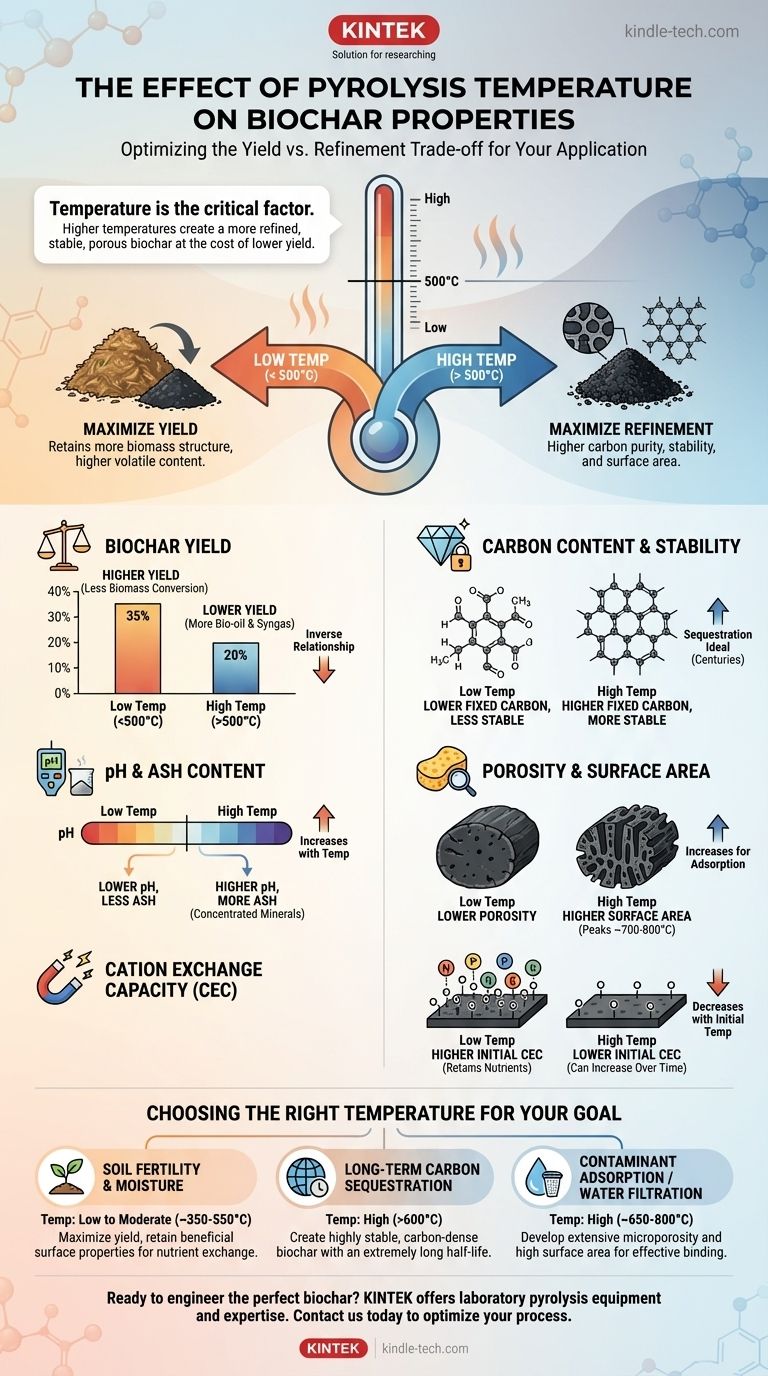
In short, pyrolysis temperature is the single most critical factor determining the final properties of biochar. As you increase the temperature, you fundamentally alter the trade-off between the quantity of biochar produced and its quality. Higher temperatures produce a more refined, stable, and porous carbon structure but at the cost of a significantly lower overall yield.
The core principle to understand is the trade-off between yield and refinement. Low temperatures maximize the amount of biochar you get from your feedstock, while high temperatures maximize its carbon purity, stability, and surface area.

The Fundamental Impact of Temperature on Biochar Formation
Pyrolysis is a process of thermal decomposition in the absence of oxygen. The temperature at which this occurs dictates which compounds are driven off as gases and liquids (volatiles) and what remains as a solid, carbon-rich biochar.
Low Temperature vs. High Temperature Pyrolysis
Low-temperature pyrolysis (< 500°C) is a less intense process. It drives off moisture and the most volatile organic compounds, leaving a biochar that retains more of the original biomass structure.
High-temperature pyrolysis (> 500°C) is far more aggressive. This intense heat breaks down more complex organic molecules, including cellulose and lignin, resulting in a greater loss of mass to gas and a final product that is a more concentrated, pure form of carbon.
Key Biochar Properties and How Temperature Governs Them
Every key characteristic of biochar responds directly to the peak temperature it was exposed to during production.
Biochar Yield
There is an inverse relationship between pyrolysis temperature and biochar yield. As temperature increases, more of the initial biomass is converted into bio-oil and syngas, leaving less solid material behind.
For example, pyrolyzing wood at 350°C might yield 35% biochar by mass, while the same feedstock at 750°C might only yield 20%.
Carbon Content and Stability
Higher temperatures produce biochar with a higher fixed carbon content. This carbon is also more stable (aromatic), meaning it is highly resistant to microbial decomposition in the soil.
This makes high-temperature biochars ideal for long-term carbon sequestration, as the captured carbon will remain locked away for centuries.
pH and Ash Content
Biochar becomes more alkaline (higher pH) as production temperature increases. This happens for two reasons. First, acidic functional groups on the surface are destroyed by the heat.
Second, as organic mass is driven off, the inorganic mineral components of the original feedstock (the ash) become more concentrated, further raising the pH.
Porosity and Surface Area
For most feedstocks, surface area generally increases with temperature, typically peaking around 700-800°C. The removal of volatiles creates an initial network of pores.
Higher temperatures then widen and deepen this pore structure, dramatically increasing the internal surface area. This property is critical for applications like water filtration or contaminant adsorption.
Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC)
The relationship here is more complex. Low-temperature biochars (< 500°C) often have a higher initial CEC. This is because they retain oxygen-containing functional groups on their surface that can hold onto plant nutrients.
High-temperature biochars have very low initial CEC, but this can increase over time in the soil as their surfaces slowly oxidize.
Understanding the Trade-offs
Choosing a pyrolysis temperature is not about finding the "best" setting, but about making a conscious decision based on your primary goal.
Quantity vs. Quality
This is the central trade-off. If your goal is to produce the maximum amount of biochar for use as a bulk soil amendment, a lower temperature is more economical. If you need a high-performance adsorbent, you must accept the lower yields of a high-temperature process.
Nutrient Retention vs. Carbon Purity
Low temperatures preserve more of the original feedstock's nutrients, such as nitrogen. However, high temperatures are more effective at driving off volatile compounds and creating a purer, more stable carbon structure.
Energy Input vs. Product Value
Achieving high temperatures requires a significant energy investment, increasing production costs. This is only justifiable if the resulting high-performance biochar can be sold at a premium for specialized applications.
Choosing the Right Temperature for Your Goal
Your target application must dictate your production parameters.
- If your primary focus is soil fertility and moisture retention: Use a lower to moderate temperature (~350-550°C) to maximize yield and retain beneficial surface properties for nutrient exchange.
- If your primary focus is long-term carbon sequestration: Use a higher temperature (>600°C) to create a highly stable, carbon-dense biochar with an extremely long half-life.
- If your primary focus is contaminant adsorption or water filtration: Use a high temperature (~650-800°C) to develop the extensive microporosity and high surface area required for effective binding.
By understanding temperature as your primary control, you can engineer biochar to meet the precise demands of your application.
Summary Table:
| Pyrolysis Temperature | Biochar Yield | Fixed Carbon & Stability | pH & Ash Content | Porosity & Surface Area | Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Low (< 500°C) | High | Lower, less stable | Lower, less ash | Lower | Higher initial CEC |
| High (> 500°C) | Low | Higher, more stable | Higher, more ash | Higher (peaks ~700-800°C) | Lower initial CEC |
Ready to engineer the perfect biochar for your specific application?
Whether your goal is maximizing soil fertility, achieving long-term carbon sequestration, or creating a high-performance adsorbent, KINTEK has the laboratory pyrolysis equipment and expertise to help you precisely control the process. Our solutions are designed for researchers and producers who need reliable, scalable results.
Contact us today to discuss how we can support your biochar production and research needs. Let's optimize your process together. Get in touch now →
Visual Guide
Related Products
- Vacuum Sealed Continuous Working Rotary Tube Furnace Rotating Tube Furnace
- Rotary Tube Furnace Split Multi Heating Zone Rotating Tube Furnace
- 1700℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- 1400℃ Laboratory High Temperature Tube Furnace with Alumina Tube
- Vertical Laboratory Tube Furnace
People Also Ask
- How is a high-temperature calcination furnace utilized in BZY20 Sol-gel? Achieve Pure Cubic Perovskite Phases
- What are the main types of biomass conversion processes? Unlock the Best Pathway for Your Energy Needs
- What is the difference between pyrolysis combustion and gasification? A Guide to Thermal Conversion Technologies
- What temperature is needed for pyrolysis waste? A Guide to Optimizing Your Waste-to-Value Process
- What are the equipment requirements for loading platinum (Pt) onto composite supports? Precise Stirring for High Dispersion



















