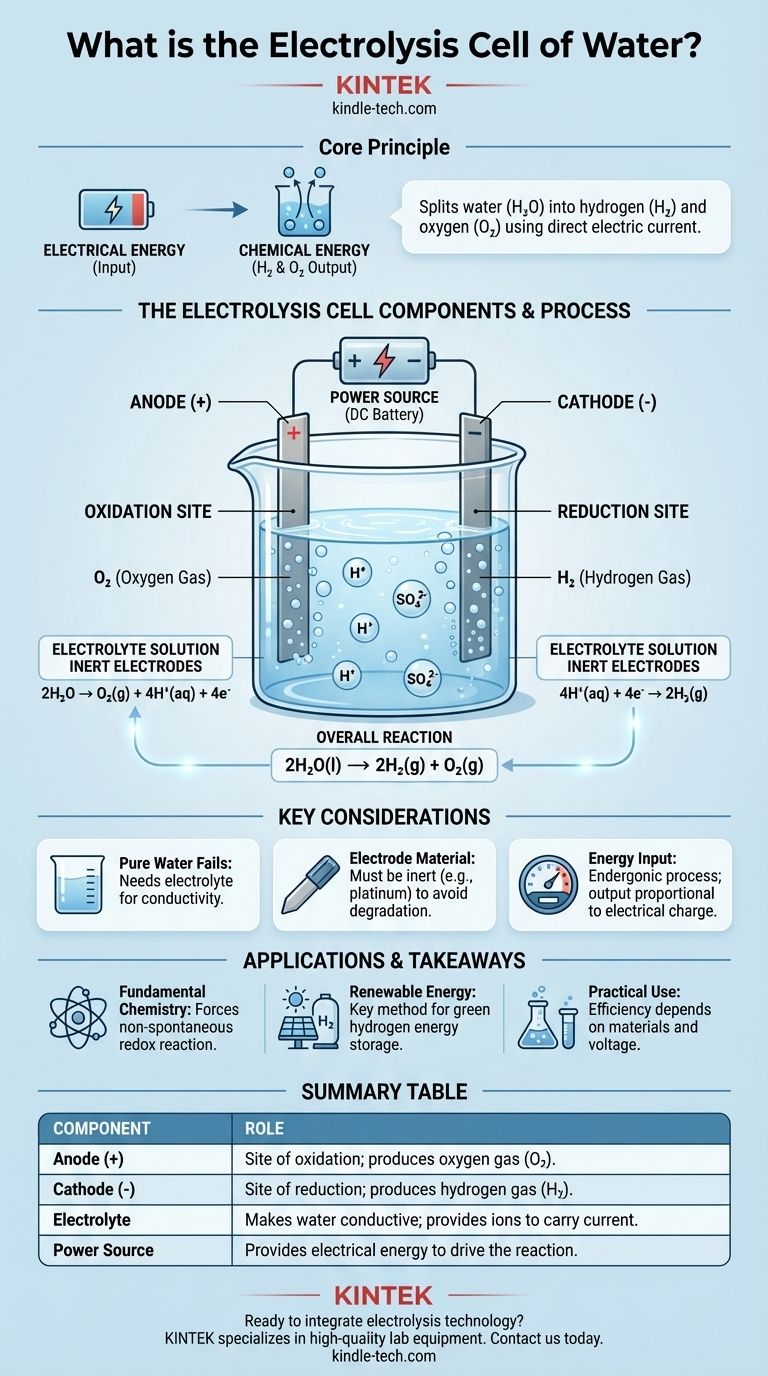
At its core, a water electrolysis cell is a device that uses electrical energy to split water (H₂O) into its constituent elements: hydrogen gas (H₂) and oxygen gas (O₂). It accomplishes this by passing a direct electric current through water that contains a small amount of an electrolyte, forcing a chemical change that would not happen on its own. The fundamental components are two electrodes (an anode and a cathode) submerged in the electrolyte and connected to an external power source.
The central purpose of an electrolysis cell is to convert electrical energy into chemical energy. It uses an external voltage to drive a non-spontaneous redox reaction, effectively storing the input energy in the chemical bonds of the resulting hydrogen and oxygen molecules.

The Core Components and Their Roles
An electrolytic cell for water operates through the precise interaction of three key parts: the electrodes, the electrolyte, and the power source. Each plays a distinct and critical role in the process.
The Electrodes: Anode and Cathode
The cell contains two electrodes, which are conductors through which electricity enters and leaves the solution. These are typically made of an inert material, like platinum or graphite, to ensure they facilitate the reaction without being consumed by it.
The anode is the positive electrode. This is the site of oxidation, where substances lose electrons.
The cathode is the negative electrode. This is the site of reduction, where substances gain electrons.
The Electrolyte: Making Water Conductive
Pure water is a very poor conductor of electricity because it contains too few free-moving ions to carry a current effectively.
To solve this, a small amount of an electrolyte, such as sulfuric acid (H₂SO₄), is added. The electrolyte dissolves in the water and provides mobile ions (in this case, H⁺ and SO₄²⁻) that can transport charge between the electrodes, completing the electrical circuit.
The Power Source: Driving the Reaction
Splitting water is an endergonic reaction, meaning it requires an input of energy to occur. Water is stable and will not spontaneously decompose.
An external power source, like a battery or DC supply, provides the necessary voltage. This electrical pressure "pushes" electrons into the cathode and "pulls" them from the anode, forcing the chemical decomposition of water to proceed.
The Chemical Process: How Water is Split
The overall process is a redox (reduction-oxidation) reaction, divided into two distinct half-reactions occurring at each electrode.
Oxidation at the Anode (+)
At the positive anode, water molecules are oxidized. They give up their electrons, which then flow out of the cell into the external circuit.
This reaction produces oxygen gas (O₂) and hydrogen ions (H⁺). The half-reaction is: 2H₂O → O₂(g) + 4H⁺(aq) + 4e⁻
Reduction at the Cathode (-)
The hydrogen ions (H⁺) generated at the anode (and present from the acidic electrolyte) are attracted to the negative cathode.
At the cathode, these ions gain electrons that are flowing in from the external circuit. This reduction reaction produces hydrogen gas (H₂). The half-reaction is: 4H⁺(aq) + 4e⁻ → 2H₂(g)
The Overall Reaction
When you combine the two half-reactions, the electrons and hydrogen ions on both sides cancel out, revealing the simple and elegant overall result of water electrolysis.
The net chemical change is: 2H₂O(l) → 2H₂(g) + O₂(g). For every two molecules of water split, two molecules of hydrogen gas and one molecule of oxygen gas are produced.
Understanding the Key Considerations
While the concept is straightforward, several factors are critical for the cell to function correctly and efficiently. Understanding these limitations reveals the true nature of the process.
Why Pure Water Fails
Without an electrolyte, the resistance of the water is extremely high. Applying a voltage would result in a negligible current flow, and therefore, virtually no hydrogen or oxygen production. The electrolyte is not consumed; its only job is to act as a charge carrier.
Electrode Material is Crucial
Using inert electrodes like platinum is essential. If you were to use a reactive metal like zinc or copper for the anode, the anode itself would oxidize and dissolve into the solution instead of the water. This would produce different, unintended products and destroy the electrode.
Energy Input Dictates Output
Electrolysis is not a source of free energy; it is an energy conversion process. The amount of hydrogen and oxygen produced is directly proportional to the amount of electrical charge passed through the cell. It takes a significant amount of electrical energy to produce a small amount of hydrogen gas.
Making the Right Choice for Your Goal
Understanding the electrolysis cell is valuable for several disciplines. Your takeaway depends on your underlying objective.
- If your primary focus is fundamental chemistry: See this as a perfect demonstration of how electrical energy can force a non-spontaneous redox reaction, separating a stable compound into its elements.
- If your primary focus is renewable energy: Recognize electrolysis as a key method for energy storage, converting surplus electricity from sources like solar or wind into hydrogen fuel.
- If your primary focus is practical application: Remember that the efficiency, rate, and products of electrolysis are entirely dependent on the specific materials used—the electrolyte, the electrode material, and the applied voltage.
Ultimately, the electrolysis of water is a powerful process that uses electricity to unlock the chemical energy stored within a simple molecule.
Summary Table:
| Component | Role in the Electrolysis Cell |
|---|---|
| Anode (Positive Electrode) | Site of oxidation; produces oxygen gas (O₂). |
| Cathode (Negative Electrode) | Site of reduction; produces hydrogen gas (H₂). |
| Electrolyte | Makes water conductive; provides ions to carry current. |
| Power Source | Provides the electrical energy to drive the non-spontaneous reaction. |
Ready to integrate electrolysis technology into your laboratory workflows? KINTEK specializes in high-quality lab equipment and consumables for advanced chemical processes. Whether you're developing new energy storage solutions or conducting fundamental research, our expertise ensures you have the reliable equipment you need. Contact our team today to discuss how we can support your specific laboratory requirements.
Visual Guide
Related Products
- H-Type Double-Layer Optical Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Water Bath
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell with Five-Port
- Double Layer Five-Port Water Bath Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell
- H Type Electrolytic Cell Triple Electrochemical Cell
- Electrolytic Electrochemical Cell Gas Diffusion Liquid Flow Reaction Cell
People Also Ask
- What is the structure of an H-type exchangeable membrane electrolytic cell? A Guide to Precise Electrochemical Separation
- What is a H type cell? A Guide to Divided Electrochemical Cells for Accurate Experiments
- What are the key features of a double-layer water-bath electrolytic cell? Achieve Precise Temperature Control for Your Experiments
- What is the purpose of the double-layer structure in the H-type electrolytic cell? Achieve Precise Thermal Control
- What is the overall structure of the H-type double-layer optical water bath electrolytic cell? Precision Design for Controlled Experiments



















