and stability.
- If your primary focus is boosting nutrient cycling in degraded soil: Use a co-composted or "charged" biochar to provide both habitat and an immediate food source for microbes, avoiding nutrient lock-up.
- If your primary focus is correcting soil acidity: Choose a biochar known to have a high pH (often from hardwood or manure feedstocks) to provide a liming effect.
- If your primary focus is general health in already fertile soil: Apply biochar conservatively and always ensure it is co-composted to integrate it smoothly into the existing high-functioning ecosystem.
Ultimately, using biochar means thinking of it not as a simple fertilizer, but as a permanent architectural foundation for a thriving underground ecosystem.
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Biochar's Effect on Microbes |
|---|---|
| Habitat | Provides a porous "microbial hotel" for shelter and protection. |
| Water | Increases water-holding capacity, ensuring stable moisture. |
| Nutrients | Enhances CEC, creating a nutrient pantry for sustained feeding. |
| pH | Buffers acidic soils, creating a favorable environment. |
| Community | Favors beneficial fungi (AMF) and nutrient-cycling bacteria. |
| Pathogens | Suppresses soil-borne diseases through microbial competition. |
Ready to build a resilient foundation for your soil's microbial life?
At KINTEK, we understand that healthy soil is the heart of a successful laboratory or research operation. Just as biochar provides a permanent infrastructure for microbial communities, KINTEK provides the reliable, high-performance lab equipment and consumables that form the foundation of your research.
Whether you are studying soil science, agronomy, or environmental microbiology, having the right tools is critical. Let us help you achieve precise and reproducible results.
Contact our experts today to discuss how our solutions can support your specific laboratory needs and help your research thrive.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Laboratory Sterilizer Lab Autoclave Herbal Powder Sterilization Machine for Plant
- Powerful Plastic Crusher Machine
- Inclined Rotary Plasma Enhanced Chemical Vapor Deposition PECVD Equipment Tube Furnace Machine
- Mini Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Milling
- High Energy Planetary Ball Mill Machine for Laboratory Horizontal Tank Type
People Also Ask
- How does an autoclave ensure the reliability of experimental results? Achieving a Sterile Baseline for Lab Research
- What are the standard operating parameters for an autoclave? Master Temperature, Pressure, and Time for Sterilization
- Why is the prevention of air entrapment critical for the autoclave sterilization process? Ensure 100% Sterility Today
- What is the necessity of using a steam autoclave for dental alloys? Ensure Pure Bacterial Adhesion Data
- What is the primary purpose of an autoclave in the preparation of media for the biological leaching of uranium?



















